Abstract
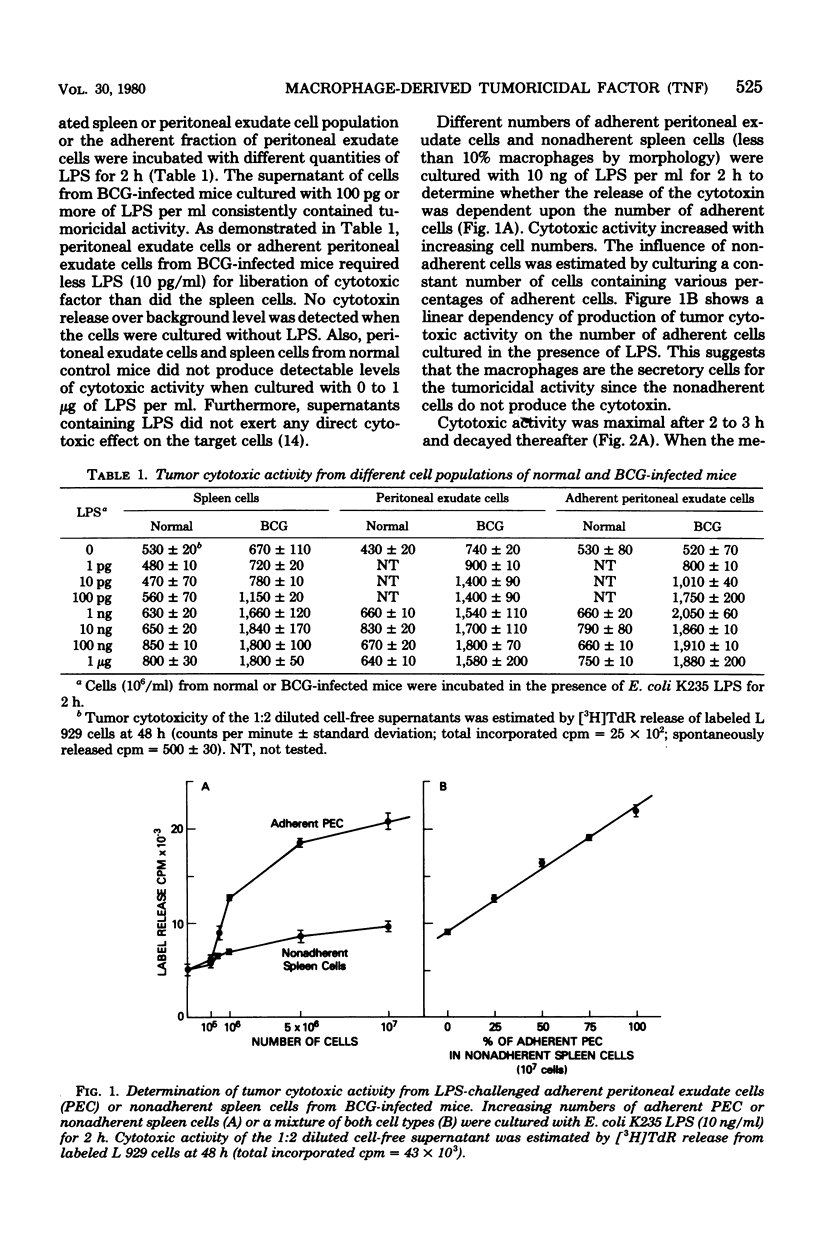
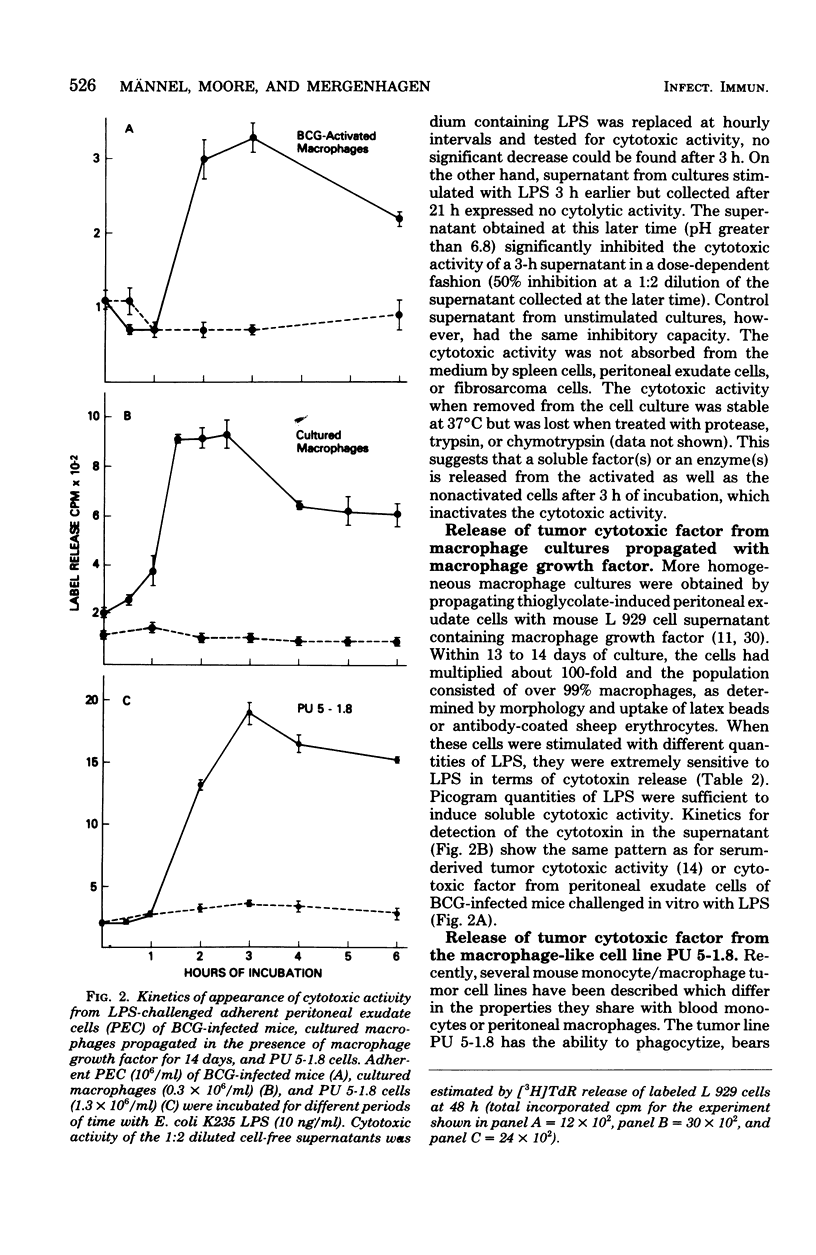
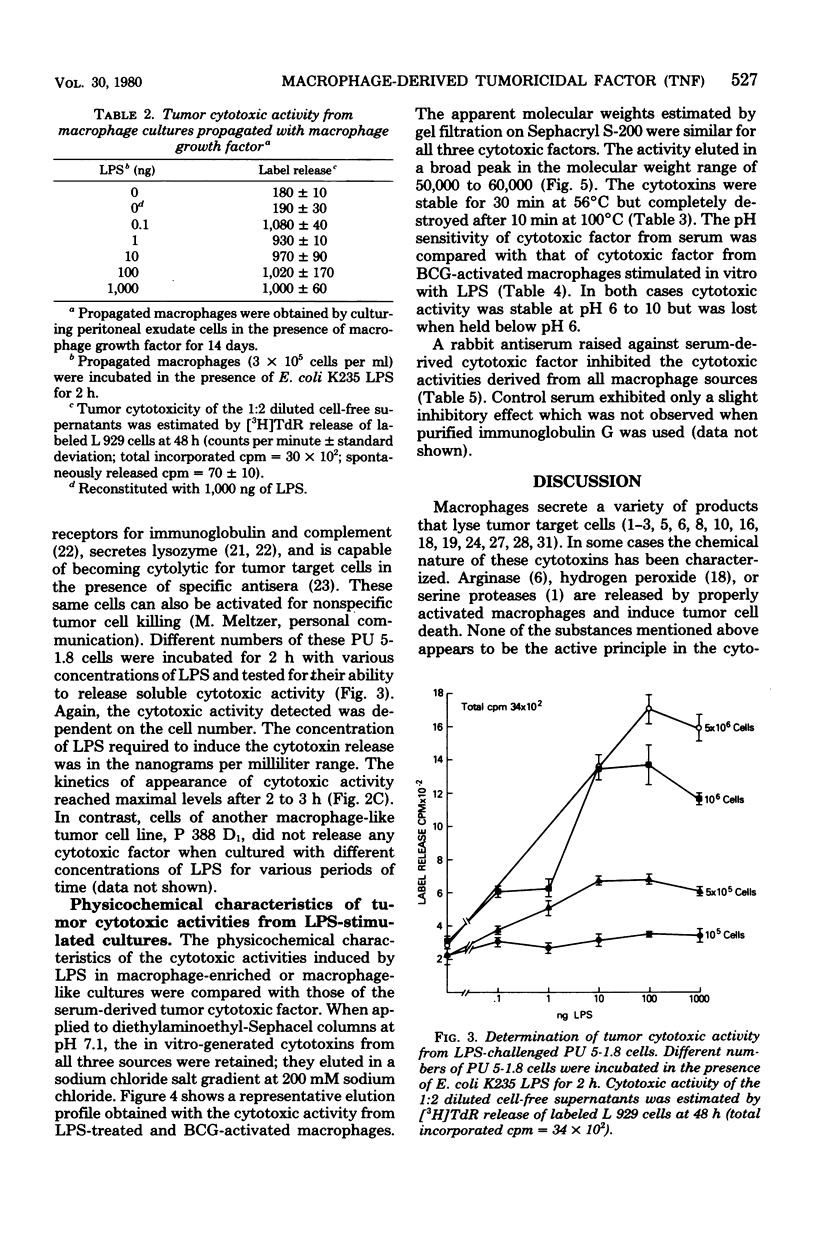
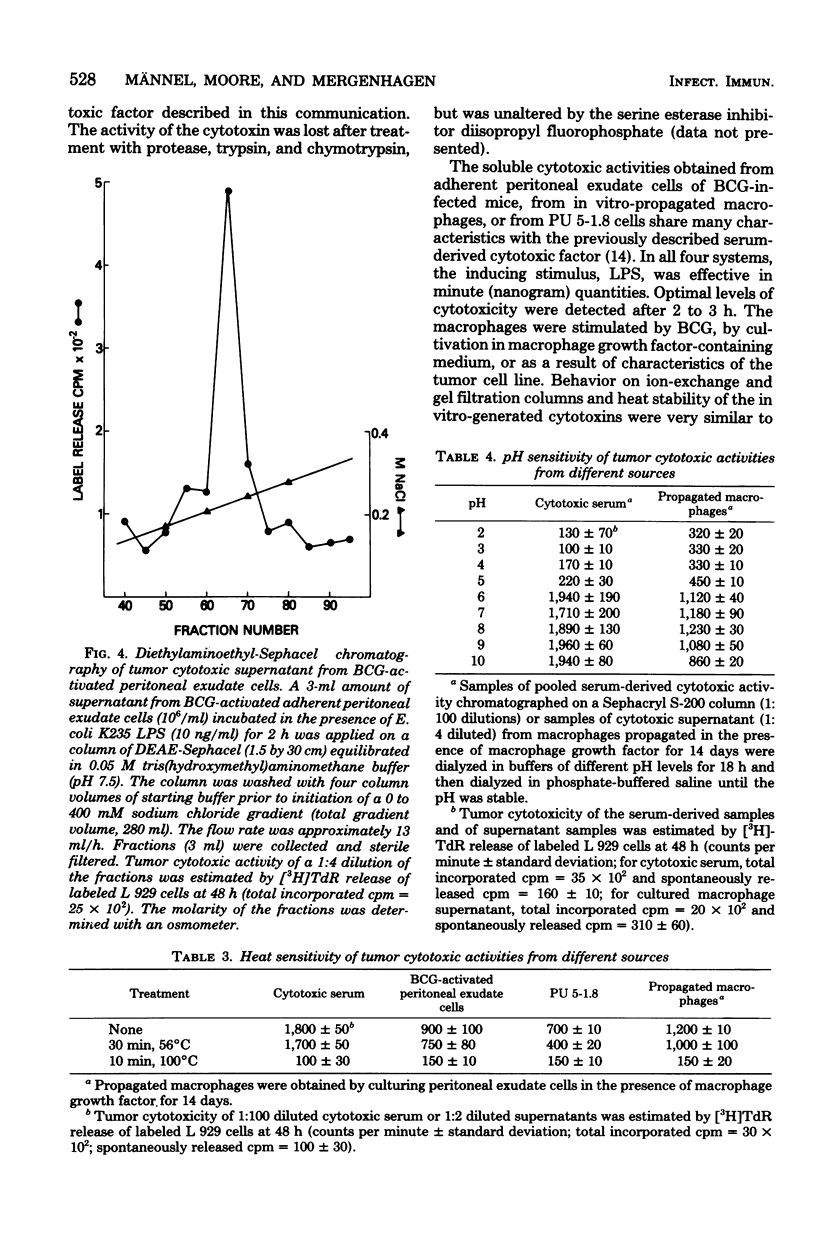
Macrophage-enriched peritoneal exudate cells from mice infected with Mycobacterium bovis BCG, macrophage-like tumor cells (PU 5-1.8), and peritoneal macrophages propagated in vitro with macrophage growth factor released tumoricidal activity into the culture medium within 2 to 3 h after stimulation with nanogram quantities of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. The cytotoxic activities from each of the macrophage culture supernatants eluted from diethylaminoethyl-Sephacel columns at a sodium chloride concentration of 200 mM exhibited a molecular weight of 50,000 to 60,000 as estimated by gel filtration, were stable at 56 degrees C for 30 min, and were active at a pH range of 6 to 10. A rabbit antiserum directed against serum-derived cytotoxic activity (tumor-necrotizing factor) from BCG-infected and lipopolysaccharide-challenged mice inhibited all of the cytotoxic activities generated in vitro. This suggests that the macrophage-derived cytotoxins are identical with serum-derived cytotoxic factor, which further implies that the macrophage is the cellular source of tumor-necrotizing factor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Kao K. J., Farb R., Pizzo S. V. Effector mechanisms of cytolytically activated macrophages. II. Secretion of a cytolytic factor by activated macrophages and its relationship to secreted neutral proteases. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit R. R., Kim K. J. Macrophage cell lines produce a cytotoxin. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1785–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon J., Williams R. T., Unanue E. R. An inhibitor of cell proliferation released by cultures of macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4273–4277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. C., Gaetjens E., Broome J. D. Macromolecular inhibitory factor for lymphoid cells produced by mouse macrophages. Immunology. 1977 Sep;33(3):391–398. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie G. A. Activated macrophages kill tumour cells by releasing arginase. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):758–759. doi: 10.1038/273758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Williams R. M., Benacerraf B. Specific and nonspecific antitumor immunity. II. Macrophage-mediated nonspecific effector activity induced by BCG and similar agents. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Mar;54(3):709–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heise E. R., Weiser R. S. Factors in delayed sensitivity: lymphocyte and macrophage cytotoxins in the tuberculin reaction. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):570–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helson L., Green S., Carswell E., Old L. J. Effect of tumour necrosis factor on cultured human melanoma cells. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):731–732. doi: 10.1038/258731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. J., Granger G. A. The in vitro induction and release of a cell toxin by immune C57B1-6 mouse peritoneal macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jan;3(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Stewart C. C. Colony formation by mouse peritoneal exudate cells in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 6;243(127):176–177. doi: 10.1038/newbio243176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. II. Production by monocytes. Br J Cancer. 1978 Aug;38(2):310–315. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Sievert H. W., Barlow G. H., Finley R. A., Lee A. Y. Chemical, physical, biological properties of a lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K-235. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2363–2372. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melsom H., Sanner T., Seljelid R. Macrophage cytolytic factor. Some observations on its physicochemical properties and site of action. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Sep;94(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90488-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Tucker R. W., Breuer A. C. Interaction of BCG-activated macrophages with neoplastic and noneoplastic cell lines in vitro: cinemicrographic analysis. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):30–42. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Farrar J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Separation of a serum-derived tumoricidal factor from a helper factor for plaque-forming cells. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1106–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Meltzer M. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Generation and characterization of a lipopolysaccharide-induced and serum-derived cytotoxic factor for tumor cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.204-211.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Silverstein S. C., Brukner L. H., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. II. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):100–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper C. E., McIvor K. L. Alloimmune peritoneal macrophages as specific effector cells: characterization of specific macrophage cytotoxin. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jun;17(2):423–430. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Broxmeyer H. E., Nakoinz I. Immunostimulators induce granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating activity and block proliferation in a monocyte tumor cell line. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):611–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Moore M. A., Nilsson K. Lysozyme synthesis by established human and murine histiocytic lymphoma cell lines. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1528–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Antibody-dependent killing of erythrocyte and tumor targets by macrophage-related cell lines: enhancement by PPD and LPS. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):950–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Direct toxic effects of immunopotentiators on monocytic, myelomonocytic, and histiocytic or macrophage tumor cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1977 Feb;37(2):546–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Lucas Z. J. Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes. V. Role of soluble toxin in macrophage-inhibited cultures of tumor cells. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):395–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: development of macrophage cytotoxic activity requires completion of a sequence of short-lived intermediary reactions. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2035–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. W., Doe W. F., McIntosh A. T. Functional characterization of a stable, noncytolytic stage of macrophage activation in tumors. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1511–1520. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Brandis H. Cytotoxicity mediated by soluble macrophage product(s). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Aug;55(2):393–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sintek D. E., Pincus W. B. Cytotoxic factor from peritoneal cells: purification and characteristics. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Dec;8(6):508–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. C., Adles C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Interaction of macrophages with tumor cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;73(Pt B):423–433. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3300-5_36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. C., Lin H. Macrophage growth factor and its relationship to colony stimulating factor. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Apr;23(4):269–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trivers G., Braungart D., Leonard E. J. Mouse lymphotoxin. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):130–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Chapman H. A., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr Characterization of the effects of endotoxin on macrophage tumor cell killing. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):72–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


