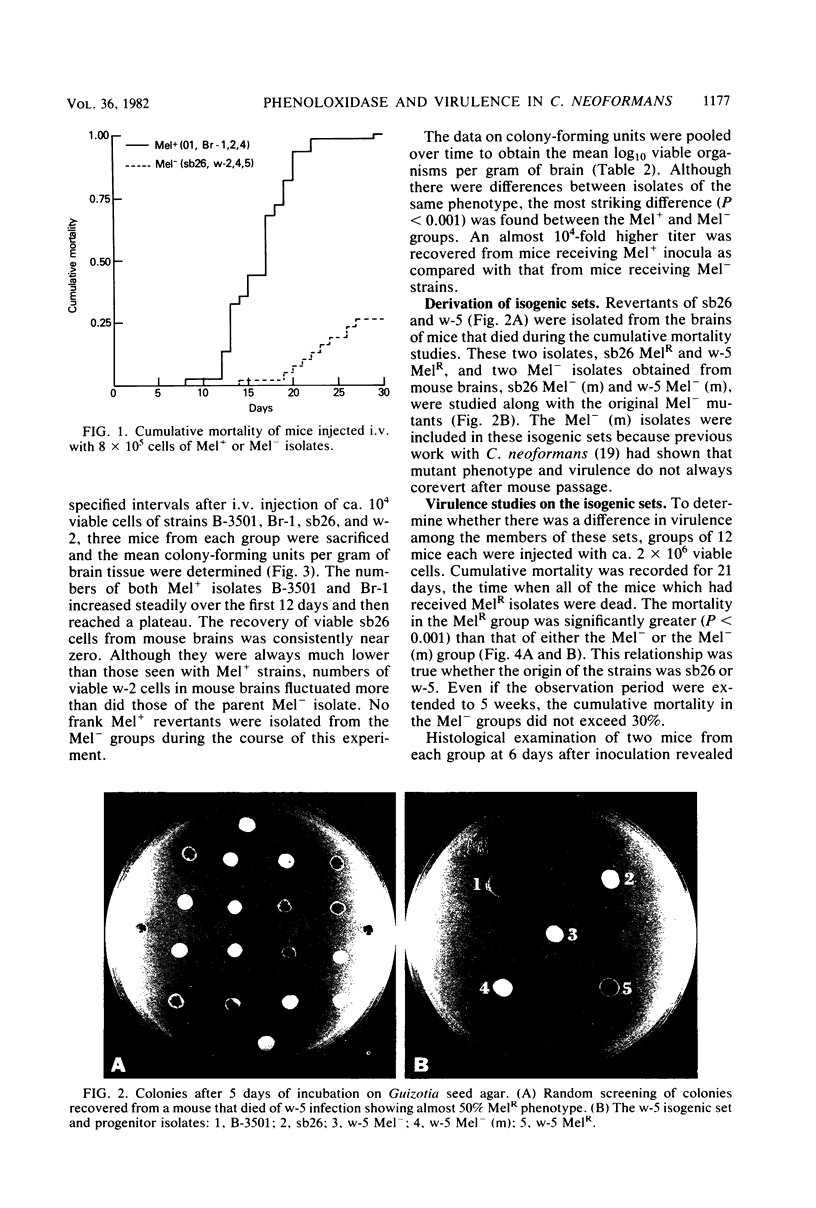
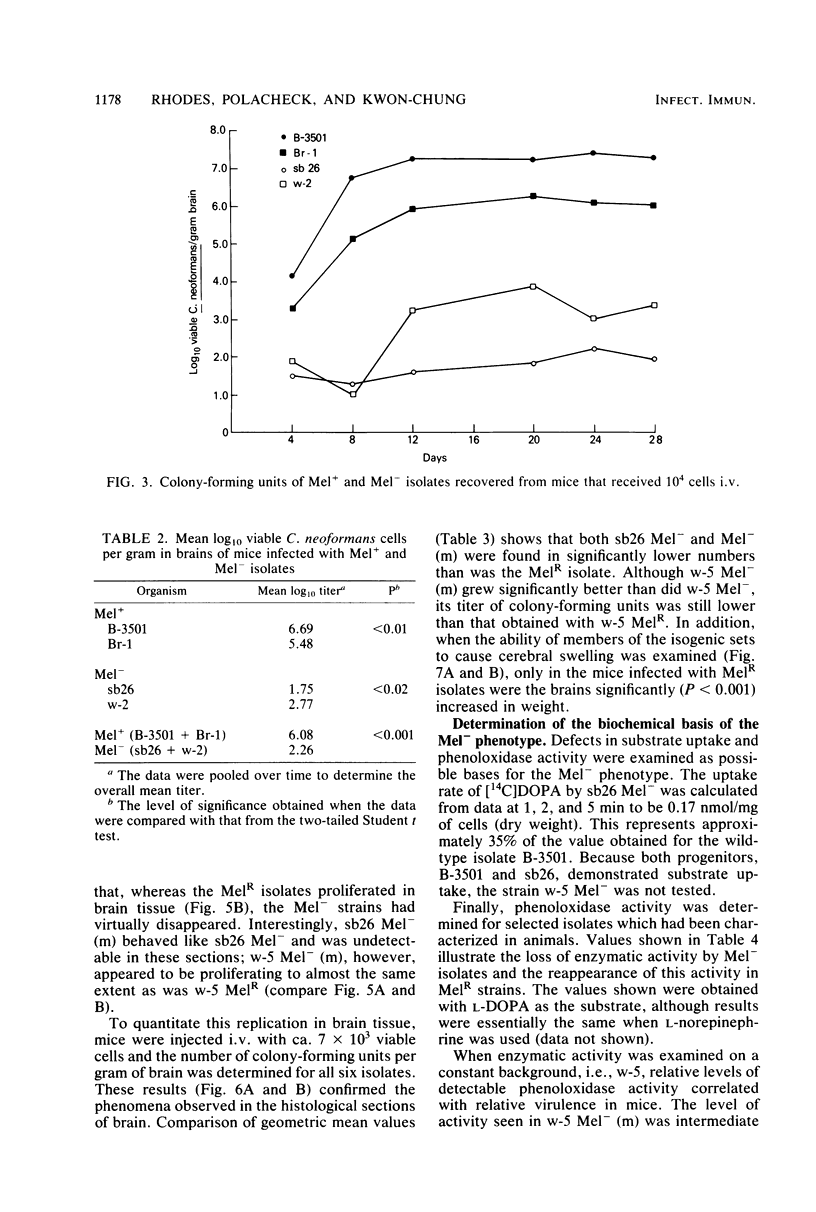
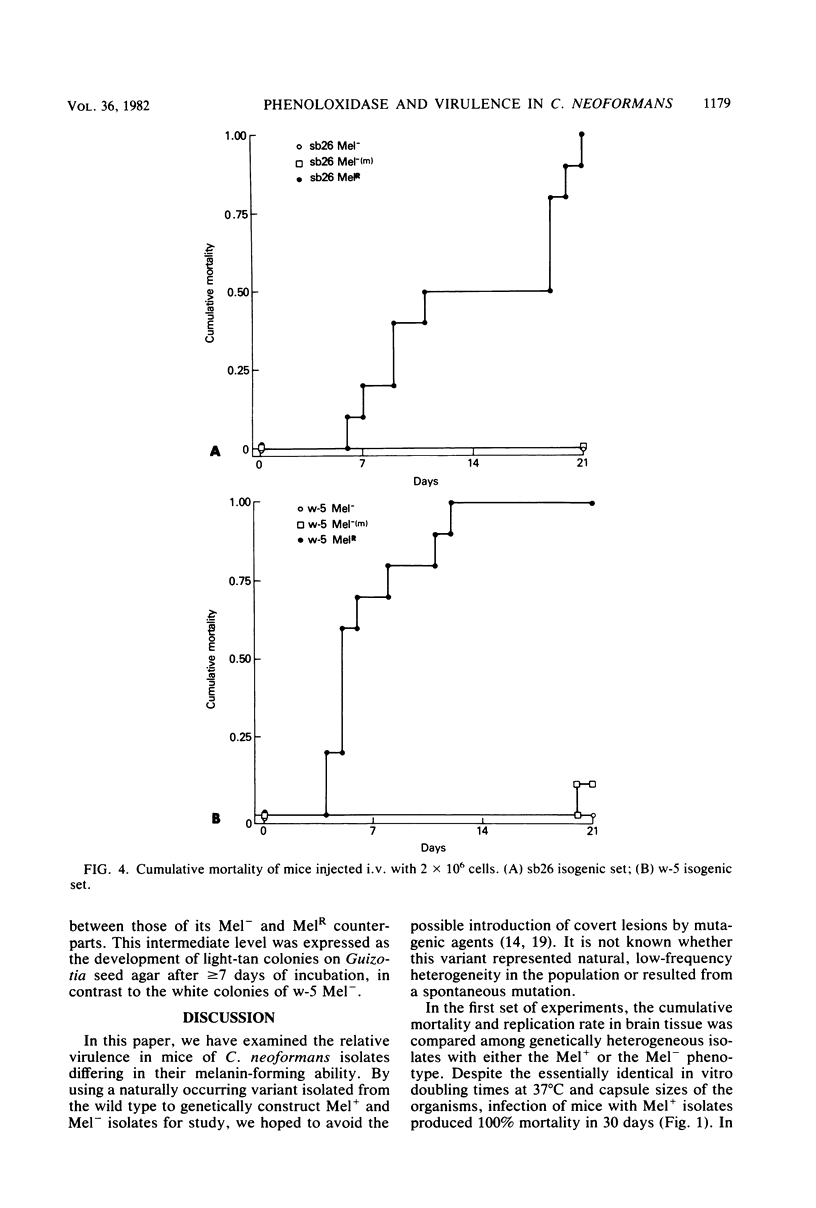
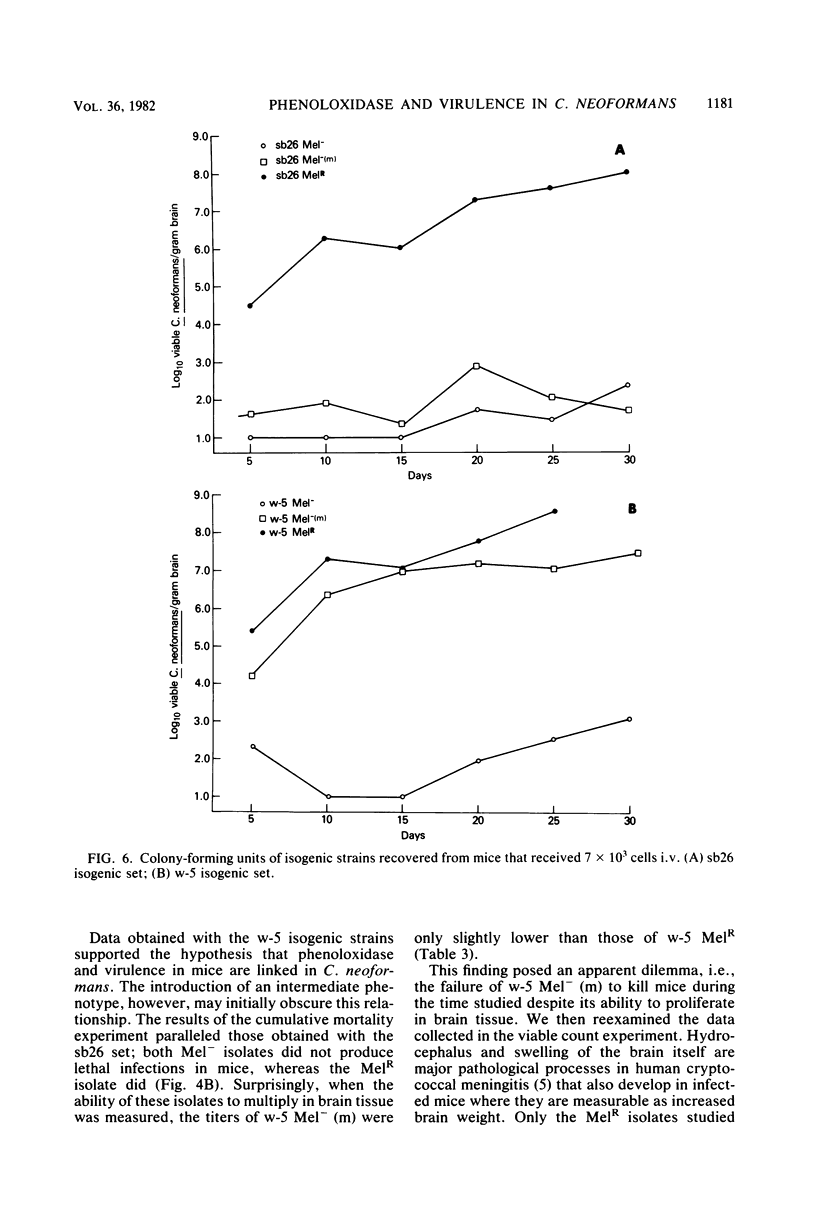
Abstract
A naturally occurring Mel- variant of Cryptococcus neoformans was isolated from the wild type. The effect of phenoloxidase activity on virulence was analyzed on genetically constructed Mel+ and Mel- isolates. The traits Mel+ and virulence in mice, as measured by cumulative mortality and replication potential in brain tissue, cosegregated among the progeny of a Mel+ X Mel- cross. Revertants (MelR) isolated during the course of the cumulative mortality experiment were used to compare virulence in isogenic sets of Mel- and MelR. In two separate sets of such isolates, Mel+ phenotype and virulence coreverted. Measurement of substrate uptake and phenoloxidase activity showed that loss of detectable phenoloxidase was the basis for the Mel- phenotype and that enzyme activity reappeared in the MelR isolates. An intermediate phenotype, Melbg, was also described. Cosegregation and coreversion of the melanin phenotype and virulence suggest that phenoloxidase is a virulence factor in C. neoformans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulmer G. S., Sans M. D. Cryptococcus neoformans. 3. Inhibition of phagocytosis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):5–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.5-8.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer G. S., Sans M. D., Gunn C. M. Cryptococcus neoformans. I. Nonencapsulated mutants. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1475–1479. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1475-1479.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer G. S., Tacker J. R. Phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):73–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.73-79.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaskes S., Tyndall R. L. Pigment production by Cryptococcus neoformans from para- and ortho-Diphenols: effect of the nitrogen source. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):509–514. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.509-514.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra M. A., Friedman L., Murphy J. W. Capsule size of Cryptococcus neoformans: control and relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.129-135.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRANO A., ZIMMERMAN H. M., LEVINE S. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF CEREBRAL FLUID ACCUMULATION. III. EXTRACELLULAR SPREAD OF CRYPTOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDES IN THE ACUTE STAGE. Am J Pathol. 1964 Jul;45:1–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Zimmerman H. M., Levine S. The fine structure of cerebral fluid accumulation: reactions of ependyma to implantation of cryptococcal polysaccharide. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):149–155. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Cazin J. Nonencapsulated Variant of Cryptococcus neoformans I. Virulence Studies and Characterization of Soluble Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):287–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.287-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Mastroianni R. P. Inhibition of phagocytosis by cryptococcal polysaccharide: dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):62–67. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.62-67.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. Morphogenesis of Filobasidiella neoformans, the sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1976 Jul-Aug;68(4):821–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Polacheck I., Popkin T. J. Melanin-lacking mutants of Cryptococcus neoformans and their virulence for mice. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1414–1421. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1414-1421.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. G., Friedman L. In vitro phagocytosis and intracellular fate of variously encapsulated strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):491–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.491-498.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurudeen T. A., Ahearn D. G. Regulation of melanin production by Cryptococcus neoformans. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):724–729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.724-729.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacheck I., Hearing V. J., Kwon-Chung K. J. Biochemical studies of phenoloxidase and utilization of catecholamines in Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1212–1220. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1212-1220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Howard D. H. Isolation and characterization of arginine auxotrophs of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):910–914. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.910-914.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. E., Kapica L. Production of diagnostic pigment by phenoloxidase activity of cryptococcus neoformans. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):824–830. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.824-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A. B., Ajello L. Medium for selective isolation of Cryptococcus neoformans. Science. 1966 Jan 14;151(3707):208–209. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3707.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. S., Zeimis R. T., Roberts G. D. Evaluation of a caffeic acid-ferric citrate test for rapid identification of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.445-449.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




