Abstract
Synergistic hemolysis of sheep erythrocytes caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Corynebacterium renale resulted from the combined action of extracellular staphylococcal sphingomyelinase C and a newly described extracellular agent of C. renale (renalin). The affinity of renalin for ceramide was considered to play a key role in causing hemolysis in erythrocytes in which ceramide had been generated through the action of sphingomyelinase C.
Full text
PDF
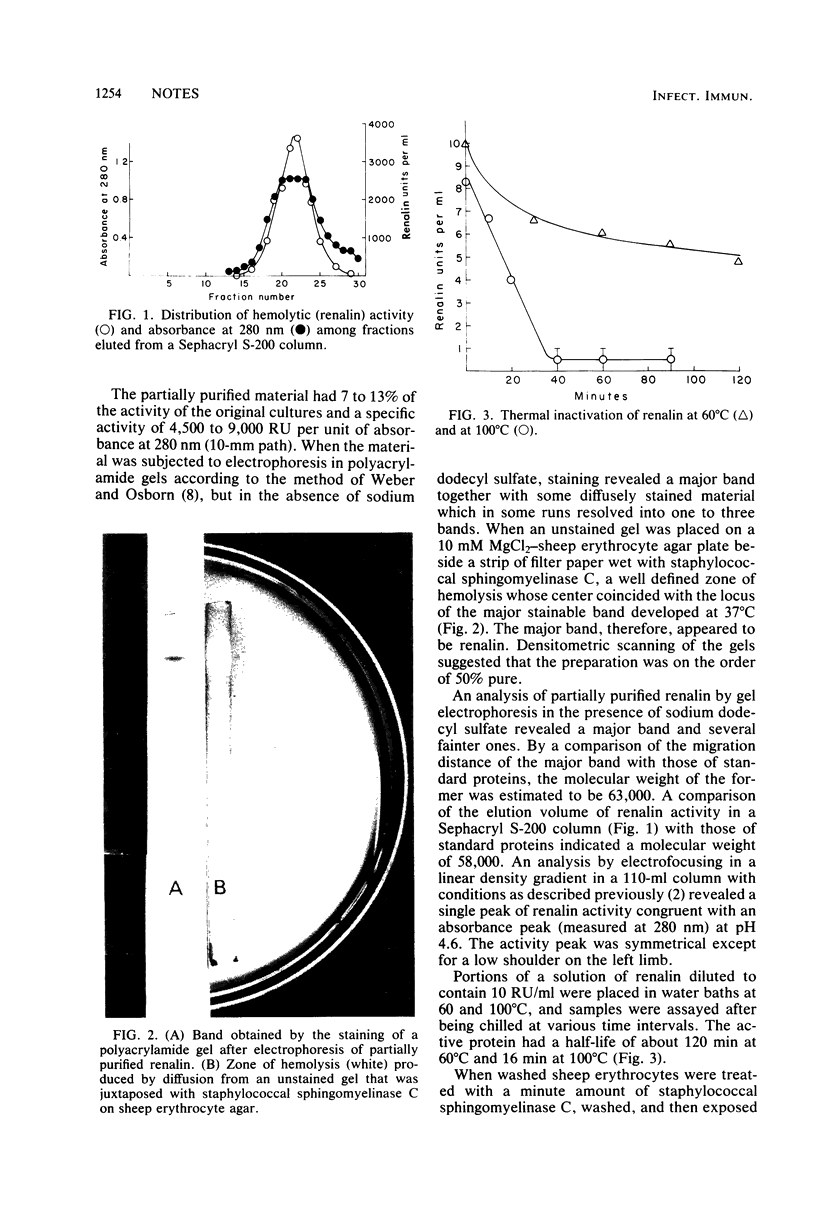
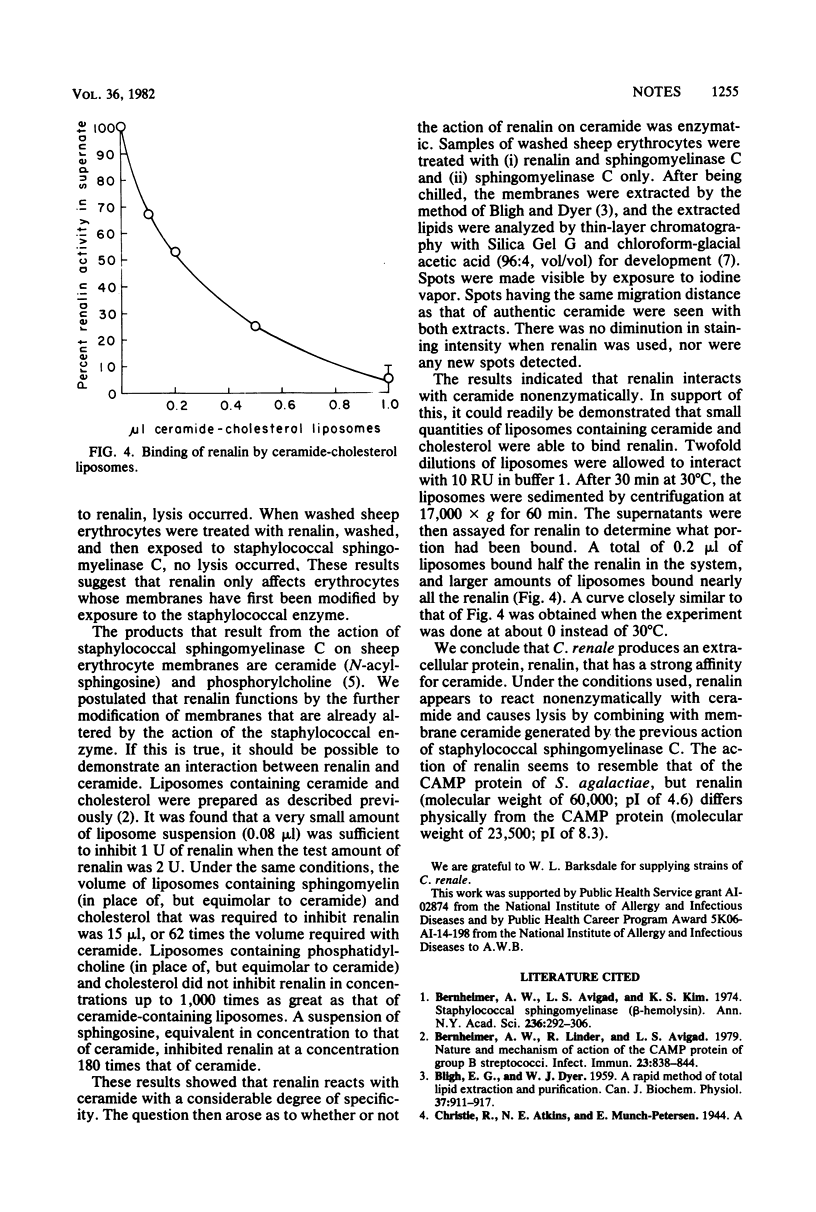

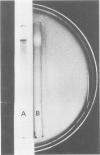
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Kim K. S. Staphylococcal sphingomyelinase (beta-hemolysin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):292–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Linder R., Avigad L. S. Nature and mechanism of action of the CAMP protein of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):838–844. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.838-844.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doery H. M., Magnusson B. J., Gulasekharam J., Pearson J. E. The properties of phospholipase enzymes in staphylococcal toxins. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Aug;40(2):283–296. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]