Figure 1. Cell functions controlled by lncRNAs.
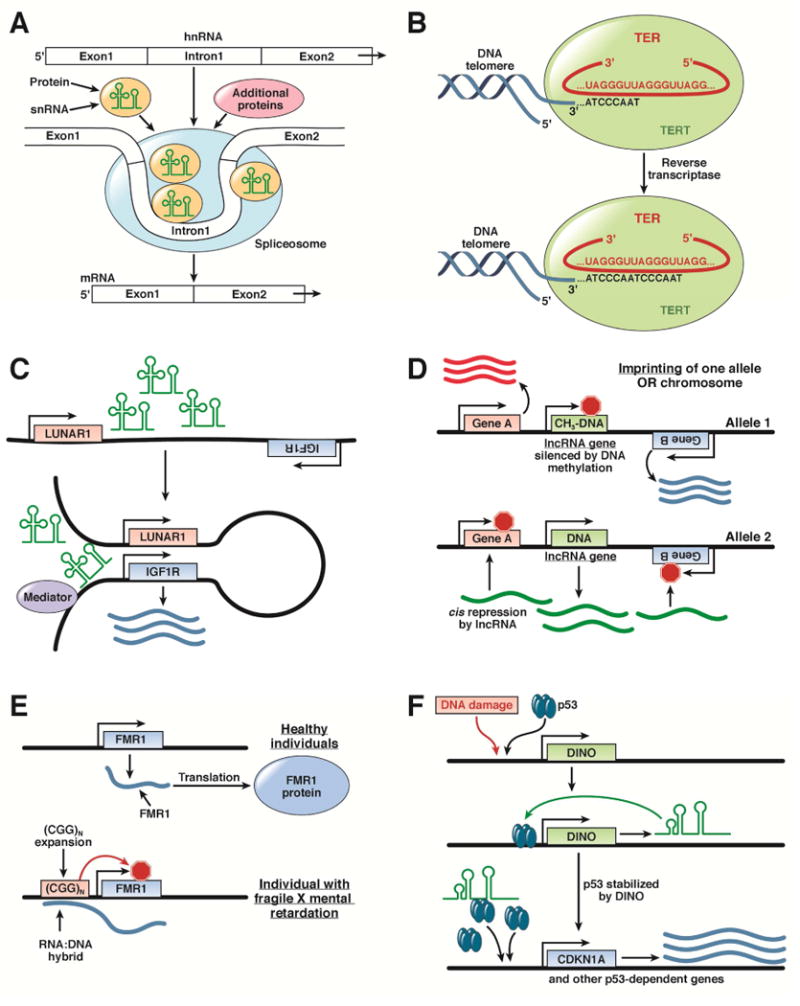
A. snRNAs form part of a nuclear spliceosome, which precisely removes introns from heterogeneous RNA to yield mature mRNAs consisting only of exons. B. Telomerase comprises the TERT protein subunit and a noncoding telomerse RNA (TER), which provides the template for synthesis and extension of telomeres. C. The lncRNA LUNAR causes chromosomal looping, resulting in placement of a transcriptional activating complex named mediator to act as an enhancer near the promoter of the IGF1R gene. D. During imprinting, 1 allele of a gene (such as an inhibitory lncRNA) is silenced by DNA methylation, permitting expression of neighboring genes. The other allele has reduced or absent methylation, resulting in lncRNA expression and cis repression of neighboring genes. E. The FMR1 mRNA encodes the FMR1 protein; the 5′ untranslated region of the FMR1 mRNA binds an expanded CGG triplet sequences at the gene promoter. This DNA–RNA hybrid prevents transcription of the FMR1 gene, leading to fragile X mental retardation. F. In response to DNA damage, cell levels of the lncRNA DINO greatly increase. DINO binds to and stabilizes TP53, allowing TP53 to regulate hundreds of gene targets.
