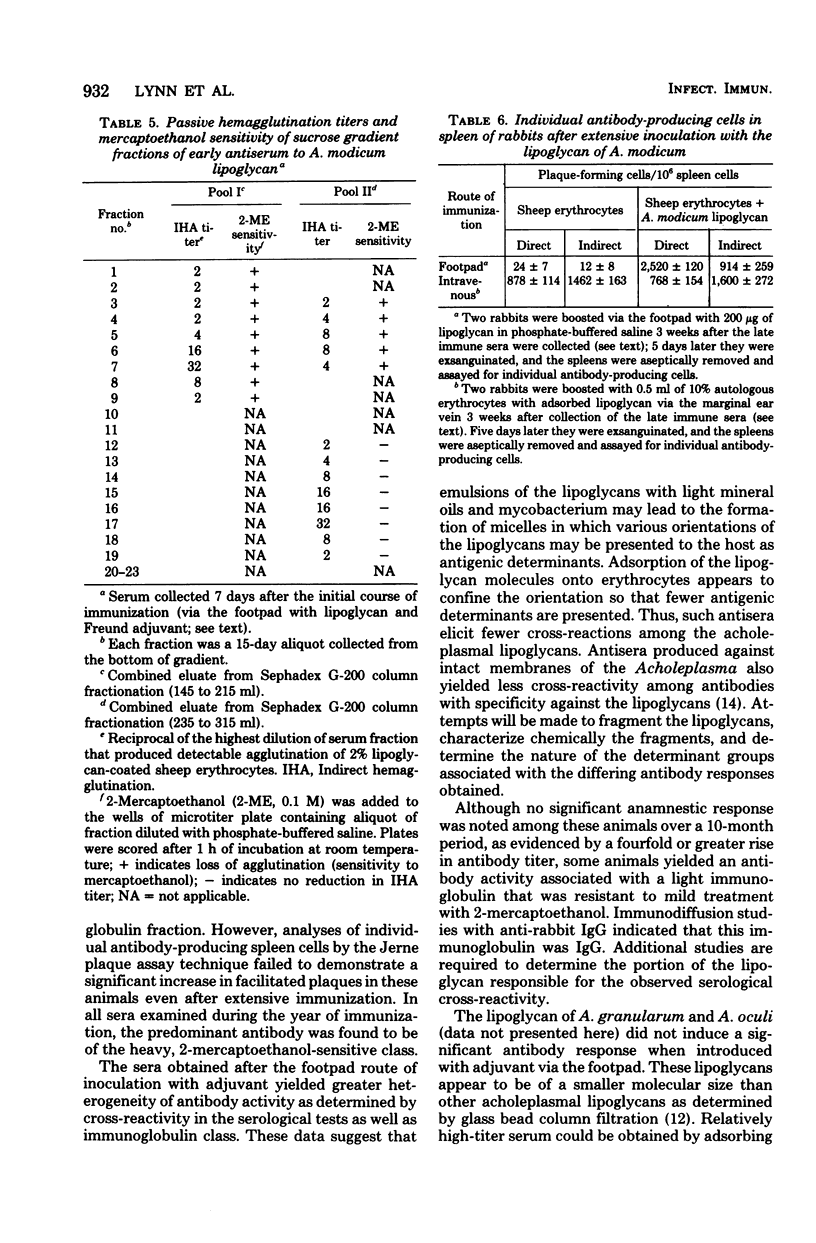
Abstract
Lipoglycans extracted from Acholeplasma species with hot aqueous phenol were immunogenic for rabbits when introduced by an appropriate method. All lipoglycans examined elicited antibody associated with a heavy, 2-mercaptoethanol-sensitive immunoglobulin fraction when inoculated intravenously adsorbed to autologous rabbit erythrocytes. This antibody was specific for the Acholeplasma species from which the lipoglycan was extracted. Extensive immunization of these animals with acholeplasmal lipoglycans produced significant increases in sheep erythrocyte hemolysin. Some, but not all, Acholeplasma species yielded lipoglycans that were immunogenic when emulsified with Freund complete adjuvant and introduced via the footpad into rabbits. Such animals produced antibodies corresponding to the M and G immunoglobulin classes that reacted with both homologous and heterologous acholeplasmal lipoglycans by precipitation in immunodiffusion as well as passive hemagglutination. None of the animals inoculated demonstrated a significant anamnestic response after booster injections either intravenously or via the footpads.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlstedt S., Holmgren J., Hanson L. A. The primary and secondary antibody response to Escherichia coli O6 lipopolysaccharide analysed at the humoral and cellular level. Amount and avidity of the antibodies in relation to protective capacity. Immunology. 1973 Feb;24(2):191–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciznár I., Shands J. W., Jr Effect of alkali-treated lipopolysaccharide on erythrocyte membrane stability. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):362–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.362-367.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLODIN P., KILLANDER J. Fractionation of human-serum proteins by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:402–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Preparation and properties of antisera against the lipid-A component of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):116–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. The antibody response in rabbits to E. coli O antigen. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;37(5):546–559. doi: 10.1159/000230242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling U., Westphal O. Synthesis and use of O-stearoyl polysaccharides in passive hemagglutination and hemolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry-Carson K. J., Langworthy T. A., MAyberry W. R., Smith P. F. A new class of lipopolysaccharide from Thermoplasma acidophilum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 22;360(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O., GORZYNSKI E. A., EICHENBERGER E. Studies of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides; effects of heat and chemicals on erythrocyte-modifying, antigenic, toxic and pyrogenic properties. J Immunol. 1956 May;76(5):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F. Homogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from Acholeplasma. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):393–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.393-398.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R. Distribution and composition of lipopolysaccharides from mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):916–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.916-922.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R. Immunological analysis of glycolipids and lipopolysaccharides derived from various mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1273–1279. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1273-1279.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDANZ W. P., JACKSON A. L., LANDY M. SOME ASPECTS OF THE ANTIBODY RESPONSE OF RABBITS TO IMMUNIZATION WITH ENTEROBACTERIAL SOMATIC ANTIGENS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jul;116:832–837. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]