Abstract
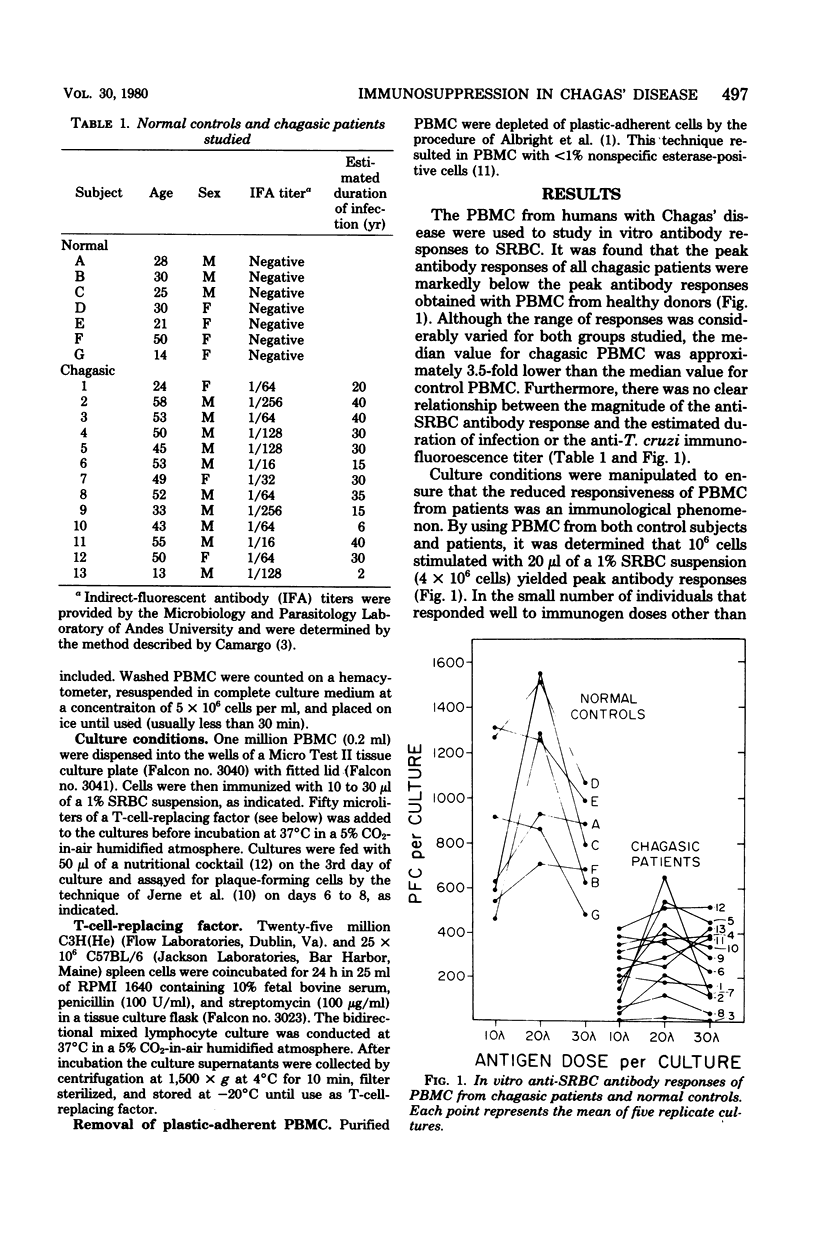
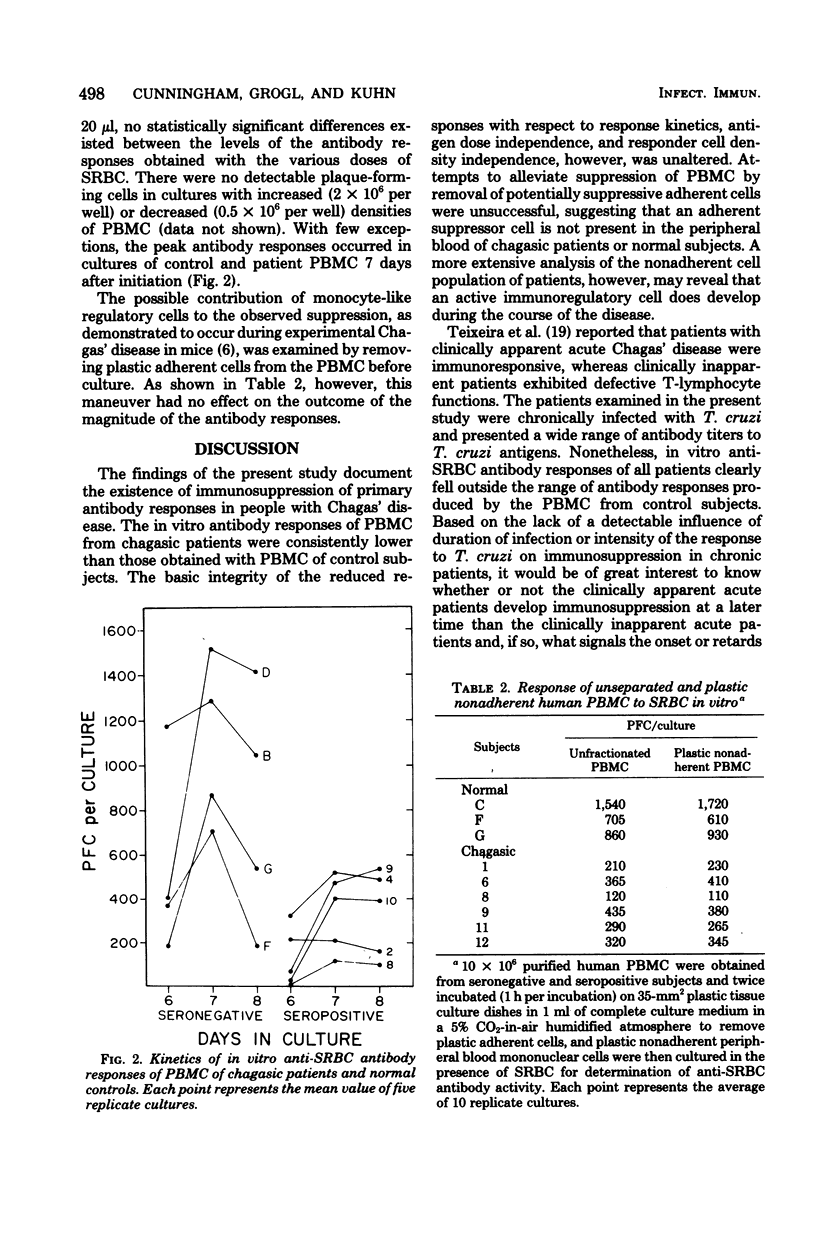
Peripheral blood leukocytes from patients serologically positive for Chagas' disease were examined for their ability to respond to heterologous antigens in vitro. It was found that mononuclear cells from chagasic patients had greatly reduced ability to respond to sheep erythrocytes (SRBC) as compared with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from control subjects. The reduction in anti-SRBC antibody activity was independent of antigen dose and was not a result of differences in antibody response kinetics. Depletion of plastic-adherent result of differences in antibody response kinetics. Depletion of plastic-adherent cells from the PBMC of patients did not affect the suppressed state of the nonadherent lymphocytes. No relationship was evident between the duration of Trypanosoma cruzi infection and the degree of humoral responsiveness.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright J. F., Deitchman J. W., Hassell S. A., Ozato K. Differential antibody production of adherent and nonadherent spleen cells transferred to irradiated and cyclophosphamide-treated recipient mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Apr;17(4):195–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo M. E. Fluorescent antibody test for the serodiagnosis of American trypanosomiasis. Technical modification employing preserved culture forms of Trypanosoma cruzi in a slide test. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1966 Sep-Oct;8(5):227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Click R. E., Benck L., Alter B. J. Immune responses in vitro. I. Culture conditions for antibody synthesis. Cell Immunol. 1972 Feb;3(2):264–276. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton B. A., Ortiz-Ortiz L., Garcia W., Martinez T., Capin R. Trypanosoma cruzi: early immune responses in infected mice. Exp Parasitol. 1975 Jun;37(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(75)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. S., Kuhn R. E., Rowland E. C. Suppression of humoral responses during Trypanosoma cruzi infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):155–160. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.155-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. S., Kuhn R. E. Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppression of the primary immune response in murine cell cultures to T-cell-dependent and -independent antigens. J Parasitol. 1980 Feb;66(1):16–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham D. S., Kuhn R. E. Trypanosoma cruzi-induced suppressor substance. I. cellular involvement and partial characterization. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2122–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K., Henry C., Nordin A. A., Fuji H., Koros A. M., Lefkovits I. Plaque forming cells: methodology and theory. Transplant Rev. 1974;18:130–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati A. L., Taussig M. J., Meo T., Pernis B. Induction of an antibody response in cultures of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):573–585. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos C., Lamoyi E., Feoli M., Rodriguez M., Perez M., Ortiz-Ortiz L. Trypanosoma cruzi: immunosuppressed response to different antigens in the infected mouse. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Aug;45(2):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos C., Schädtler-Siwon I., Ortiz-Ortiz L. Suppressor cells present in the spleens of Trypanosoma cruzi-infected mice. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1243–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Larson C. L., Speer C. A. Contact sensitivity responses in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):548–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.548-554.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G., Larson C. L., Speer C. A. Suppression of cell-mediated immunity in experimental Chagas' disease. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Jun 3;52(1):11–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00380553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland E. C., Kuhn R. E. Suppression of anamnestic cellular responses during experimental American trypanosomiasis. J Parasitol. 1978 Aug;64(4):741–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland E. C., Kuhn R. E. Suppression of cellular responses in mice during Trypanosoma cruzi infections. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):393–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.393-397.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira A. R., Teixeira G., Macêdo V., Prata A. Acquired cell-mediated immunodepression in acute Chagas' disease. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1132–1141. doi: 10.1172/JCI109232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


