Abstract
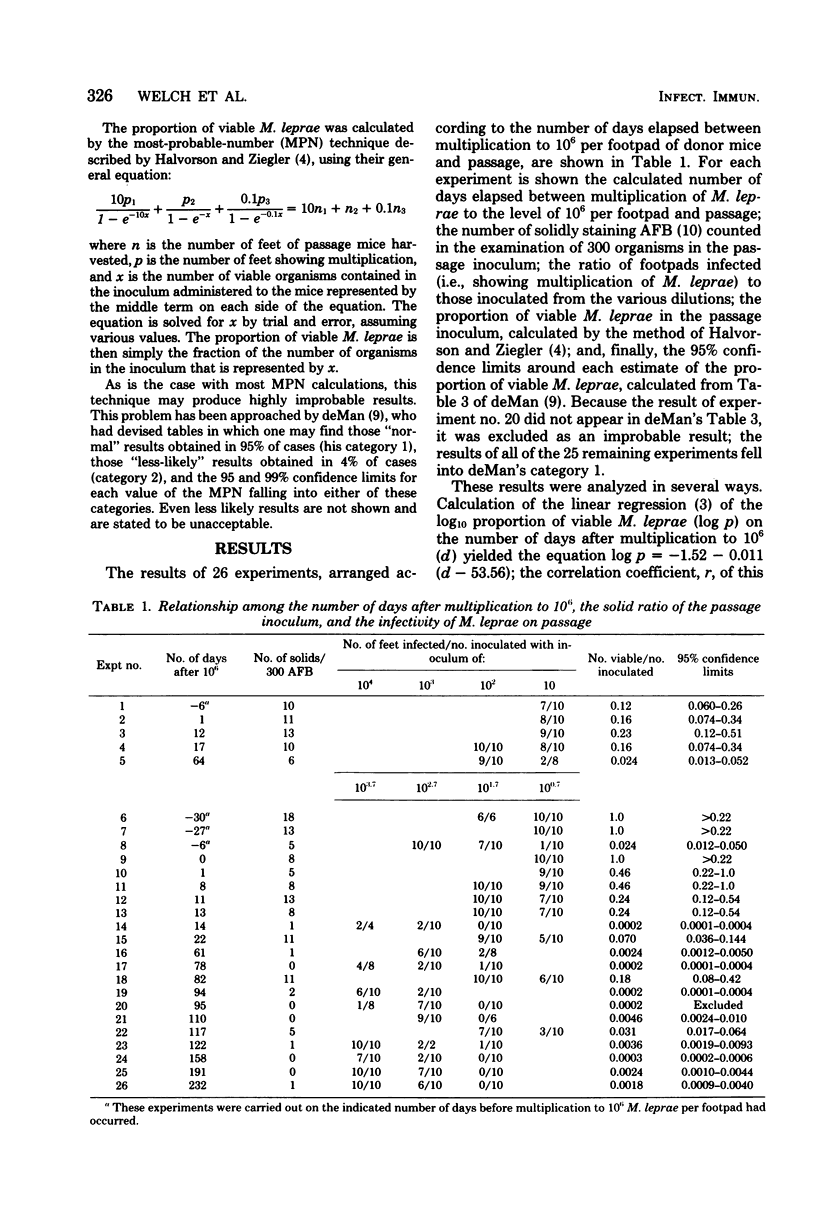
To measure the rate at which Mycobacterium leprae are killed in the course of the mouse footpad infection after the maximum of multiplication has been achieved, M. leprae were harvested shortly before and at intervals after multiplication had reached the level of 10(6) organisms per footpad, serially diluted, and inoculated into the footpads of passage mice. Beginning 1 year later, foot-by-foot harvests of M. leprae were performed from passage mice, and the proportion of viable organisms in the passage inocula was calculated by means of a most-probable-number calculation. In addition, the proportion of solidly staining M. leprae was measured in the passage inocula. The proportion of viable M. leprae in the passage inocula was found to decrease with the time after multiplication to 10(6) organisms per footpad of donor mice; the half-time of loss of viable M. leprae was 25 days. The proportion of solidly staining organisms appeared to be directly related to the proportion of viable organisms, as measured by mouse passage, and inversely proportional to the time after multiplication to 10(6) organisms per footpad.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colston M. J., Hilson G. R., Banerjee D. K. The "proportional bactericidal test": a method for assessing bactericidal activity in drugs against Mycobacterium leprae in mice. Lepr Rev. 1978 Mar;49(1):7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Levy L. Ultrastructural changes in cells of the mouse footpad infected with Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):238–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.238-247.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson H. O., Ziegler N. R. Application of Statistics to Problems in Bacteriology: I. A Means of Determining Bacterial Population by the Dilution Method. J Bacteriol. 1933 Feb;25(2):101–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.25.2.101-121.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy L. Death of Mycobacterium leprae in mice, and the additional effect of dapsone administration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Dec;135(3):745–749. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy L., Moon N., Murray L. P., O'Neill S. M., Gustafson L. E., Evans M. J. Studies of the mouse foot pad technic for cultivation of Mycobacterium leprae. 1. Fate of inoculated organisms. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1974 Apr-Jun;42(2):165–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy L. Prolongation of the lag phase of Mycobacterium leprae by dapsone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jan;139(1):263–266. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy L. Studies of the mouse foot pad technique for cultivation of Mycobacterium leprae. 3. Doubling time during logarithmic multiplication. Lepr Rev. 1976 Jun;47(2):103–106. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19760019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRae D. H., Shepard C. C. Relationship Between the Staining Quality of Mycobacterium leprae and Infectivity for Mice. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):116–120. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.116-120.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REES R. J. LIMITED MULTIPLICATION OF ACID-FAST BACILLI IN THE FOOT-PADS OF MICE INOCULATED WITH MYCOBACTERIUM LEPRAE. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Apr;45:207–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD C. C. Acid-fast bacilli in nasal excretions in leprosy, and results of inoculation of mice. Am J Hyg. 1960 Mar;71:147–157. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD C. C., MCRAE D. H. MYCOBACTERIUM LEPRAE IN MICE: MINIMAL INFECTIOUS DOSE, RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STAINING QUALITY AND INFECTIVITY, AND EFFECT OF CORTISONE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:365–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.365-372.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., Chang Y. T. Effect of DDS on established infections with Mycobacterium leprae in mice. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1967 Jan-Mar;35(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., McRae D. H. A method for counting acid-fast bacteria. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jan-Mar;36(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., McRae D. H. Hereditary Characteristic that Varies Among Isolates of Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):121–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.121-126.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


