Abstract
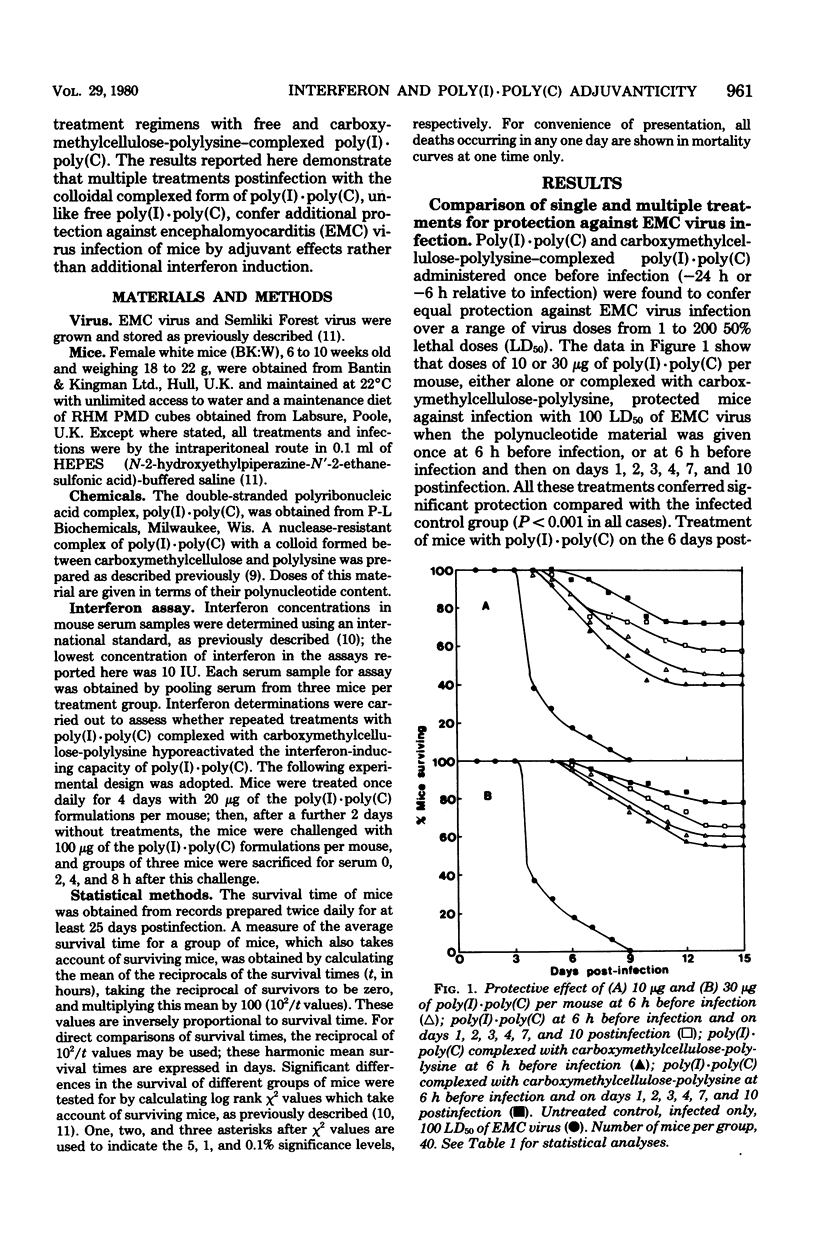
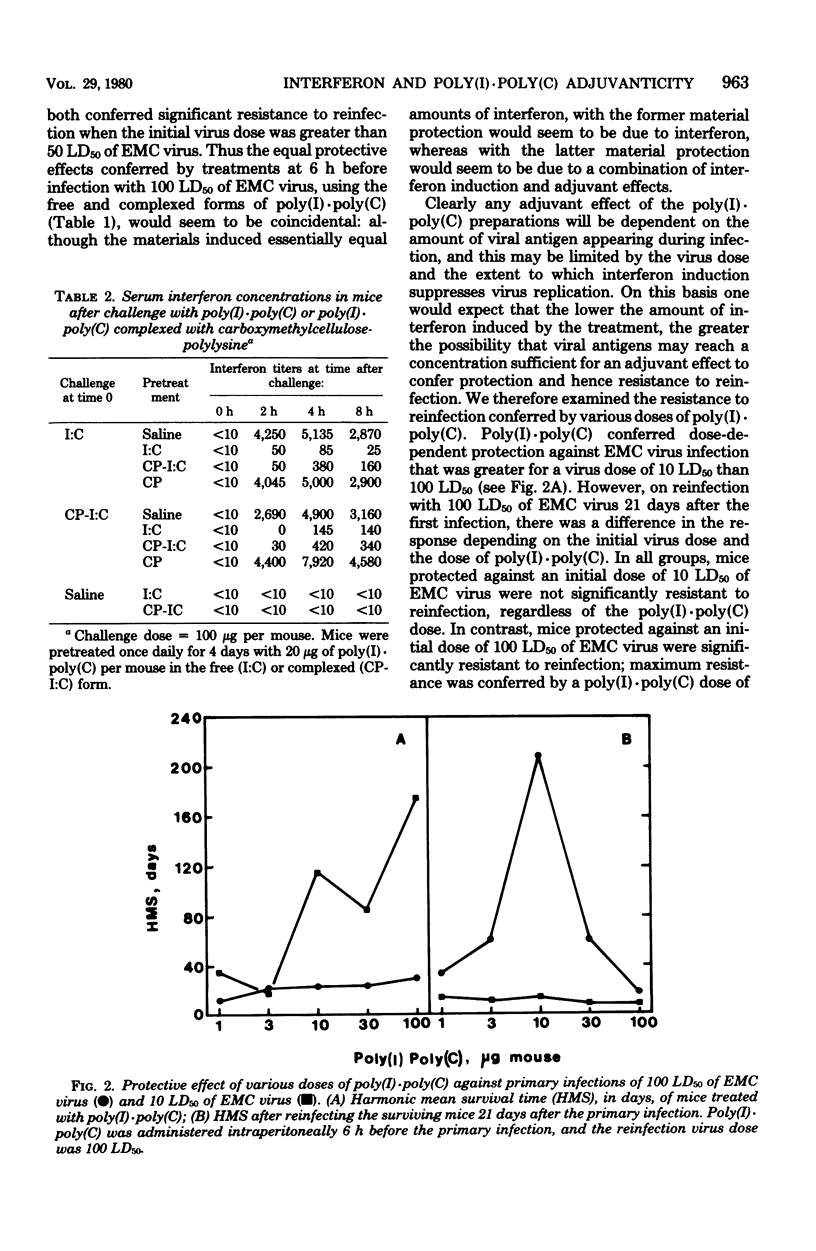
Treatment of mice with polyinosinic acid . polycytidylic acid [poly(I) . poly(C)] 6 h before infection and once daily on days 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, and 10 after infection with encephalomyocarditis virus was found to confer no additional protection as compared with a single treatment 6 h before infection. When complexed with a colloid formed between carboxymethylcellulose and polylysine, poly(I) . poly(C) conferred significant additional protection with the multiple treatment regimen compared with a single treatment of 6 h before infection. The additional antiviral activity of multiple treatments could not be entirely attributed to interferon induction by the complexed form of poly(I) . poly(C), because free and complexed poly(I) . poly(C) both caused hyporesponsiveness to interferon induction after multiple treatments. However, mice protected against encephalomyocarditis virus infection by multiple treatments with the colloidal complex form of poly(I) . poly(C) showed a significant increase in resistance to reinfection, and this was attributable to adjuvant effects of the colloidal complex form of poly(I) . poly(C). The contribution of interferon induction and adjuvanticity of the poly(I) . poly(C) formulations varied with the times of treatment relative to infection, the dose of polynucleotide material, and the virus dose.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billiau A., Muyembe J. J., De Somer P. Mechanism of antiviral activity in vivo of polycarboxylases which induce interferon production. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 11;232(2):183–186. doi: 10.1038/newbio232183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunnington P. G., Naysmith J. D. Naturally occurring double-stranded RNA and immune responses. Effects on plaque-forming cells and antibody formation. Immunology. 1975 Mar;28(3):451–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston W. E., Crabbs C. L., Stephen E. L., Levy H. B. Modified polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid, an immunological adjuvant. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):318–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.318-319.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Baer G., Baron S., Buckler C. E., Gibbs C. J., Iadarola M. J., London W. T., Rice J. A modified polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex that induces interferon in primates. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):434–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., London W., Fuccillo D. A., Baron S., Rice J. Prophylactic control of simian hemorrhagic fever in monkeys by an interferon inducer, polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid-poly-L-lysine. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A256–A259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. K., Johnson A. G. Regulation of the immune system by synthetic polynucleotides. VII. Suppression induced by pretreatment with poly A:U. Cell Immunol. 1978 Sep;39(2):345–354. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., London W. T., McAuliffe V. J., Palmer A. E., Kaplan P. M., Gerin J. L., Wagner J., Popper H., Lvovsky E., Wong D. C. Modification of chronic hepatitis-B virus infection in chimpanzees by administration of an interferon inducer. Lancet. 1976 Oct 9;2(7989):757–761. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90598-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammons M. L., Stephen E. L., Levy H. B., Baron S., Hilmas D. E. Interferon induction in cynomolgus and rhesus monkey after repeated doses of a modified polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):80–83. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbing N., Dawson K. M., Lindley I. J. Requirement for macrophages for interferon to be effective against encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):5–11. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.5-11.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbing N., Grantham C. A., Carey N. H. Anti-viral activity of single-stranded homopolynucleotides against encephalomyocarditis virus and Semliki Forest virus in adult mice without interferon induction. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jan;30(1):21–39. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen E. L., Hilmas D. E., Levy H. B., Spertzel R. O. Protective and toxic effects of a nuclease-resistant derivative of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid on Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus in rhesus monkeys. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):267–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen E. L., Hilmas D. E., Mangiafico J. A., Levy H. B. Swine influenza virus vaccine: potentiation of antibody responses in rhesus monkeys. Science. 1977 Sep 23;197(4310):1289–1290. doi: 10.1126/science.408923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


