Abstract
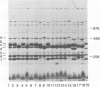
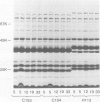
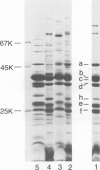
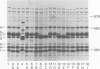
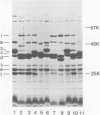
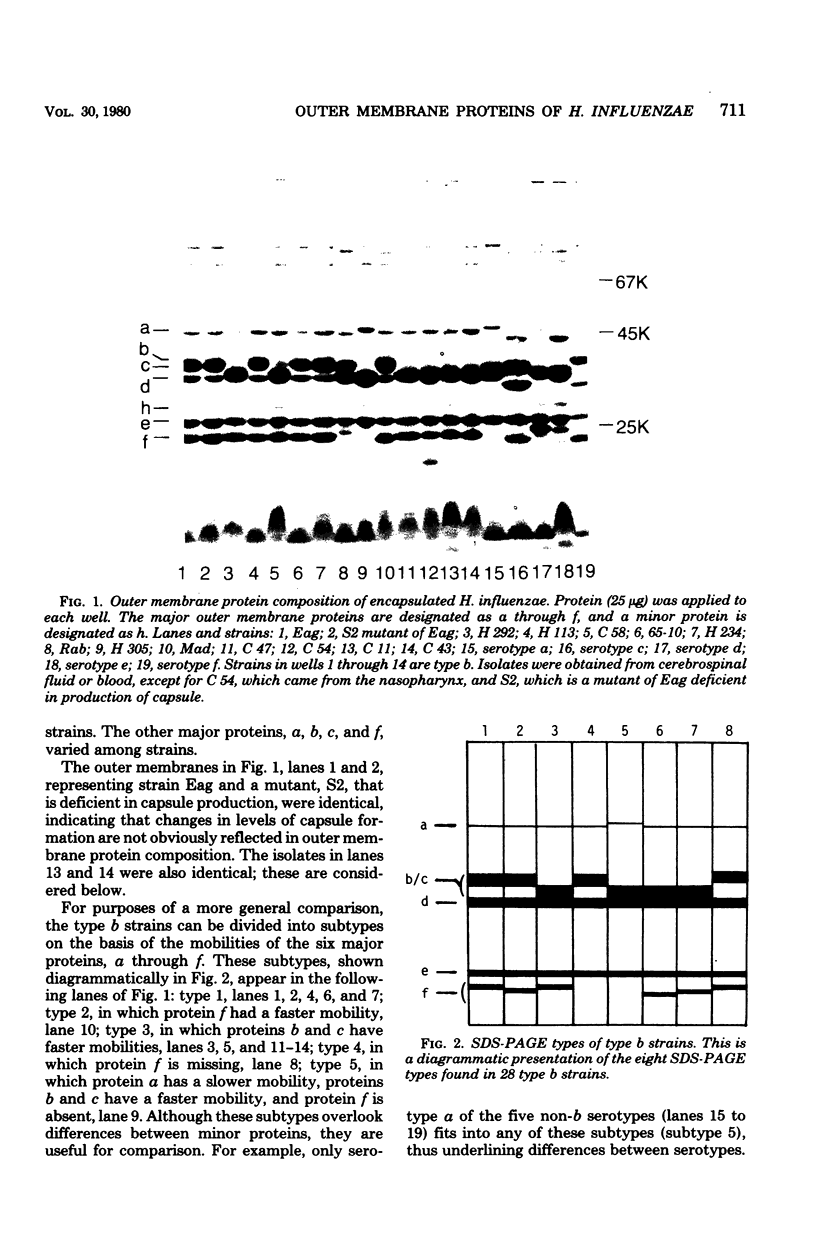
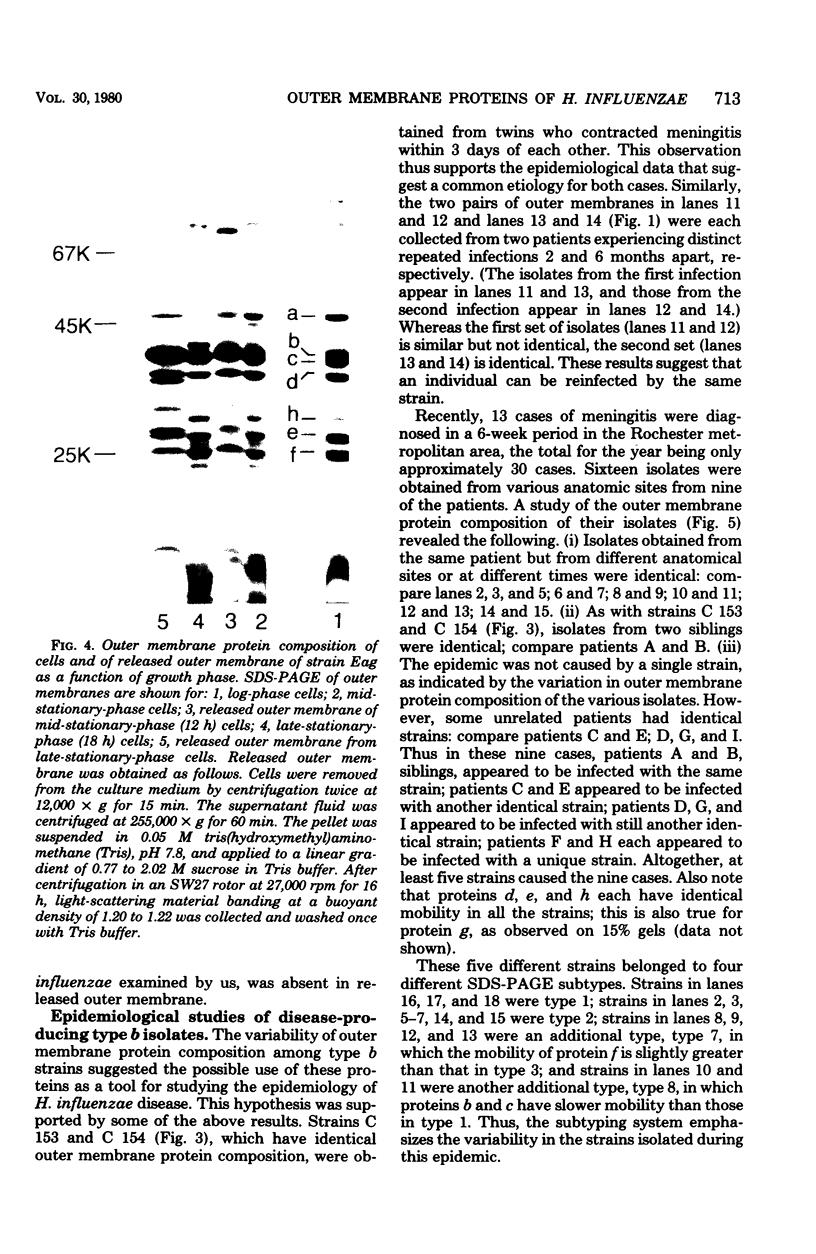
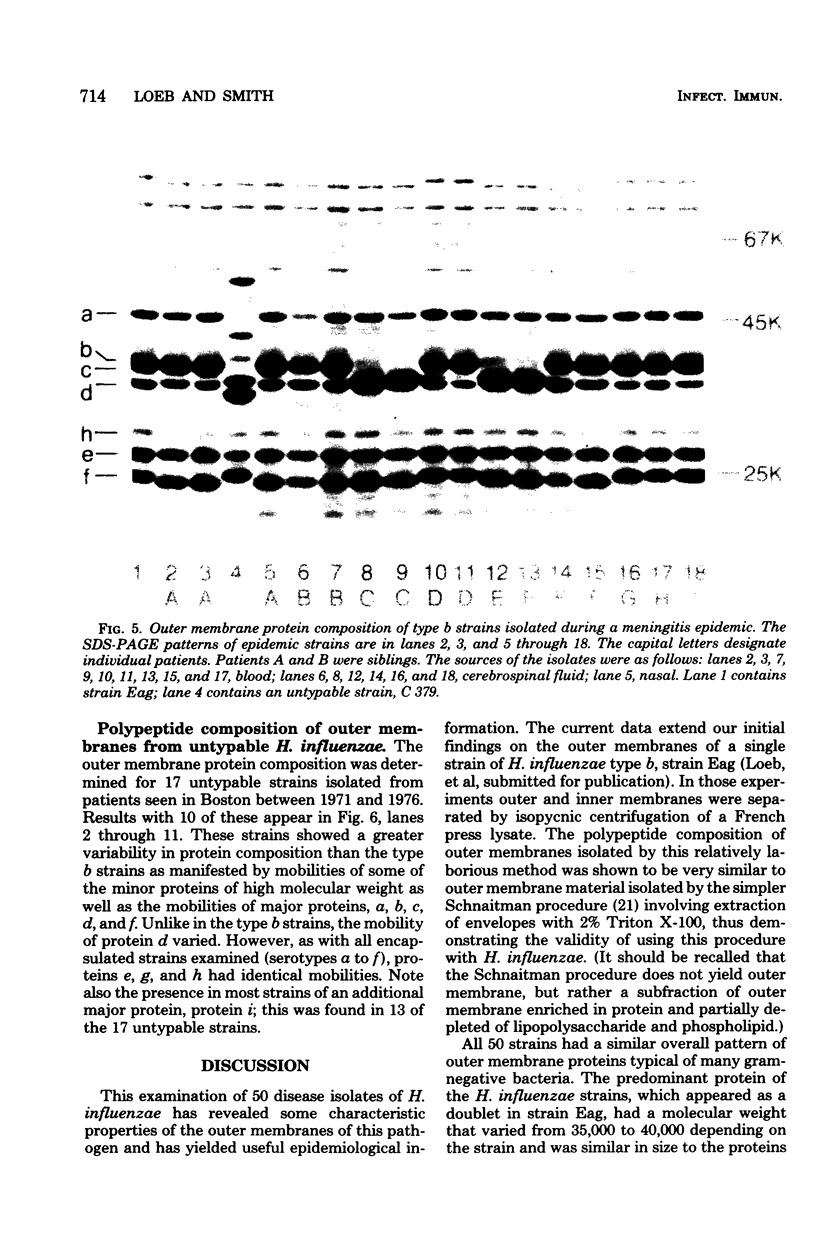
The outer membrane protein composition of 50 disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae has been determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. All strains, including 28 strains of serotype b, one strain each of serotypes a, c, d, e, and f, and 17 untypable strains, had an outer membrane protein composition typical of gram-negative bacteria, i.e., these membranes contained two to three dozen proteins with four to six proteins accounting for most of their protein content. Variation in the mobility of these major outer membrane proteins from strain to strain was common but not universal; the observed patterns provided useful data and new insight into the epidemiology of type b disease. The basic findings can be summarized as follows: (i) All 50 strains possessed three proteins (one minor and two major) each having identical mobilities. The other proteins, both major and minor, varied in mobility. (ii) All type b strains possessed a fourth (major) protein of identical mobility. (iii) The 28 type b strains, on the basis of the mobility of the six major outer membrane proteins, could be divided into eight subtypes. Of all the other strains examined, both typable and untypable, only the serotype a strain belonged to one of these subtypes. (iv) The untypable strains showed considerable variation in the mobilities of their major outer membrane proteins. Of these 17 strains, 13 had an additional major outer membrane protein not present in encapsulated strains. (v) The outer membrane protein composition of a single strain remained unchanged after many passages on solid media, but varied with the growth phase. (vi) The outer membrane protein composition of isolates obtained from nine patients during an epidemic of type b meningitis varied, indicating that a single strain was not responsible for the epidemic. At least five different strains were responsible for these nine cases. (vii) Identical outer membrane protein compositions were observed in the following: in a type b strain and a mutant of this strain deficient in capsule production, indicating that the level of capsule synthesis is not obviously related to outer membrane protein composition; in type b strains isolated from different anatomic sites of patients acutely ill with meningitis, indicating that the strain associated with bacteremia is the same as that isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid; in type b strains isolated from siblings who contracted meningitis at about the same time, indicating infection with the same strain; and in type b strains isolated from the initial and repeat infection of a single patient, suggesting that reinfection was due to the same strain.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Flesher A., Shaw S., Harding A. L., Smith D. H. Phenotypic and genetic variation in the susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae type b to antibodies to somatic antigens. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):885–891. doi: 10.1172/JCI109741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Johnston R. B., Jr, Smith D. H. Human serum activities against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Peter G., Johnston R. B., Jr, Wetterlow L. H., Smith D. H. Immunization of humans with polyribophosphate, the capsular antigen of Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):39–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI106794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branefors-Helander P., Nylén O., Jeppsson P. H. Acute otitis media. Assay of complement-fixing antibody against Haemophilus influenzae as a diagnostic tool in acute otitis media. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Oct;81(5):508–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Strain-specific variation in the protein and lipopolysaccharide composition of the group B meningococcal outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.973-981.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Rockwell R. Experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis: immunological investigation of the infant rat model. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):705–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.705-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Anderson P., Rosen F. S., Smith D. H. Characterization of human antibody to polyribophosphate, the capsular antigen of Hemophilus influenzae, type B. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Jan;1(2):234–240. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koplow J., Goldfine H. Alterations in the outer membrane of the cell envelope of heptose-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):527–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.527-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Kilner J. Effect of growth medium on the relative polypeptide composition of cellular outer membrane and released outer membrane material in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):1031–1034. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.1031-1034.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B possessing a TEM-type beta-lactamase but little permeability barrier to ampicillin. Lancet. 1975 Mar 29;1(7909):716–719. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91630-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mpairwe Y. Immunity to Haemophilus influenzae type B: the role of the capsular antibody. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Feb;4(1):85–88. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Norden C. W., Demchak T. A. Significance of noncapsular antigens in protection against experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b disease: cross-reactivity. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):619–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.619-626.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Outer membrane of Salmonella. Isolation of protein complex that produces transmembrane channels. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2176–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Käyhty H., Sivonen A., Mäkelä H. Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide vaccine in children: a double-blind field study of 100,000 vaccinees 3 months to 5 years of age in Finland. Pediatrics. 1977 Nov;60(5):730–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Averill D. R., Jr, Marino J., Moxon E. R. Production of Haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in infant rats by intraperitoneal inoculation. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):278–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.278-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]