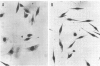
Abstract
Several serotypes of Salmonella were shown to release increased amounts of a cholera toxin-like toxin during culture in vitro with mitomycin C (MTC). Filter-sterilized culture supernatants containing the toxin caused elongation of Chinese hamster ovary cells, which could be blocked by heating the supernatants at 100 degrees C for 15 min or by adding mixed gangliosides or monospecific cholera antitoxin. When MTC was not added to the Salmonella cultures, little or no toxin was detected in crude, unconcentrated culture supernatants. Optimal production of toxin was observed in the presence of 0.5 micrograms of MTC per ml in shake flask cultures of Casamino Acids-yeast extract medium, Syncase, or peptone saline at 37 degrees C. Meat infusion media (heart infusion and brain heart infusion) plus MTC resulted in poor toxin yield. Culture filtrates frequently could be diluted 1:8 and still result in elongation of Chinese hamster ovary cells.
Full text
PDF

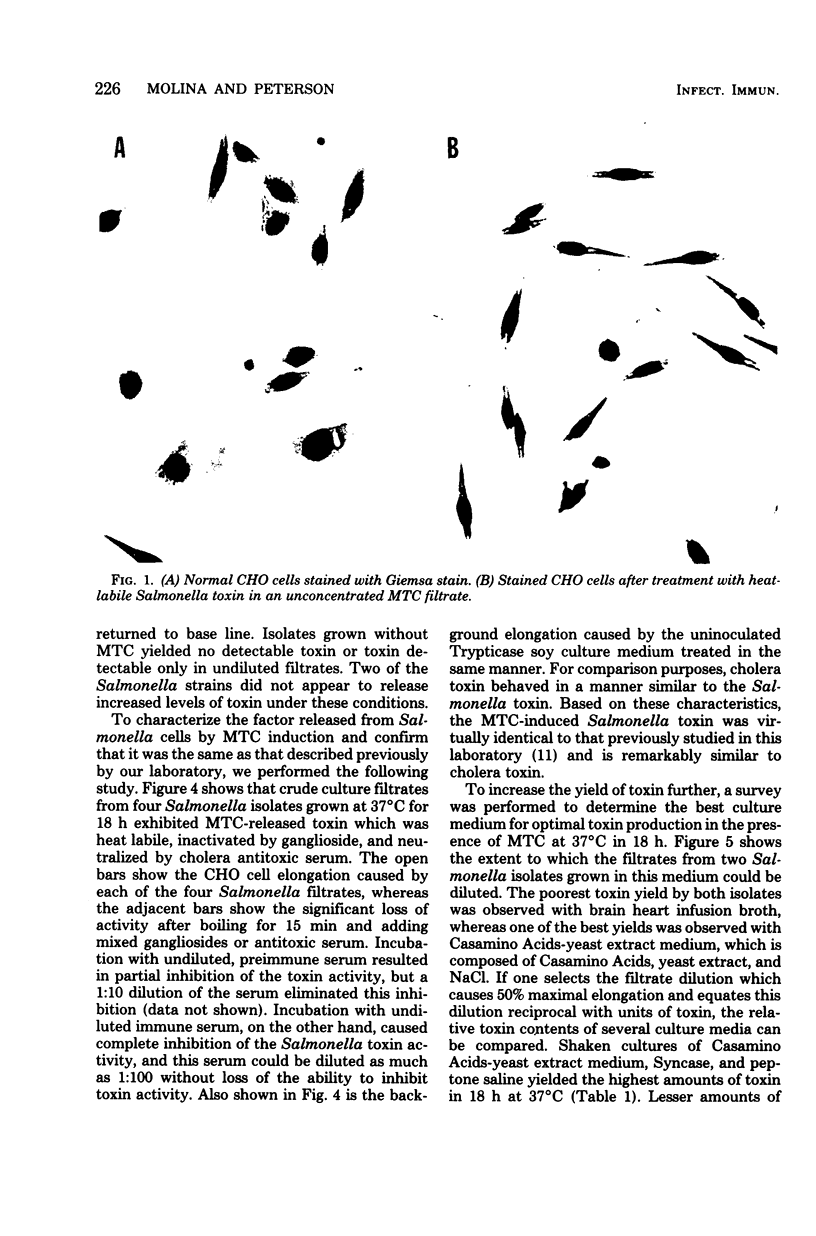
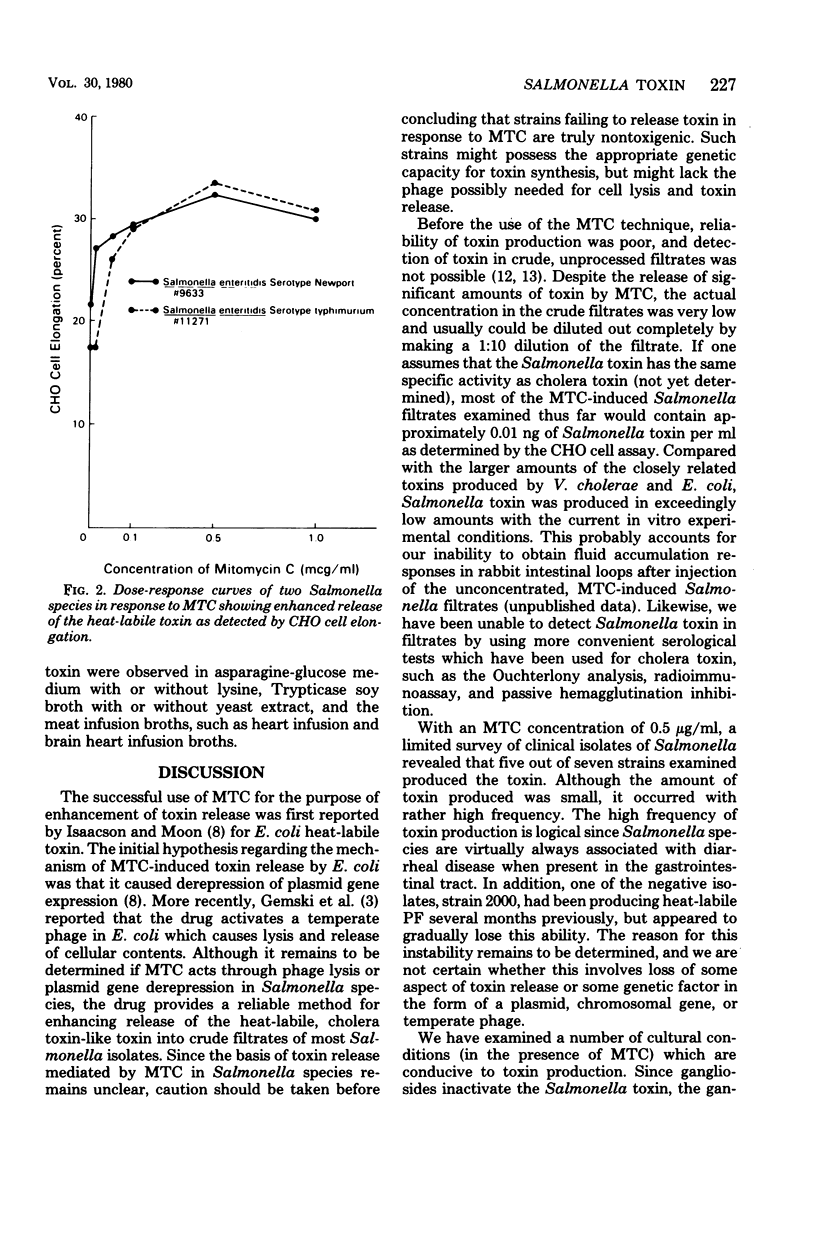
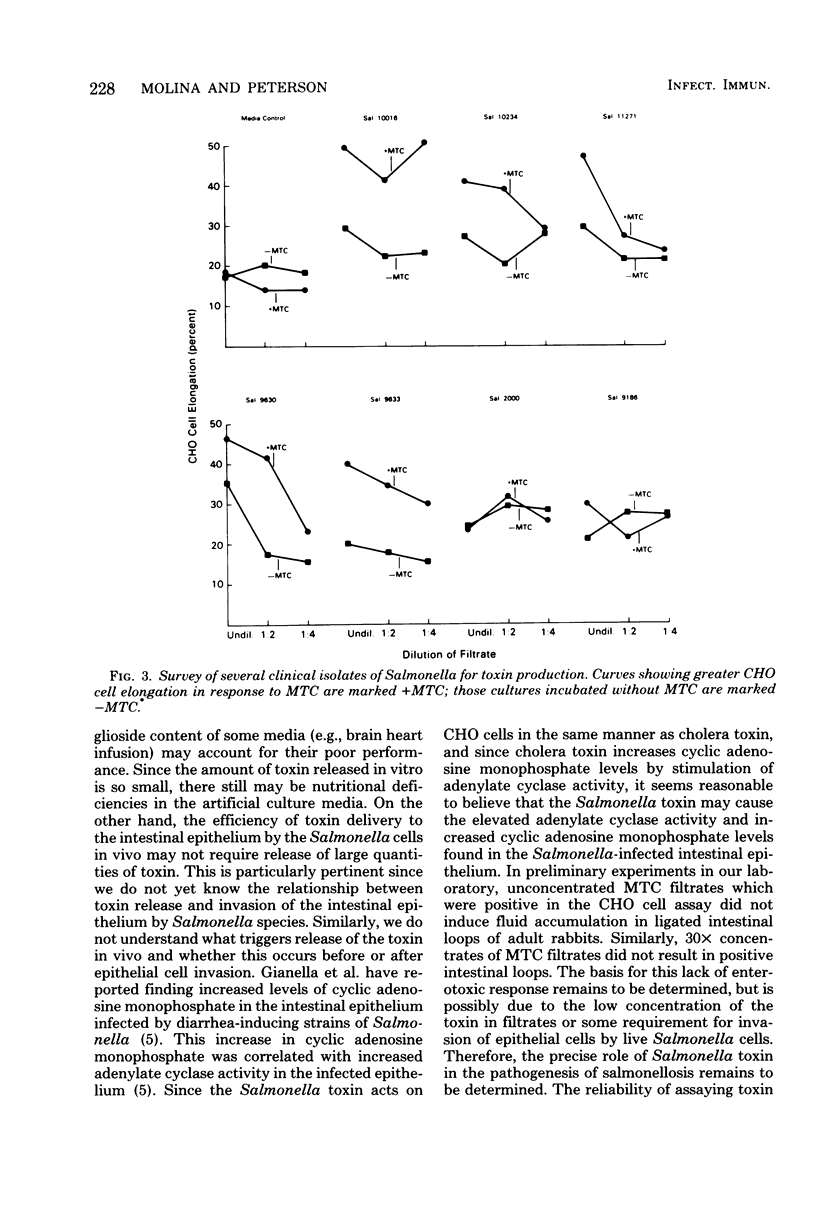

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Callahan L. T., 3rd, Richardson S. H. Biochemistry of Vibrio cholerae virulence. 3. Nutritional requirements for toxin production and the effects of pH on toxin elaboration in chemically defined media. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):567–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.567-572.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Atthasampunna P., Chulasamaya M., Charunmethee P. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera: biologic ativities of purified procholeragen A. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., O'Brien A. D., Wohlhieter J. A. Cellular release of heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage induction. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1076–1082. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1076-1082.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Formal S. B., Dammin G. J., Collins H. Pathogenesis of salmonellosis. Studies of fluid secretion, mucosal invasion, and morphologic reaction in the rabbit ileum. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):441–453. doi: 10.1172/JCI107201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Gots R. E., Charney A. N., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Formal S. B. Pathogenesis of Salmonella-mediated intestinal fluid secretion. Activation of adenylate cyclase and inhibition by indomethacin. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1238–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejtmancik K. E., Peterson J. W., Markel D. E., Kurosky A. Radioimmunoassay for the antigenic determinants of cholera toxin and its components. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):621–628. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.621-628.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson R. E., Moon H. W. Induction of heat-labile enterotoxin synthesis in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli mitomycin C. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1271–1275. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1271-1275.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koupal L. R., Deibel R. H. Assay, characterization, and localization of an enterotoxin produced by Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):14–22. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.14-22.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosky A., Markel D. E., Peterson J. W. Covalent structure of the beta chain of cholera enterotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7257–7264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Sandefur P. D. Evidence of a role for permeability factors in the pathogenesis of salmonellosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):197–209. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Isolation of skin permeability factors from culture filtrates of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):671–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.671-679.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandefur P. D., Peterson J. W. Neutralization of Salmonella toxin-induced elongation of Chinese hamster ovary cells by cholera antitoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):988–992. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.988-992.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedlock D. M., Koupal L. R., Deibel R. H. Production and partial purification of Salmonella enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):375–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.375-380.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]