Abstract
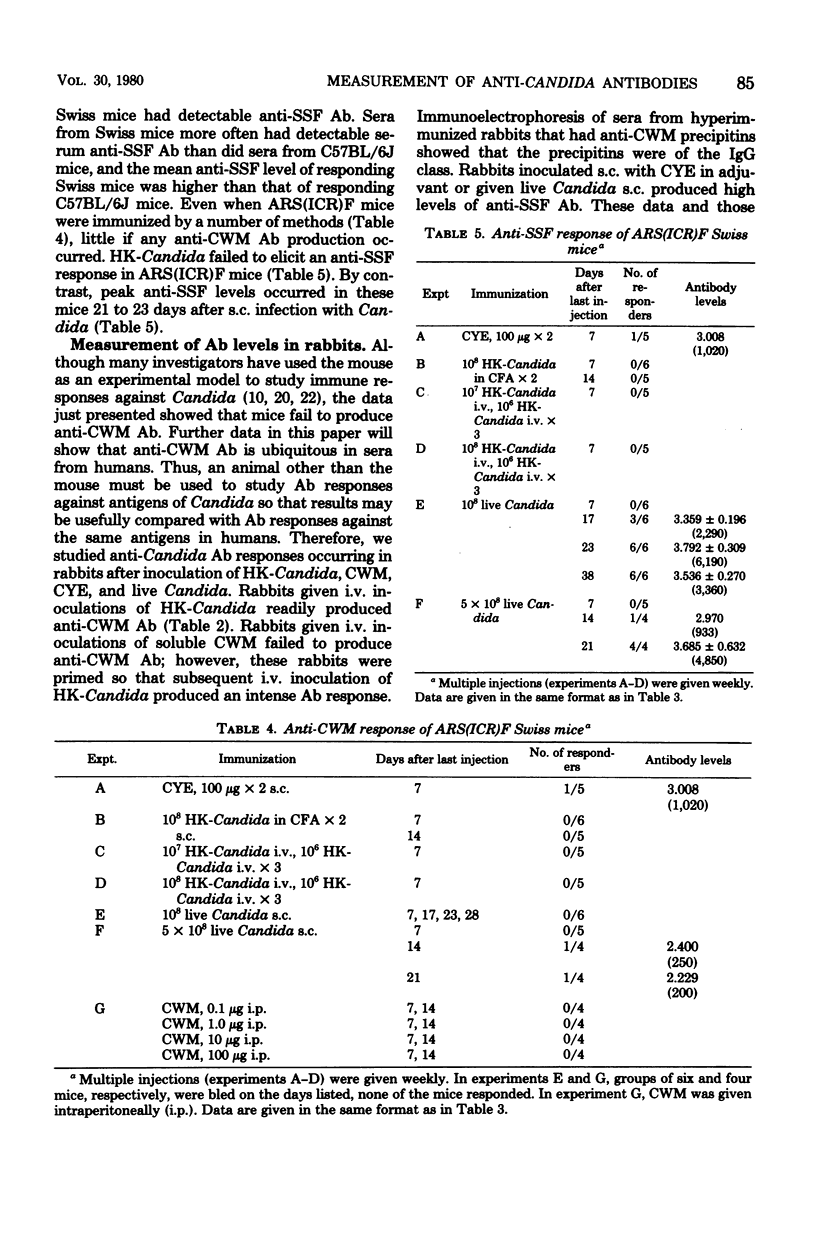
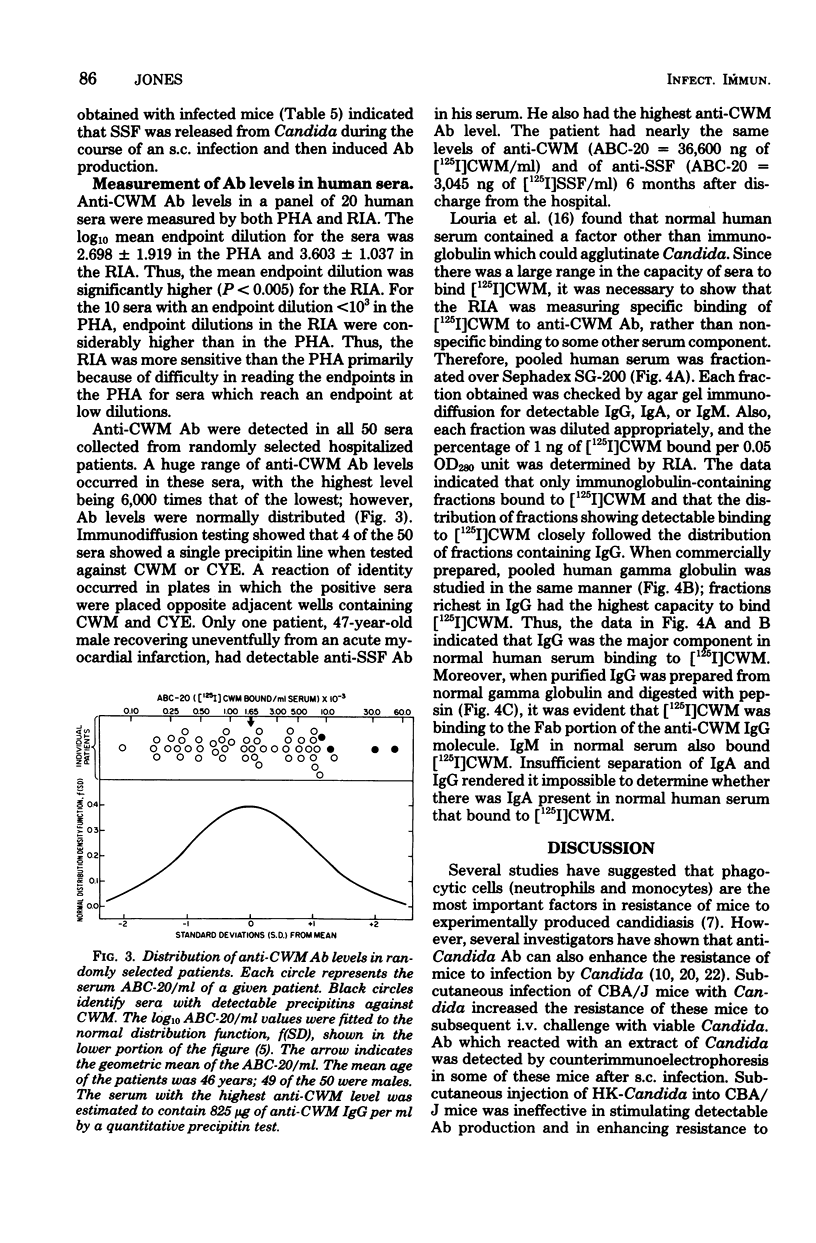
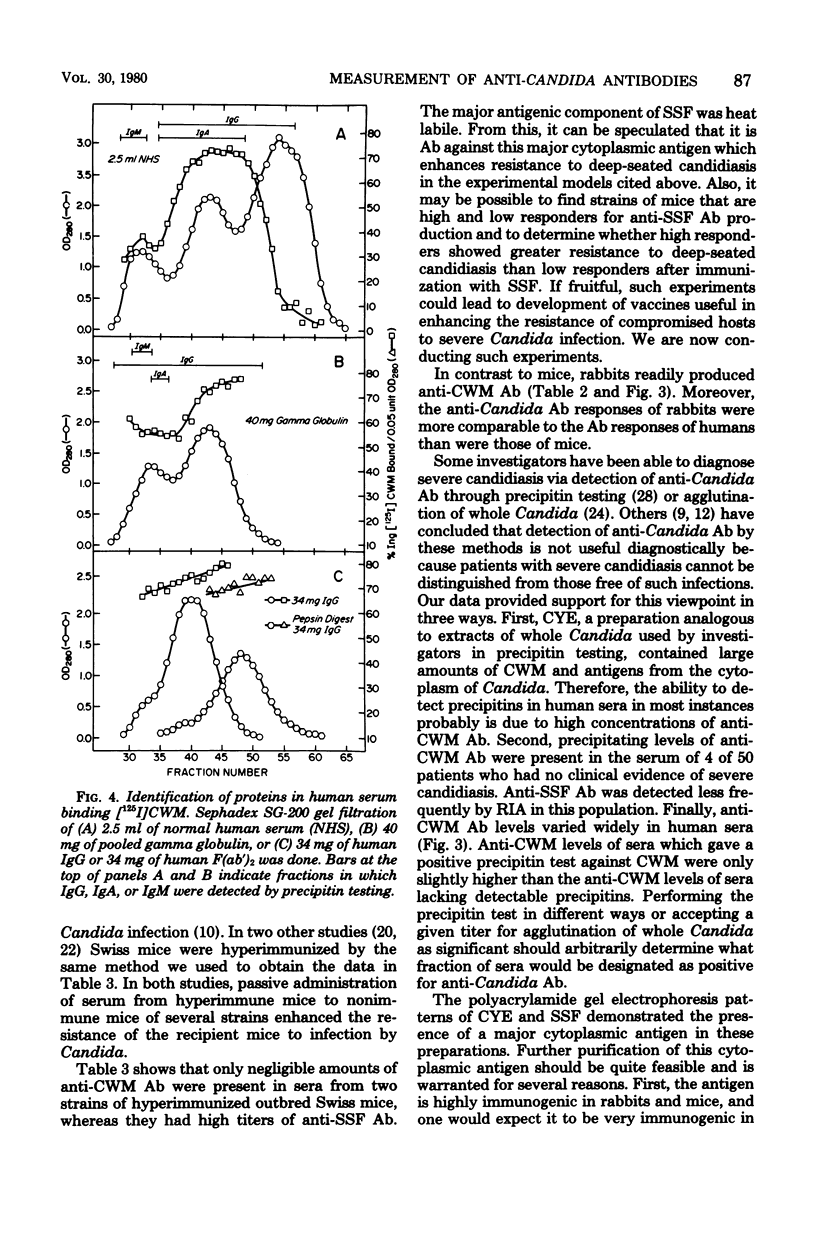
Cell wall mannan of type A Candida albicans was purified, conjugated with tyramine, and labeled with 125I. Labeled cell wall mannan was used in a radioimmunoassay to measure serum antimannan antibody levels. An ammonium sulfate-soluble fraction of a cytoplasmic extract of C. albicans contained a large amount of a major cytoplasmic antigen of this organism. When the sulfate-soluble fraction was labeled with 125I, much more 125I attached to this major antigen than to the other antigens present in the sulfate-soluble fraction. Thus, when serum antisulfate-soluble fraction antibody levels were measured by a radioimmunoassay which used the iodine-labeled sulfate-soluble fraction, antibody against this major cytoplasmic antigen was quantitated. Both radioimmunoassays were used to measure antimannan and antisulfate-soluble fraction antibody levels in mice, rabbits, and humans. Irrespective of the procedure used to elicit antibody against C. albicans antigens, mice failed to produce antimannan antibody. By contrast, all strains of mice tested produced antisulfate-soluble fraction antibody after immunization, and the magnitude of this antibody response depended on the strain of mice immunized. Rabbits readily produced antibody against both mannan and sulfate-soluble fraction when immunized by a variety of methods. Antimannan antibody was detected in 100% of sera from a randomly selected sample of 50 hospitalized patients. Only 1 of 50 patients had antisulfate-soluble fraction antibody detectable by radioimmunoassay. In pooled normal human serum, most antimannan antibody was of the immunoglobulin G class.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chattaway F. W., Holmes M. R., Barlow A. J. Cell wall composition of the mycelial and blastospore forms of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 May;51(3):367–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-3-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb S. J., Parratt D. Determination of antibody levels to Candida albicans in healthy and hospitalised adults using a radioimmunoassay. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Dec;31(12):1161–1166. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.12.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dee T. H., Rytel M. W. Clinical application of counterimmunoelectrophoresis in detection of Candida serum precipitins. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jan;85(1):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Krzesicki R., Jao W. Damage to pseudohyphal forms of Candida albicans by neutrophils in the absence of serum in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):349–359. doi: 10.1172/JCI108945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Lehrer R. I., Stiehm E. R., Fischer T. J., Young L. S. Severe candidal infections: clinical perspective, immune defense mechanisms, and current concepts of therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):91–106. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G., Yu B., Armstrong D. Immunodiffusion and agglutination tests for Candida in patients with neoplastic disease: inconsistent correlation of results with invasive infections. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):349–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger D. K., Domer J. E., McQuitty J. T., Jr Experimental murine candidiasis: pathological and immune responses to cutaneous inoculation with Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):499–509. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.499-509.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger D. K., Domer J. E., Moser S. A., McQuitty J. T., Jr Experimental murine candidiasis: pathological and immune responses in T-lymphocyte-depleted mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):729–737. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.729-737.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinan M. E., Portas M. R., Hill H. R. The candida precipitin test in an immunosuppressed population. Cancer. 1979 Jan;43(1):299–302. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197901)43:1<299::aid-cncr2820430143>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B. Kinetics of the antibody response to type III pneumococcal polysaccharide (SSS-III). I. Use of 125I-labeled SSS-III to study serum antibody levels, as well as the distribution and excretion of antigen after immunization. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):41–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP G., SOLOTOROVSKY M. LOCALIZATION OF ANTIGENS IN MECHANICALLY DISRUPTED CELLS OF CERTAIN SPECIES OF THE GENERA CANDIDA AND TORULOPSIS. J Immunol. 1964 Aug;93:305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Smith J. K., Brayton R. G., Buse M. Anti-Candida factors in serum and their inhibitors. I. Clinical and laboratory observations. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):102–114. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden P., Farr R. S. Binding between components of the tubercle bacillus and humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):931–954. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourad S., Friedman L. Passive immunization of mice against Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1968 Feb;6(2):103–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., WISSLER F. C., LIPMAN L. N., WOERNLEY D. L. Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:230–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearsall N. N., Adams B. L., Bunni R. Immunologic responses to Candida albicans. III. Effects of passive transfer of lymphoid cells or serum on murine candidiasis. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1176–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisler H. D., Hasenclever H. F., Levitan A. A., Henderson E. S. Serologic diagnosis of disseminated candidiasis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Jan;70(1):19–30. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMMERS D. F., GROLLMAN A. P., HASENCLEVER H. F. POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGENS OF CANDIDA CELL WALL. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:491–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M. J., McClatchy J. K., Farr R. S., Minden P. Primary interaction between antibody and components of Alternaria. I. Immunology and chemical characteristics of labeled antigens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Jul;56(1):39–53. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Kozinn P. J., Caroline L. Immune studies in candidiasis. 3. Precipitating antibodies in systemic candidiasis. Sabouraudia. 1964 Oct;3(4):312–320. doi: 10.1080/00362176485190551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. H., Yount W. J. Mannan antigenemia in the diagnosis of invasive Candida infections. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1045–1053. doi: 10.1172/JCI108555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingard J. R., Merz W. G., Saral R. Candida tropicalis: a major pathogen in immunocompromised patients. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Oct;91(4):539–543. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-4-539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]