Abstract
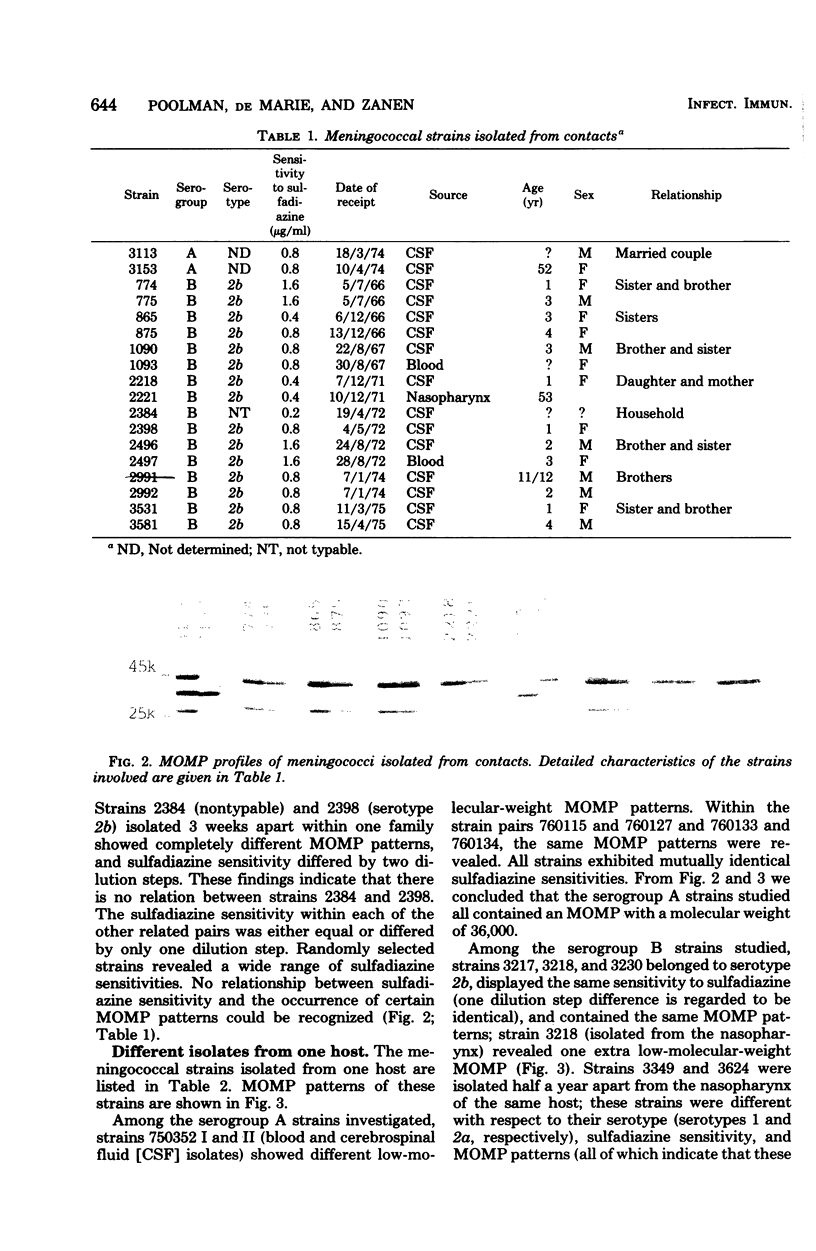
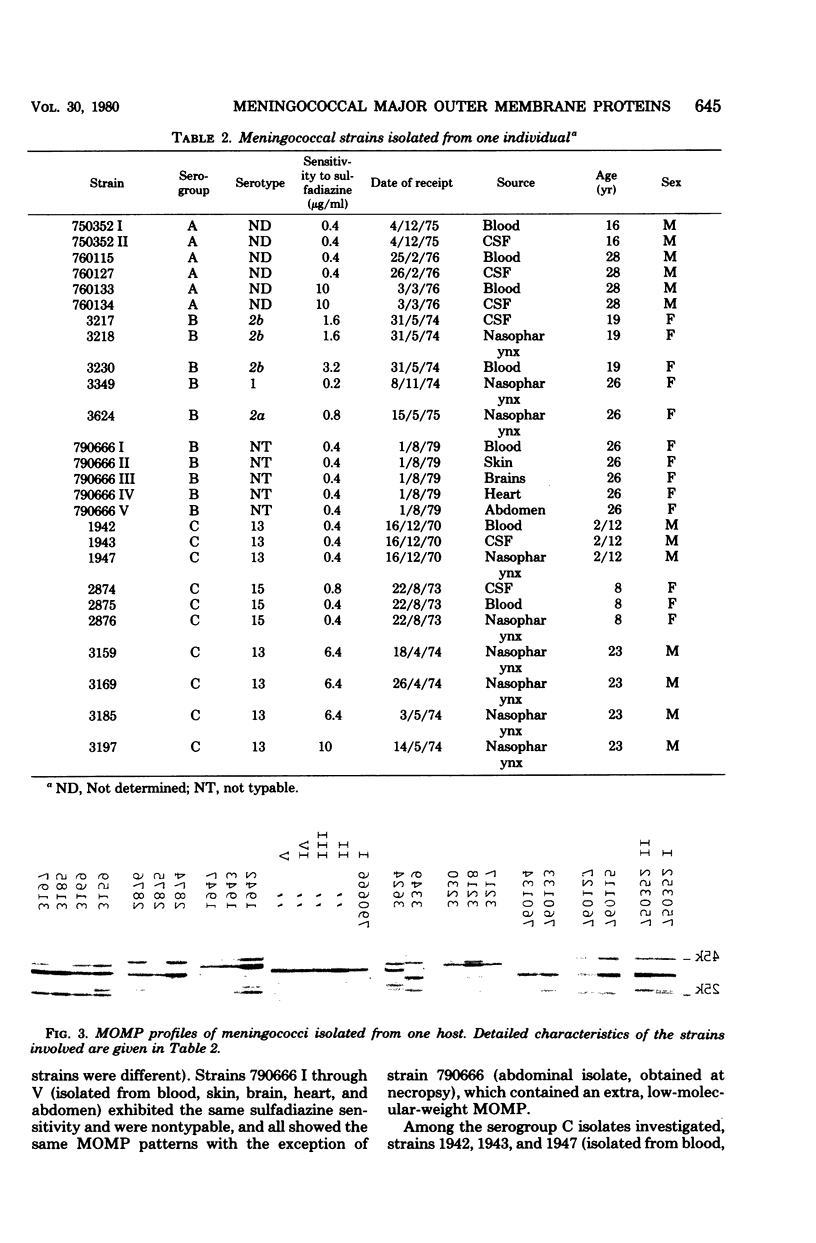
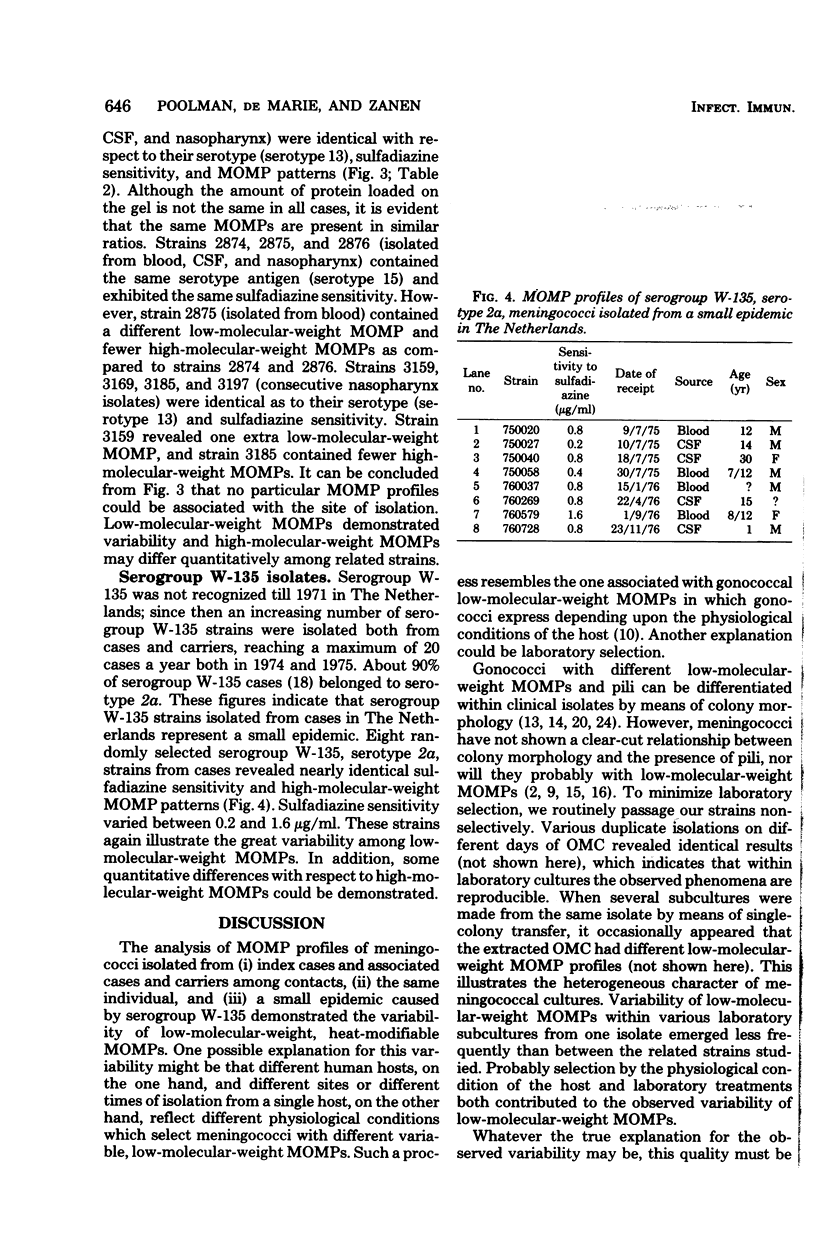
Analysis of major outer membrane protein (MOMP) profiles of various meningococci by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) revealed the presence of 0 to 2 low-molecular-weight, heat-modifiable MOMPs (molecular weight, 25,000 to 32,000) and 1 to 3 high-molecular-weight MOMPs (molecular weight, 32,000 to 46,000). Heat modifiability was investigated by comparing MOMP profiles after heating in SDS solutions at 100°C for 5 min or at 40°C for 1 h. Low-molecular-weight MOMPs shifted to higher apparent molecular weights after being heated at 100°C. Heat modifiability of high-molecular-weight MOMPs varied among strains; whenever modified these proteins shifted to lower apparent molecular weights after complete denaturation. Variability of low-molecular-weight, heat-modifiable MOMPs was demonstrated when MOMP profiles were compared of (i) isolates from index cases and associated cases and carriers among contacts, (ii) different isolates from the same individual, and (iii) isolates from a small epidemic caused by serogroup W-135. In some cases high-molecular-weight MOMPs revealed quantitative differences among related strains. The observed variability and quantitative differences indicate that MOMP serotyping and typing on the basis of SDS-PAGE profiles (PAGE typing) need careful reevaluation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott J. D., Adams D., Collins T. J. Sensitivity of meningococci to sodium sulphadiazine and six antibiotics. J Med Microbiol. 1970 May;3(2):233–241. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Piliation and colonial morphology among laboratory strains of meningococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):379–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.379-384.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diderichsen B. flu, a metastable gene controlling surface properties of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):858–867. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.858-867.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Gotschlich E. C. An outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis group B responsible for serotype specificity. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):87–104. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Strain-specific variation in the protein and lipopolysaccharide composition of the group B meningococcal outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.973-981.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Mocca L. F. Heat-modifiable outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis and their organization within the membrane. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1127–1134. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1127-1134.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E. Role of protein serotype antigens in protection against disease due to Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S84–S90. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froholm L. O., Jyssum K., Bovre K. Electron microscopical and cultural features of Neisseria meningitidis competence variants. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Oct;81(5):525–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIII. Occurrence of color/opacity colonial variants in clinical cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.332-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T. A trans-acting factor mediates inversion of a specific DNA segment in flagellar phase variation of Salmonella. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):479–481. doi: 10.1038/284479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Robertson J. N., Watt P. J. Biological properties of two distinct pilus types produced by isogenic variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):393–396. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.393-396.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Dourmashkin R. R., Gross J. G., Clark J. B., Taylor-Robinson D. Relationship of pili to colonial morphology among pathogenic and nonpathogenic species of Neisseria. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):594–600. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.594-600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Street C. H., Chappell C. L., Cousar E. S., Morris F., Horn R. G. Pili of Neisseria meningitidis: effect of media on maintenance of piliation, characteristics of Pili, and colonial morphology. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):194–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.194-201.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Hopman C. T., Zanen H. C. Immunochemical characterization of Neisseria meningitidis serotype antigens by immunodiffusion and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis immunoperoxidase techniques and the distribution of serotypes among cases and carriers. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):465–473. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Blake M., Gotschlich E. C. Intra-strain heterogeneity of gonococcal pili is related to opacity colony variance. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):716–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Hilmen M., Simon M. Phase variation in Salmonella: genetic analysis of a recombinational switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):391–395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Mamay H. K., Weiss E., Joseph S. W., Beasley W. J. Outer membrane protein antigens in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Salmonella enteric fever and meningococcal meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):372–378. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.372-378.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel J. E., Quan A. Homogeneity of protein serotype antigens in Neisseria meningitidis group A. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.623-627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walstad D. L., Guymon L. F., Sparling P. F. Altered outer membrane protein in different colonial types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1623–1627. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1623-1627.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Kasper D. L., Veltri B. J., Artenstein M. S. Isolation and characterization of a native cell wall complex from Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):835–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.835-851.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Altieri P., Berman S. Complex of meningococcal group B polysaccharide and type 2 outer membrane protein immunogenic in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):836–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI109383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Outer-membrane protein and lipopolysaccharide serotyping of Neisseria meningitidis by inhibition of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.424-433.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Type-specific antigens of group A Neisseria meningitidis: lipopolysaccharide and heat-modifiable outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):451–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.451-458.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]