Abstract
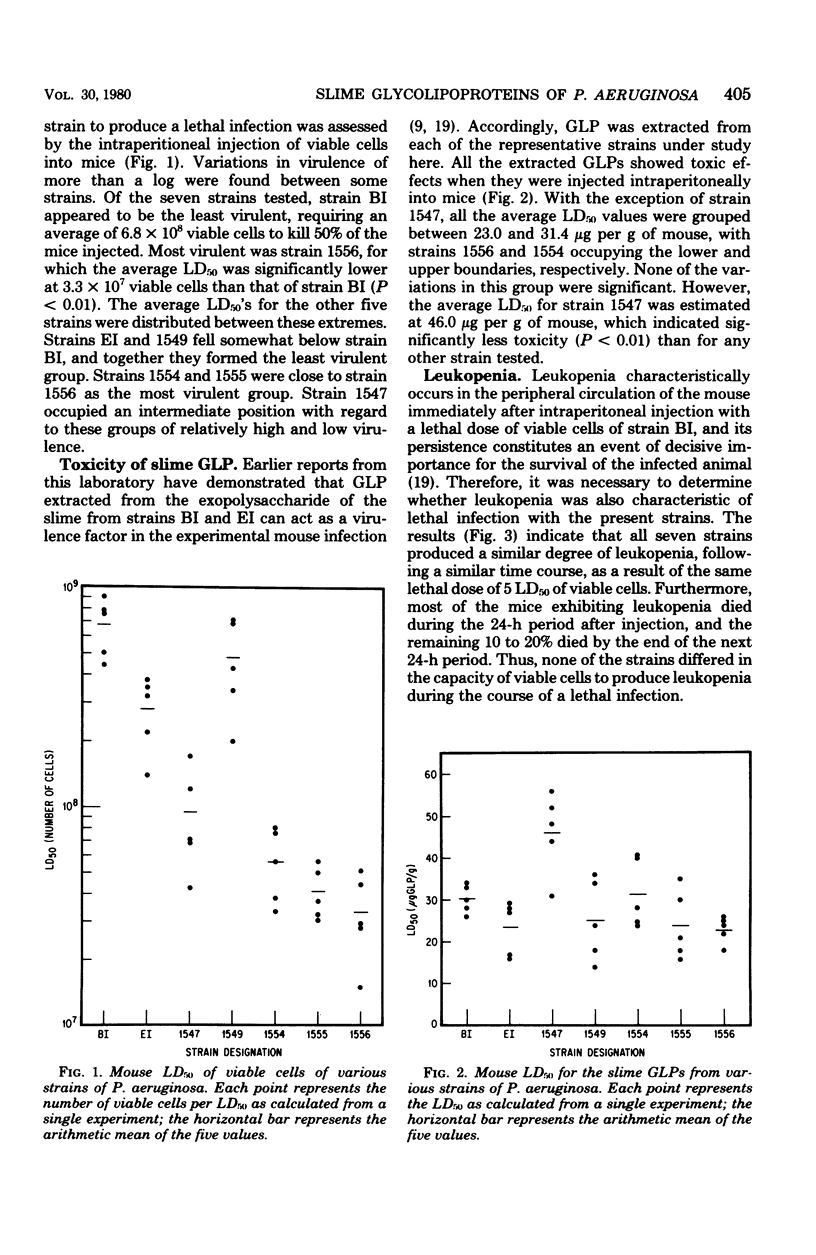
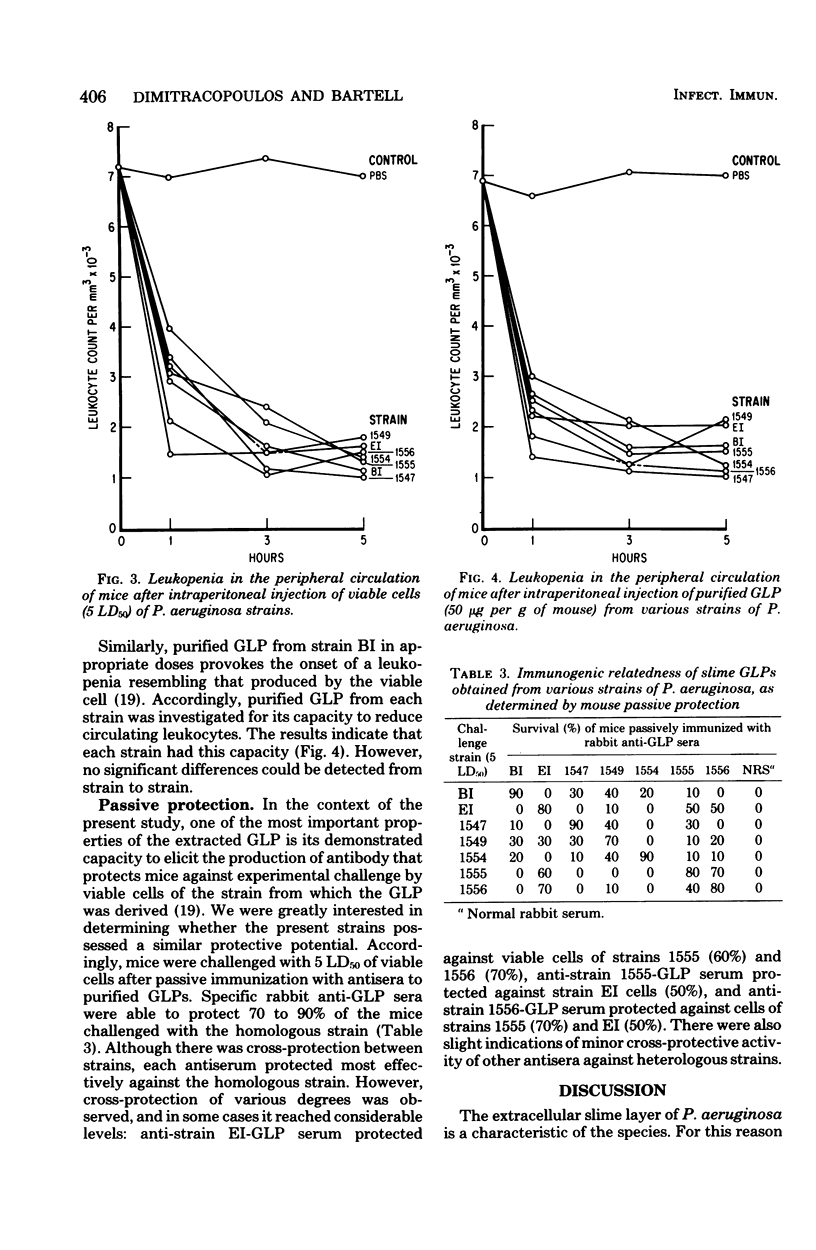
Several strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were differentiated on the basis of the surface properties of the cells. Fisher immunotype, phage type, polysaccharide depolymerase type, and indirect hemagglutination reactions were used for this purpose. Each strain was then studied with respect to events known to occur during the experimental infection of mice with P. aeruginosa. The virulence of the viable cells varied significantly, although all strains were virulent. Glycolipoproteins were isolated from the slime of each strain, and they appeared similar chemically when they were analyzed for gross composition. The toxicity of the isolated glycolipoproteins varied insignificantly, except for that of one strain. Viable cells of each strain and their respective glycolipoproteins caused leukopenia, which occurs in the course of the lethal infection. The antisera to the glycolipoproteins protected mice in every case against infection by the homologous strains. In some cases, various degrees of cross-protection were observed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alms T. H., Bass J. A. Immunization against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Induction of protection by an alcohol-precipitated fraction from the slime layer. J Infect Dis. 1967 Jun;117(3):249–256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartell P. F., Lam G. K., Orr T. E. Purification and properties of polysaccharide depolymerase associated with phage-infected Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2077–2080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartell P. F., Orr T. E., Chudio B. Purification and Chemical Composition of the Protective Slime Antigen of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):543–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.543-548.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartell P. F., Orr T. E. Distinct slime polysaccharide depolymerases of bacteriophage-infected Pseudomonas aeruginosa: evidence of close association with the structured bacteriophage particle. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):580–584. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.580-584.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartell P. F., Orr T. E., Lam G. K. Polysaccharide depolymerase associated with bacteriophage infection. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.56-62.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitracopoulos G., Bartell P. F. Phage-related surface modifications of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: effects on the biological activity of viable cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.87-93.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitracopoulos G., Sensakovic J. W., Bartell P. F. Slime of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: in vivo production. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):152–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.152-156.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. W., Devlin H. B., Gnabasik F. J. New immunotype schema for Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on protective antigens. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):835–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.835-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU P. V., ABE Y., BATES J. L. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1961 Mar-Apr;108:218–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn M., Sensakovic J. W., Bartell P. F. In vivo distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa slime glycolipoprotein: association with leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.109-114.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Sidberry H. F., Zolyomi S., Sadoff J. C. Isolation and characterization of a high-molecular-weight polysaccharide from the slime of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):908–918. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.908-918.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. IV. The composition of the cell walls of some Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Apr;10(4):512–523. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann S., Boring J. R. Antiphagocytic Effect of Slime from a Mucoid Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):762–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.762-767.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensakovic J. W., Bartell P. F. Biological activity of fragments derived from the extracellular slime glycolipoprotein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):808–812. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.808-812.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensakovic J. W., Bartell P. F. Glycolipoprotein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a protective antigen against P. aeruginosa infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):304–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.304-309.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensakovic J. W., Bartell P. F. The slime of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: biological characterization and possible role in experimental infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):101–109. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


