Abstract
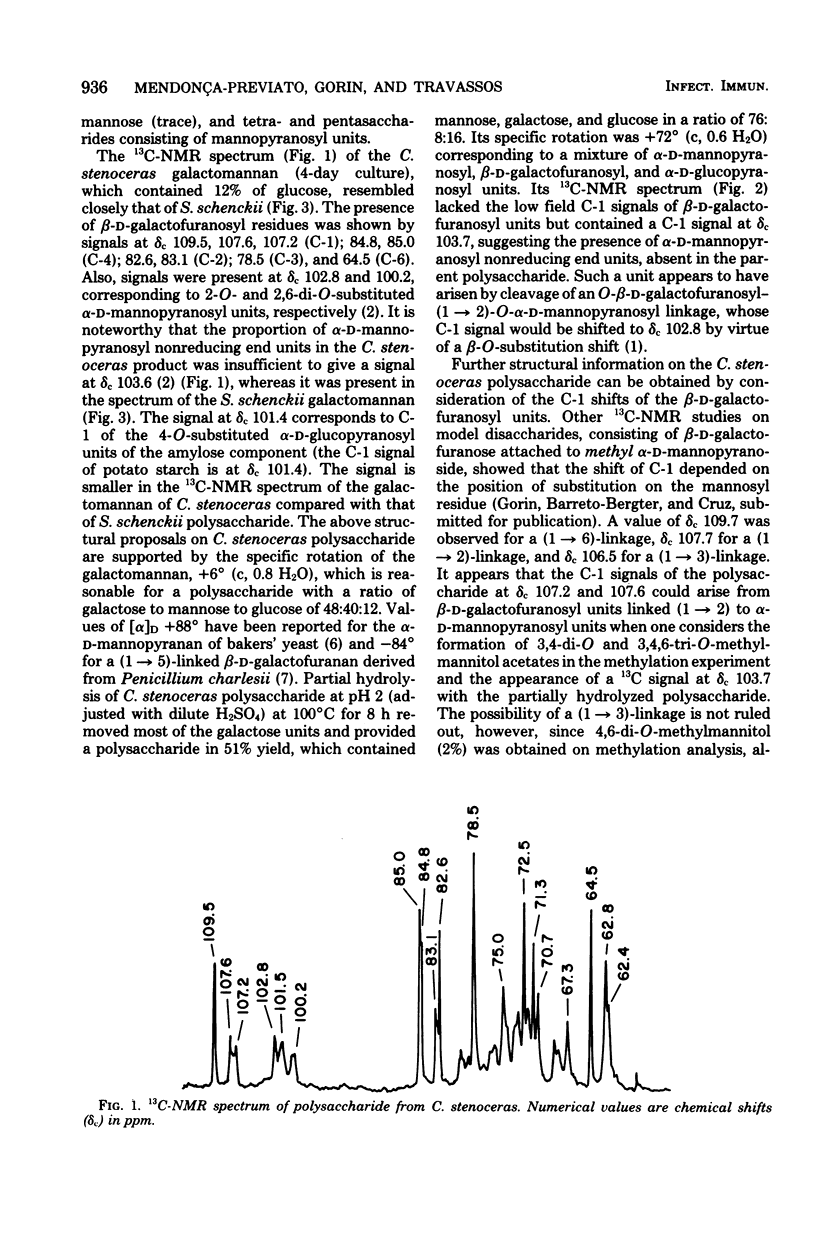
Galactose-containing polysaccharides from three strains of Sporothrix schenckii and one strain of Ceratocystis stenoceras were isolated, and their structures were paritally characterized by chemical analysis and 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (13C-NMR). S. schenckii polysaccharide preparations from all strains were not precipitated by Fehling solution and contained galactomannan (or a mixture of galactan and galactomannan), amylose, and minor amounts of rhamnomannan. C. stenoceras polysaccharide contained galactomannan and a smaller proportion of amylose. Conventional chemical techniques and 13C-NMR spectroscopy showed that the structures of the two preparations were closely related. The core of the galactomannan consisted principally of nonreducing end units and 2-O-, 2,6-di-O-, and perhaps 2,3-di-O-substituted alpha-D-mannopyranosyl units. The core was substituted by beta-D-galactofuranosyl chains; the units are interlinked (1 leads to 6). 13C-NMR evidence shows that the alpha-D-mannopyranosyl units are substituted in the two positions by the beta-D-galactofuranosyl residues. Galactomannans present at the cell surface of S. schenckii represent other potential fungal antigens in addition to the already recognized rhamnomannans and their peptide complexes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gorin P. A., Haskins R. H., Travassos L. R., Mendonca-Previato L. Further studies on the rhamnomannans and acidic rhamnomannans of Sporothrix schenckii and Ceratocystis stenoceras. Carbohydr Res. 1977 May;55:21–33. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth W. N., Raistrick H., Stacey M. Polysaccharides synthesised by micro-organisms: The molecular structure of mannocarolose produced from glucose by Penicillium Charlesii G. Smith. Biochem J. 1935 Mar;29(3):612–621. doi: 10.1042/bj0290612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki H., Nakamura Y., Kariya H., Iwatsu T., Wheat R. Delayed hypersensitivity cross-reactions between Sporothrix schenckii and Ceratocystis species in sporotrichotic patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jun;3(6):545–547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.6.545-547.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki H., Nakamura Y., Kurata Y., Iwatsu T., Wheat R. W. Delayed hypersensitivity cross-reactions among Sporothrix species in sporotrichotic patients. J Dermatol. 1980 Feb;7(1):75–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.1980.tb01946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki H., Wheat R. W., Kiel D. P., Conant N. F. Serological cross-reactivity among Sporothrix schenckii, Ceratocystis, Europhium, and Graphium species. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):585–593. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.585-593.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O., Bitoon M. A. Isolation and purification of a peptido-rhamnomannan from the yeast form of Sporothrix schenckii. Structural and immunochemical studies. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):663–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O., Travassos L. R. Immunochemical studies on L-rhamno-D-mannans of Sporothrix schenckii and related fungi by use of rabbit and human antisera. Carbohydr Res. 1975 Mar;40(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82671-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariat F. Observations sur l'écologie de Sporothrix schenckii et de Ceratocystis stenoceras en Corse et en Alsace, Provinces francaises indemnes de sporotrichose. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):217–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça L., Gorin P. A., Lloyd K. O., Travassos L. R. Polymorphism of Sporothrix schenckii surface polysaccharides as a function of morphological differentiation. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2423–2431. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Ishizaki H., Wheat R. W. Serological cross-reactivity between group B Streptococcus and Sporothrix schenckii, Ceratocystis species, and Graphium species. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):547–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.547-549.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Takeda N. Immunochemical studies on the galactomannans isolated from mycelia and culture broths of three Hormodendrum strains. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):483–490. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.483-490.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travassos L. R., Gorin P. A., Lloyd K. O. Comparison of the rhamnomannans from the human pathogen Sporothrix schenckii with those from the Ceratocystis species. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):685–693. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.685-693.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travassos L. R., Gorin P. A., Lloyd K. O. Discrimination between Sporothrix schenckii and Ceratocystis stenoceras rhamnomannans by proton and carbon-13 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):674–680. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.674-680.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


