Abstract
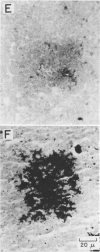
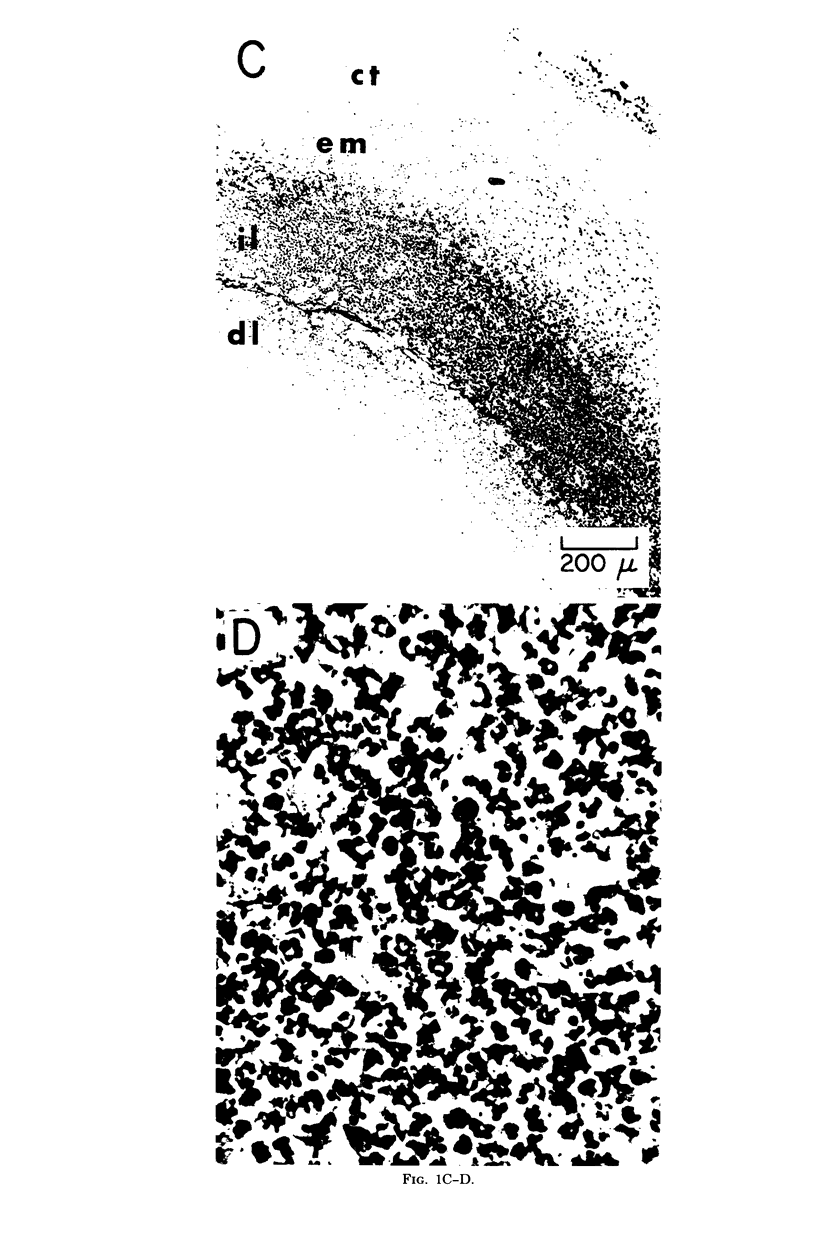
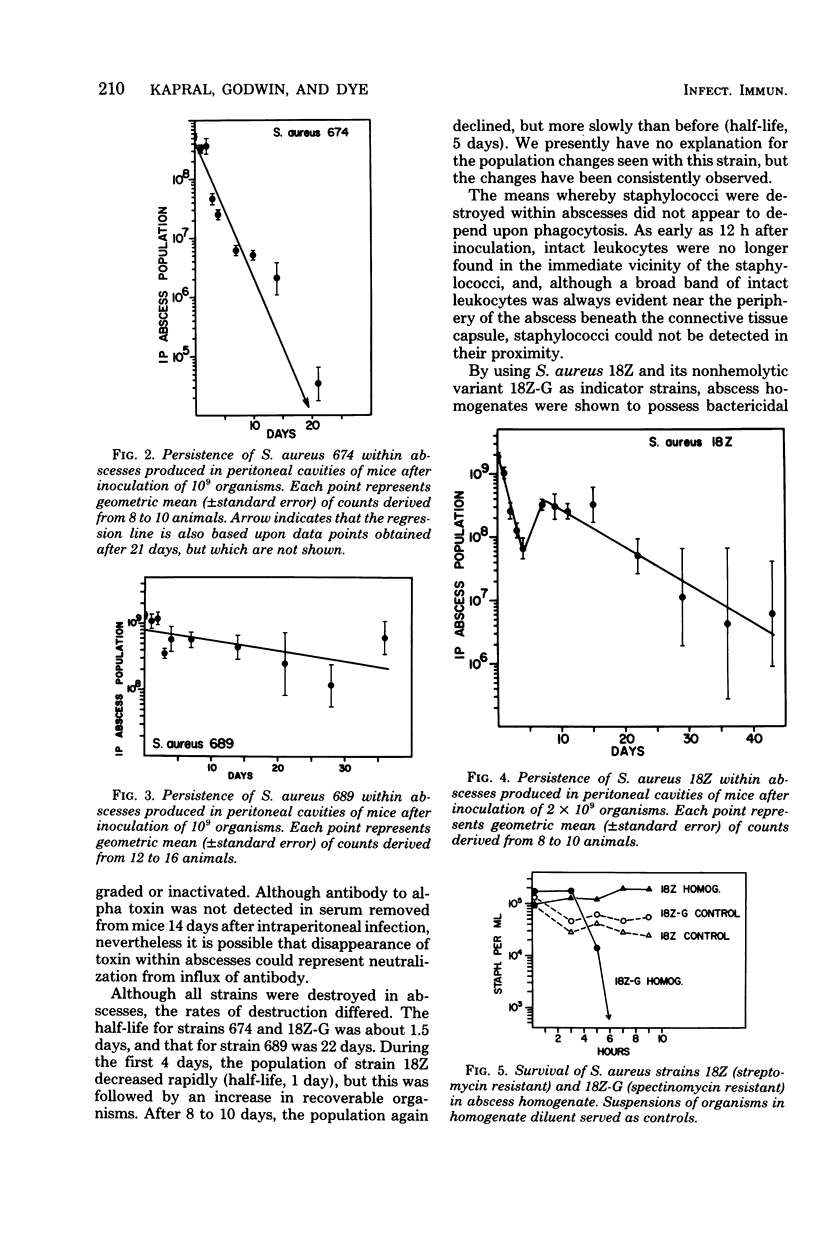
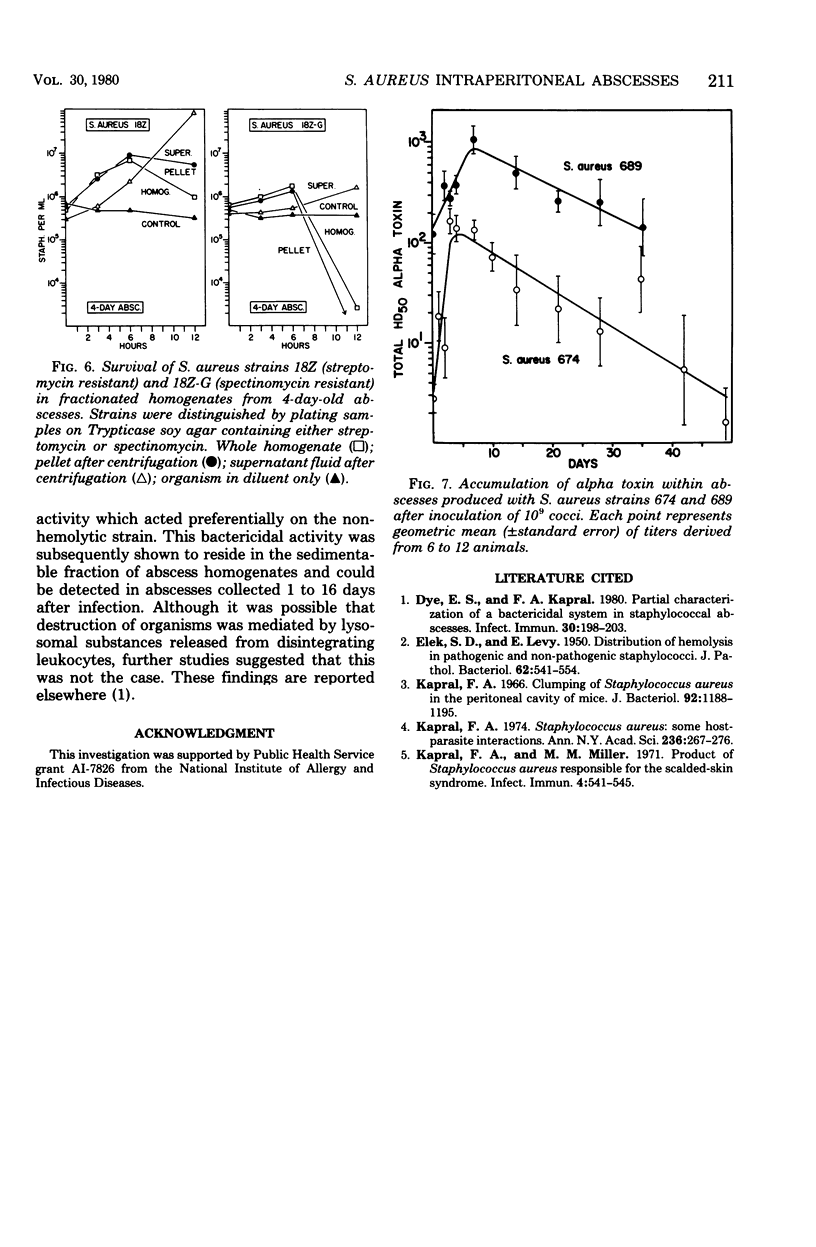
Certain Staphylococcus aureus strains, when inoculated into the peritoneal cavity of mice, were clumped and surrounded by a thick layer of leukocytes. After being enclosed with a connective tissue capsule, the structures histologically resembled staphylococcal abscesses. Of four strains examined, all were destroyed within abscesses, although at different rates. Abscess homogenates possessed bactericidal activity toward staphylococci, and this activity was associated with the sedimentable fraction of the homogenates. Leukocytes did not appear to be responsible for the bactericidal activity. Appreciable quantities of alpha toxin accumulated in these abscesses even without multiplication of the organisms. This model infection offers opportunities for studying some aspects of staphylococcal host-parasite interactions occurring in localized lesions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dye E. S., Kapral F. A. Partial characterization of a bactericidal system in staphylococcal abscesses. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):198–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.198-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., LEVY E. Distribution of haemolysins in pathogenic and non-pathogenic staphylococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;62(4):541–554. doi: 10.1002/path.1700620405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Clumping of Staphylococcus aureus in the peritoneal cavity of mice. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1188–1195. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1188-1195.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Staphylococcus aureus: some host-parasite interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):267–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]