Abstract
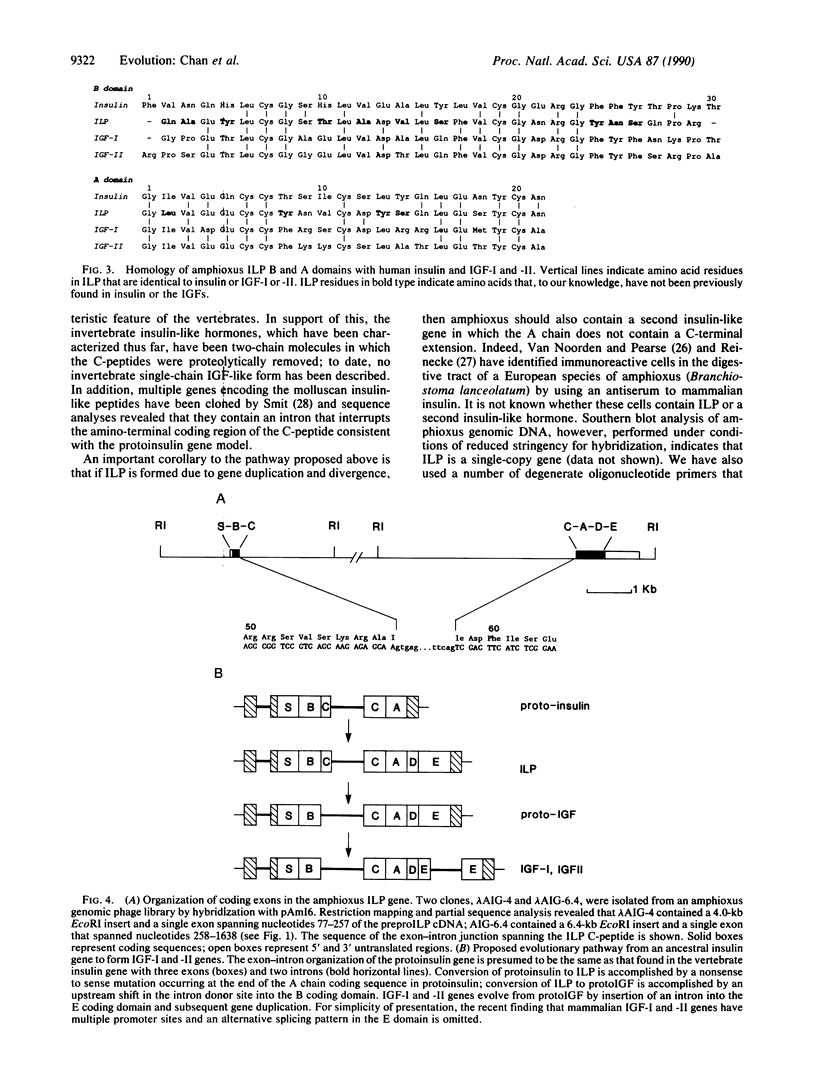
Although insulin and the insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) share marked similarities in amino acid sequence and biological activity, their evolutionary origins have not been resolved. To investigate this issue, we recently cloned a cDNA encoding an insulin-like peptide (ILP) from a primitive chordate species, amphioxus (Branchiostoma californiensis). The deduced sequence of amphioxus preproILP indicates that it is a hybrid molecule containing features characteristic of both insulin and IGF. Like proinsulin, amphioxus proILP contains a C-peptide, which is flanked by paired basic residues and is probably removed by proteolysis. However, proILP also contains an extended carboxyl-terminal peptide region that can be divided into D and E domains similar to those of proIGF. Sequence comparisons show that the amphioxus ILP A and B domains are equally homologous to those of human insulin and IGF-I and -II. Based on these results and the exon-intron organization of the amphioxus ILP gene, we propose that IGF emerged at a very early stage in vertebrate evolution from an ancestral insulin-type gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Takiya S., Suzuki Y., Iwami M., Kawakami A., Takahashi S. Y., Ishizaki H., Nagasawa H., Suzuki A. cDNA structure and expression of bombyxin, an insulin-like brain secretory peptide of the silkmoth Bombyx mori. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7681–7685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. N., Blundell T. L., Cutfield J. F., Cutfield S. M., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. M., Hubbard R. E., Isaacs N. W., Reynolds C. D. The structure of 2Zn pig insulin crystals at 1.5 A resolution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 6;319(1195):369–456. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Merryweather J. P., Sanchez-Pescador R., Stempien M. M., Priestley L., Scott J., Rall L. B. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding human preproinsulin-like growth factor II. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):775–777. doi: 10.1038/310775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Bedarkar S., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor: a model for tertiary structure accounting for immunoreactivity and receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):180–184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Q. P., Duguay S. J., Plisetskaya E., Steiner D. F., Chan S. J. Nucleotide sequence and growth hormone-regulated expression of salmon insulin-like growth factor I mRNA. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Dec;3(12):2005–2010. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-12-2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Emdin S. O., Kwok S. C., Kramer J. M., Falkmer S., Steiner D. F. Messenger RNA sequence and primary structure of preproinsulin in a primitive vertebrate, the Atlantic hagfish. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7595–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P., Gu J. L., Shymko R. M., Kaplan B. E., Bell G. I., Whittaker J. Identification of a ligand-binding region of the human insulin receptor encoded by the second exon of the gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):409–416. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dull T. J., Gray A., Hayflick J. S., Ullrich A. Insulin-like growth factor II precursor gene organization in relation to insulin gene family. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):777–781. doi: 10.1038/310777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Zapf J. Insulin-like growth factors and insulin: comparative aspects. Diabetologia. 1985 Aug;28(8):485–493. doi: 10.1007/BF00281982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Gammeltoft S. The biological activity and the binding affinity of modified insulins determined on isolated rat fat cells. Diabetologia. 1974 Apr;10(2):105–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01219665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson P., Haley J., John M., Cronk M., Crawford R., Haralambidis J., Tregear G., Shine J., Niall H. Structure of a genomic clone encoding biologically active human relaxin. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):628–631. doi: 10.1038/301628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen M., van Schaik F. M., Ricker A. T., Bullock B., Woods D. E., Gabbay K. H., Nussbaum A. L., Sussenbach J. S., Van den Brande J. L. Sequence of cDNA encoding human insulin-like growth factor I precursor. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):609–611. doi: 10.1038/306609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagueux M., Lwoff L., Meister M., Goltzené F., Hoffmann J. A. cDNAs from neurosecretory cells of brains of Locusta migratoria (Insecta, Orthoptera) encoding a novel member of the superfamily of insulins. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi M., Chan S. J., Nagamatsu S., Bell G. I., Steiner D. F. Conservation of the sequence of islet amyloid polypeptide in five mammals is consistent with its putative role as an islet hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5738–5742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke M. Immunohistochemical localization of polypeptide hormones in endocrine cells of the digestive tract of Branchiostoma lanceolatum. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;219(3):445–456. doi: 10.1007/BF00209985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Pollock K. M., Didier D. K., Krivi G. G. Organization and sequence of the human insulin-like growth factor I gene. Alternative RNA processing produces two insulin-like growth factor I precursor peptides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4828–4832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit A. B., Vreugdenhil E., Ebberink R. H., Geraerts W. P., Klootwijk J., Joosse J. Growth-controlling molluscan neurons produce the precursor of an insulin-related peptide. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):535–538. doi: 10.1038/331535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Chan S. J., Welsh J. M., Kwok S. C. Structure and evolution of the insulin gene. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:463–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]