Abstract
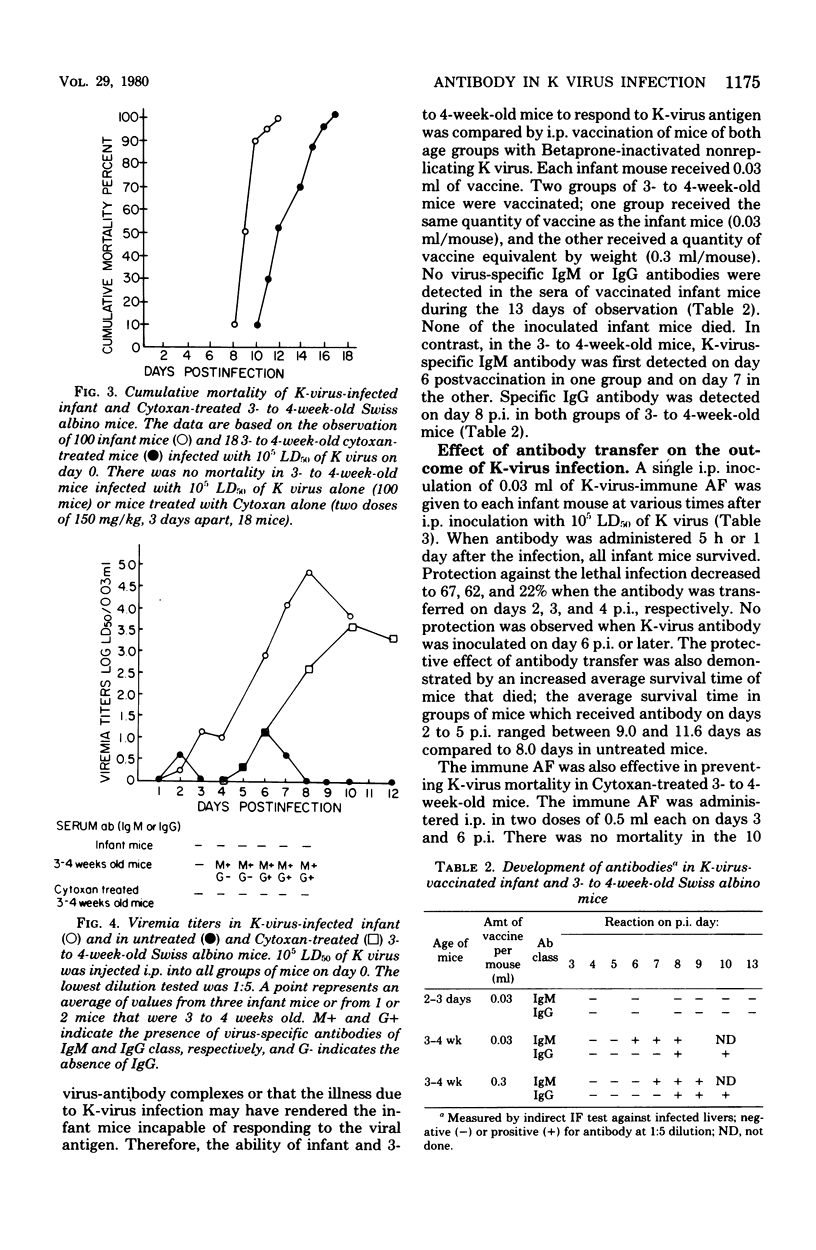
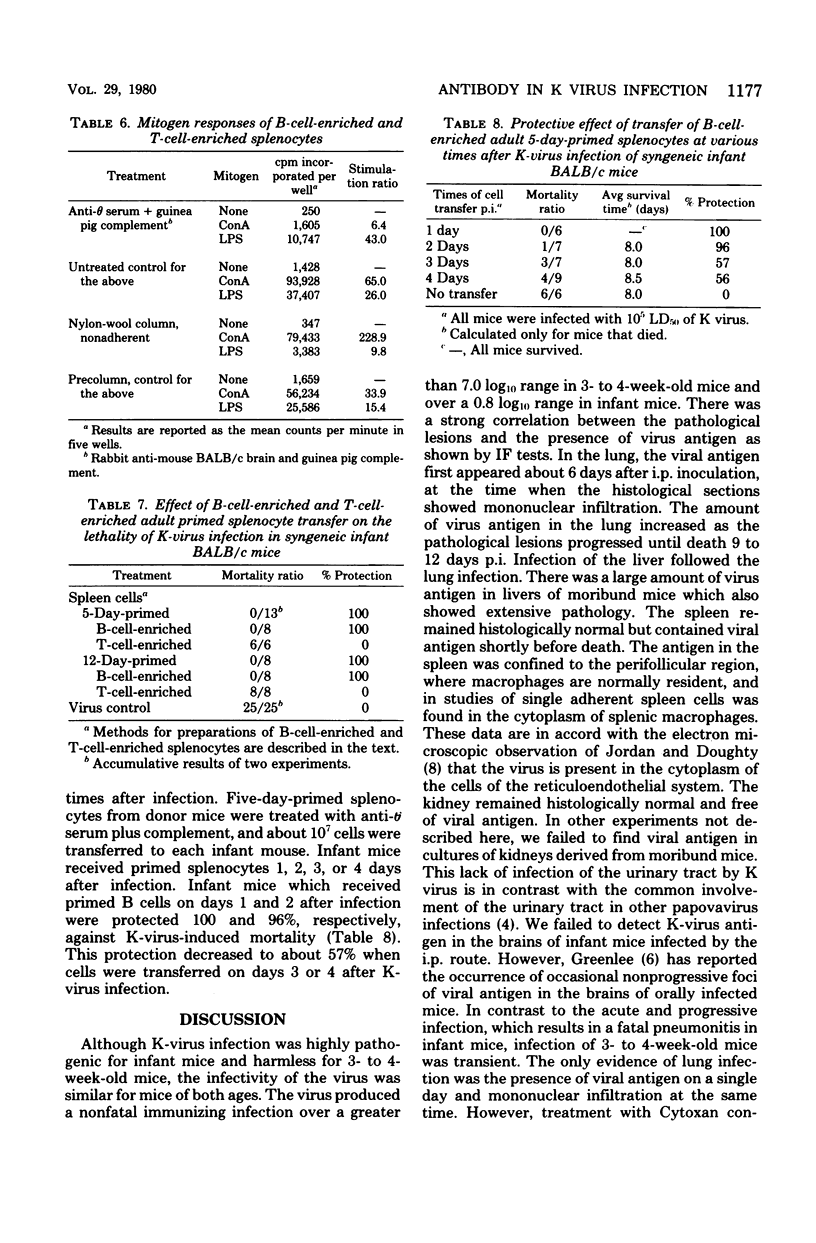
Intraperitoneal inoculation of mouse K papovavirus into infant (2 to 4 days old) Swiss albino mice produced a high-titered viremia which persisted until death due to pneumonitis on day 9 postinfection. Lungs and livers of these mice had virus-specific immunofluorescence and histological lesions. K-virus antibody was undetectable. Three- to four-week-old mice, although as susceptible to infection as infant mice, remained healthy and developed a much lower-titered viremia, a transient lung infection, and K-virus antibody on 4 to 5 days postinfection. Three- to four-week-old mice treated with cyclophosphamide developed a high-titered viremia with death 10 to 17 days postinfection and no detectable antibodies. A single intraperitoneal inoculation of K-virus antibody at 5 h or 1 day postinfection completely protected the infant Swiss albino mice. Partial protection was achieved when antibody was transferred on days 2, 3, and 4 postinoculation. Transfer of antibody to cytoxan-treated Swiss albino mice on days 3 and 6 postinfection completely portected them against K-virus-induced lesions and mortality. Transfer of normal adult BALB/c splenocytes to syngeneic infant mice before K-virus infection did not protect from death but increased survival time. Transfer of 4- to 12-day K-virus-primed adult splenocytes before infection gave a nearly 100% protection. When given before infection, the protection afforded by T-cell-enriched and B-cell-enriched adult primed splenocytes was 0 and 100%, respectively. Transfer of primed B cells on day 1 post-inoculation completely protected the infant mice. This protection decreased to 86, 57, and 56% when the primed B cells were transferred on days 2, 3, and 4 post-inoculation, respectively. These data suggest that the antibody response is of critical importance in the recovery of mice from K-virus infection. Antibody probably acts by aborting viremia, thereby preventing extensive seeding of lungs with virus.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole G. A., Wisseman C. L., Jr Pathogenesis of type 1 dengue virus infection in suckling, weanling and adult mice. 1. The relation of virus replication to interferon and antibody formation. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Jun;89(6):669–680. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER E. R., KILHAM L. Pathology of a pneumotropic virus recovered from C3H mice carrying the Bittner milk agent. AMA Arch Pathol. 1953 Jan;55(1):14–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleiser C. A., Heck F. C. The pathology of experimental K-virus infection in suckling mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1972 Dec;22(6):865–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee J. E. Pathogenesis of K virus infection in newborn mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):705–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.705-713.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Role of the immune response in recovery from Sindbis virus encephalitis in mice. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):1070–1075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. W., Doughty W. E. Ultrastructural pathology of murine pneumonitis caused by K-Papovavirus. Exp Mol Pathol. 1969 Aug;11(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(69)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILHAM L. Hemagglutination by K-virus. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:384–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILHAM L., MURPHY H. W. A pneumotropic virus isolated from C3H mice carrying the Bittner Milk Agent. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Jan;82(1):133–137. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Leblond E., Dupuy J. M. Neonatal susceptibility to MHV3 infection in mice. I. Transfer of resistance. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1219–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTERN C. F., ALLISON A. C., ROWE W. P. STRUCTURE AND COMPOSITION OF K VIRUS, AND ITS RELATION TO THE "PAPOVAVIRUS" GROUP. Virology. 1963 Jul;20:413–419. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie M. R., Warner N. L., Mitchell G. F. The binding of murine immunoglobulins to staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1493–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis G., Jacobs L. R., Kilham L. Oxygen tension and the selective tropism of K-virus for mouse pulmonary endothelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jul;114(1):45–51. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVERMAN J. R. Antibody response of suckling mice to mumps virus. II. Relation of onset of antibody production to susceptibility to mumps virus infection. J Immunol. 1954 Oct;73(4):249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. New human papovaviruses. Prog Med Virol. 1976;22:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector E. S., Carter B. G. Age-dependent changes in sensitivity to antigen in the mouse. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1591–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah K. V., Ozer H. L., Ghazey H. N., Kelly T. J., Jr Common structural antigen of papovaviruses of the simian virus 40-polyoma subgroup. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):179–186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.179-186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt H. V. Poliomyelitis in hypogammaglobulinemics. J Infect Dis. 1973 Dec;128(6):802–806. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.6.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youdim S., Stutman O., Good R. A. Studies of delayed hypersensitivity to L. Monocytogenes in mice: nature of cells involved in passive transfers. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jan;6(1):98–109. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Rhein G., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., Chun R. W., Horowitz S. D., Hong R. Pituitary function after removal of microadenomas for Cushing's disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 3;299(5):256–257. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808032990517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]