Abstract
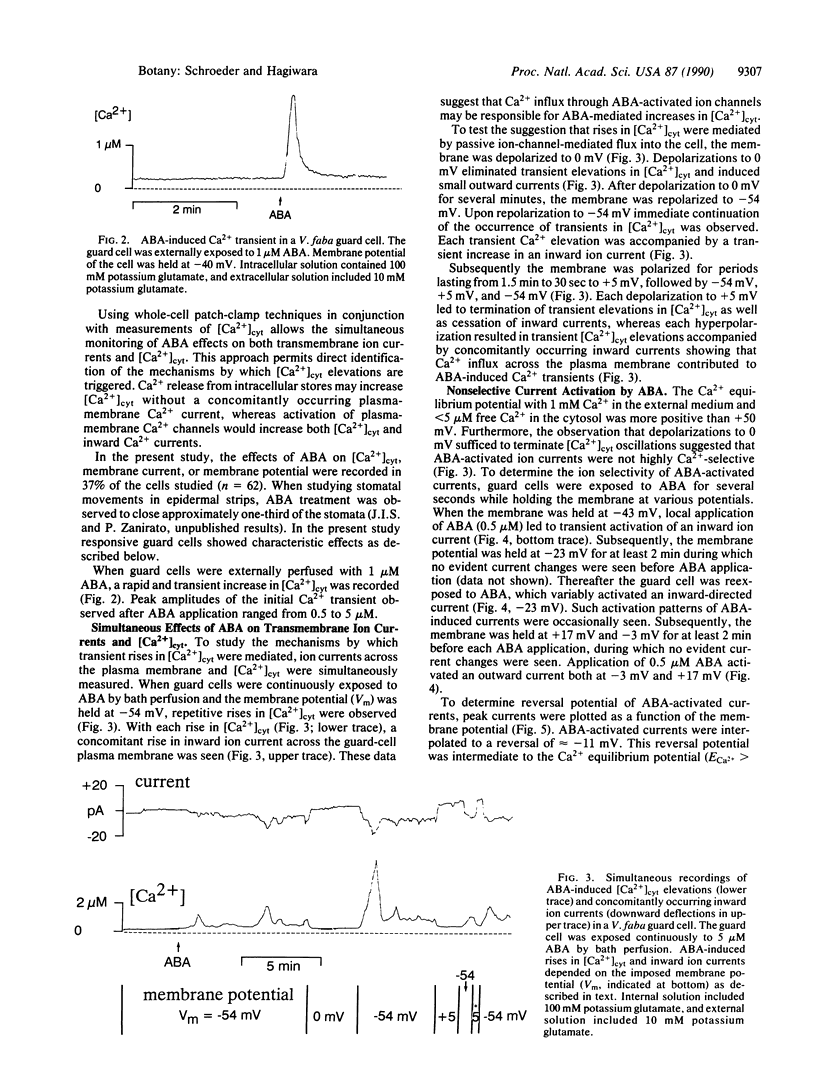
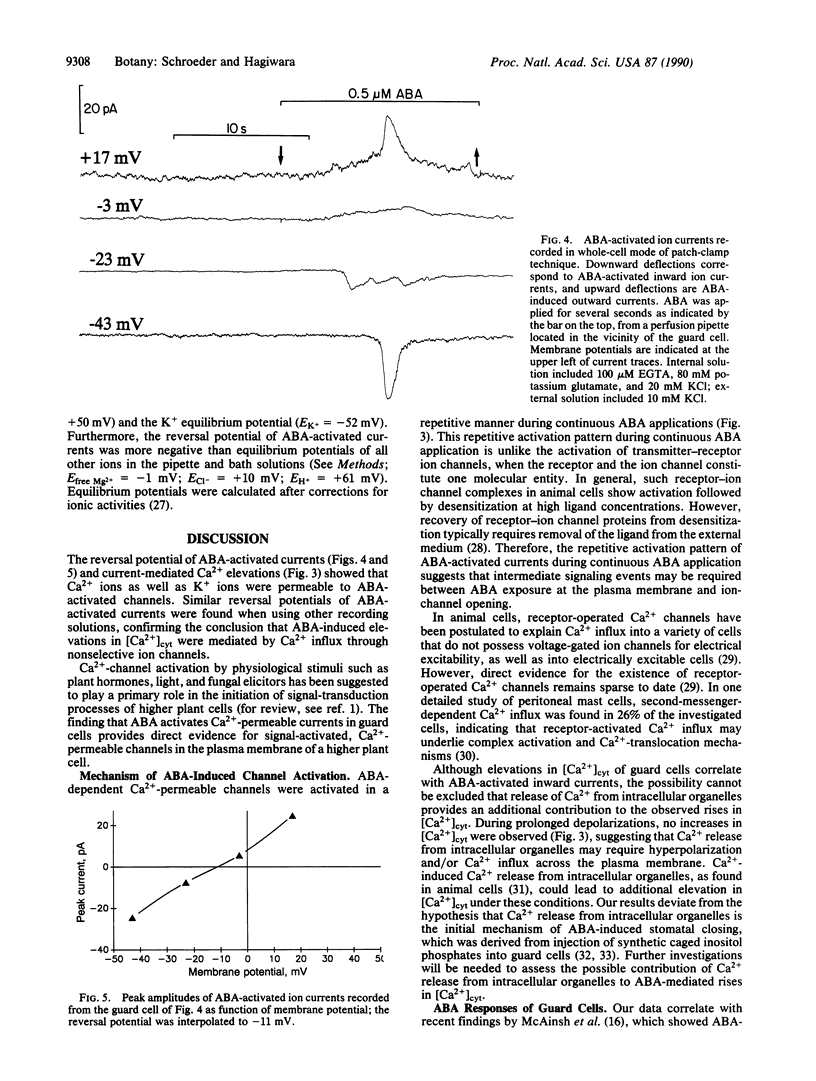
Many signal-transduction processes in higher plant cells have been suggested to be triggered by signal-induced opening of Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane. However, direct evidence for activation of plasma-membrane Ca2+ channels by physiological signals in higher plants has not yet been obtained. In this context, several lines of evidence suggest that Ca2+ flux into the cytosol of guard cells is a major factor in the induction of stomatal closing by abscisic acid (ABA). ABA closes stomatal pores, thereby reducing transpirational loss of water by plants under drought conditions. To directly investigate initial events in ABA-induced signal transduction in guard cells, we devised an experimental approach that allows simultaneous photometric measurements of cytosolic Ca2+ and patch-clamp recordings of ion currents across the plasma membrane of single Vicia faba guard cells. Using this approach, we found that the resting cytosolic Ca2+ concentration was 0.19 +/- 0.09 microM (n = 19). In responsive guard cells, external exposure to ABA produced transient repetitive increases in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration. These Ca2+ transients were accompanied by concomitantly occurring increases in an inward-directed ion current. Depolarization of the membrane terminated both repetitive elevations in cytosolic Ca2+ and inward-directed ion currents, suggesting that ABA-mediated Ca2+ transients were produced by passive influx of Ca2+ from the extracellular space through Ca2(+)-permeable channels. Detailed voltage-clamp measurements revealed that ABA-activated ion currents could be reversed by depolarizations more positive than -10 mV. Interestingly, reversal potentials of ABA-induced currents show that these currents are not highly Ca2(+)-selective, thereby permitting permeation of both Ca2+ and K+. These results provide direct evidence for ABA activation of Ca2(+)-permeable ion channels in the plasma membrane of guard cells. ABA-activated ion channels allow repetitive elevations in the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration, which, in turn, can modulate cellular responses promoting stomatal closure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt M. R., Thiel G., Trentham D. R. Reversible inactivation of K+ channels of Vicia stomatal guard cells following the photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):766–769. doi: 10.1038/346766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush D. S., Jones R. L. Measurement of cytoplasmic calcium in aleurone protoplasts using indo-1 and fura-2. Cell Calcium. 1987 Dec;8(6):455–472. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley P. F., Raschke K., Ball J. T., Berry J. A. Topography of photosynthetic activity of leaves obtained from video images of chlorophyll fluorescence. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1233–1238. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy S., Read N. D., Trewavas A. J. Elevation of cytoplasmic calcium by caged calcium or caged inositol triphosphate initiates stomatal closure. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):769–771. doi: 10.1038/346769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K., Callaham D. A. Free calcium increases during anaphase in stamen hair cells of Tradescantia. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2137–2143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. The influence of intracellular calcium concentration on degranulation of dialysed mast cells from rat peritoneum. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:193–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Matthews G., Neher E. Regulation of calcium influx by second messengers in rat mast cells. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):499–504. doi: 10.1038/334499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J. A real receptor-operated calcium channel? Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):649–650. doi: 10.1038/334649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Hedrich R. Involvement of ion channels and active transport in osmoregulation and signaling of higher plant cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I. K+ transport properties of K+ channels in the plasma membrane of Vicia faba guard cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Nov;92(5):667–683. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Raschke K., Neher E. Voltage dependence of K channels in guard-cell protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4108–4112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Ilan N., Grantz D. A. Calcium Effects on Stomatal Movement in Commelina communis L. : Use of EGTA to Modulate Stomatal Response to Light, KCl and CO(2). Plant Physiol. 1988 Jul;87(3):583–587. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R. E., Ashley C. C. Free Ca2+ and cytoplasmic streaming in the alga Chara. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):647–650. doi: 10.1038/296647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



