Abstract
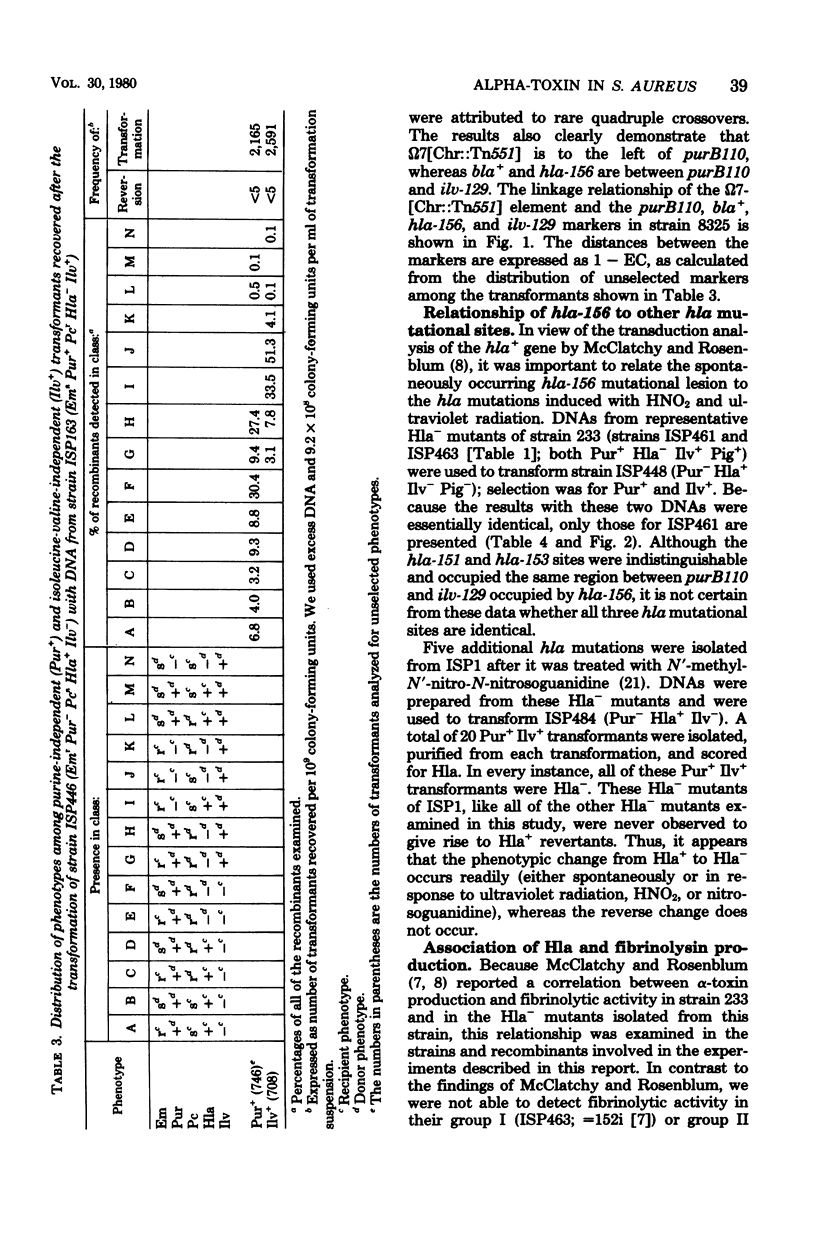
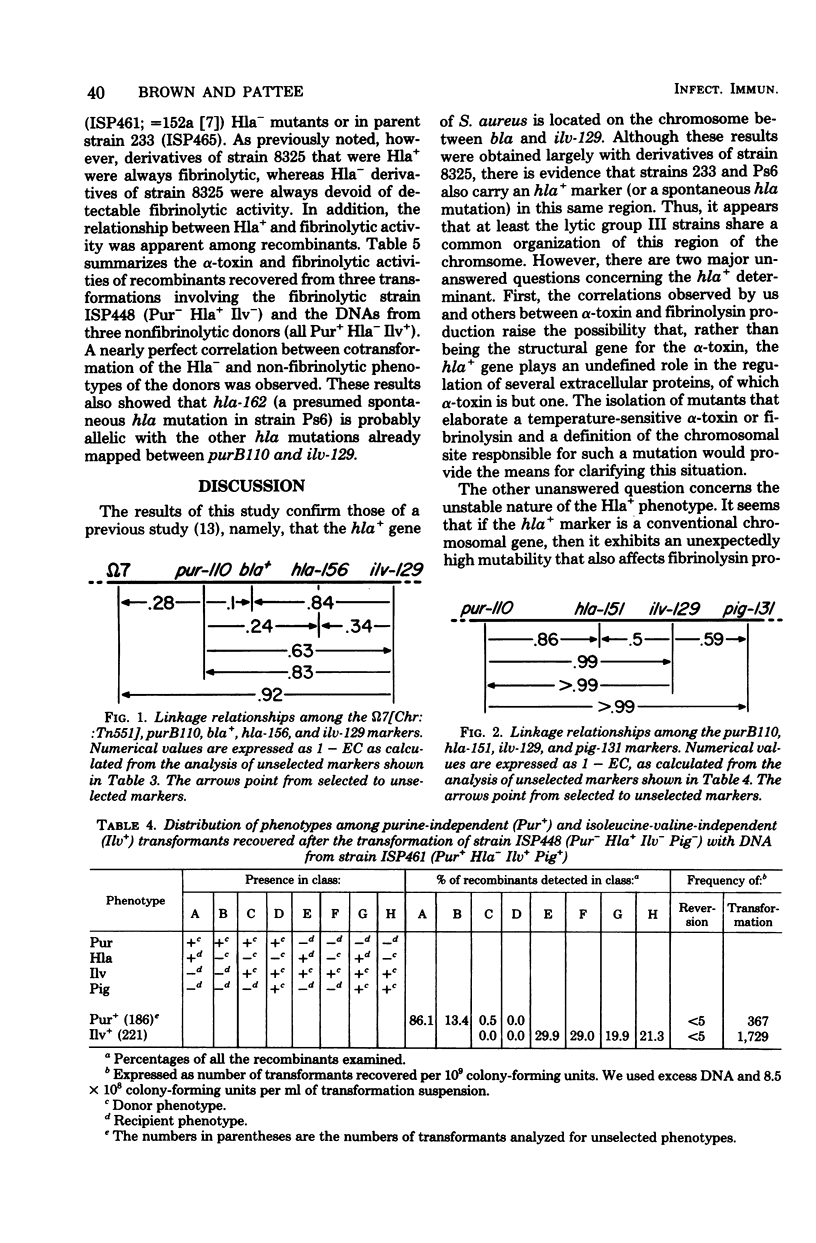
Production of alpha-toxin (the Hla+ phenotype, controlled by the Hla gene and scored as alpha-hemolytic activity) is a property of some isolates of Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 8325 and not of others. Genetic transformation between strains differing in the Hla phenotype revealed that the hla+ gene resides in the following sequence: purB110-bla+-hla+-ilv-129-pig-131; previously, the enterotoxin A (entA) gene of strain S-6 was shown to map very close to hla+. The hla+ mutations occurring naturally in strain Ps6 and after various mutagenic treatments in strains 8325 and 233 also mapped between bla+ and ilv-129. Among the isolates of strain 8325, the Hla+ phenotype was always associated with fibrinolytic activity, whereas Hla- isolates were non-fibrinolytic. This relationship was also observed among transformants selected for their Hla+ or Hla- phenotypes. The failure of Hla- strains and mutants to revert to hla+ at detectable frequencies, the instability of the Hla+ phenotype, and the previously observed pattern of recombination of the hla+ and entA+ determinants lend support to the view that hla+ may reside on a transposon; according to this view, Hla- mutants have lost the hla+-bearing transposon. It remains unclear whether hla+ is the structural gene for alpha-toxin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAIR J. E., CARR M. Lysogeny in staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:984–993. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.984-993.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., LEVY E. The nature of discrepancies between haemolysins in culture filtrates and plate haemolysin patterns of staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1954 Jul;68(1):31–40. doi: 10.1002/path.1700680105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks C. W., Altenbern R. A. Studies on the synthesis of staphylococcal alpha toxin. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Dec;14(12):1277–1281. doi: 10.1139/m68-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchy J. K., Rosenblum E. D. Biological properties of alpha-toxin mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):575–579. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.575-579.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchy J. K., Rosenblum E. D. Genetic recombination between alpha-toxin mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):580–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.580-583.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Brodsky R. Studies on plasmid replication. I. Plasmid incompatibility and establishment in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):285–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Edelman I., Schwesinger M. D., Gruss A. D., Swanson E. C., Pattee P. A. Genetic translocation in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):400–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):29–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A. Genetic linkage of chromosomal tetracycline resistance and pigmentation to a purine auxotrophic marker and the isoleucine-valine-leucine structural genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1167–1172. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1167-1172.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Glatz B. A. Identification of a chromosomal determinant of enterotoxin A production in Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):186–193. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.186-193.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Neveln D. S. Transformation analysis of three linkage groups in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):201–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.201-211.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Thompson N. E., Haubrich D., Novick R. P. Chromosomal map locations of integrated plasmids and related elements in Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):38–51. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S., Novick R. P. Tn554--a site-specific repressor-controlled transposon in Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):476–478. doi: 10.1038/278476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M. Nonenteric toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):320–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.320-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGELSANG T. M., WORMNES A., OSTERVOLD B. Correlation between staphylococcal phage groups and some staphylococcal enzymes demonstrated by simple methods. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1962;54:218–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1962.tb01239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zyskind J. W., Imsande J. Regulation of penicillinase synthesis: a mutation in Staphylococcus aureus unlinked to the penicillinase plasmid that reduced penicillinase inducibility. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):116–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.116-121.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



