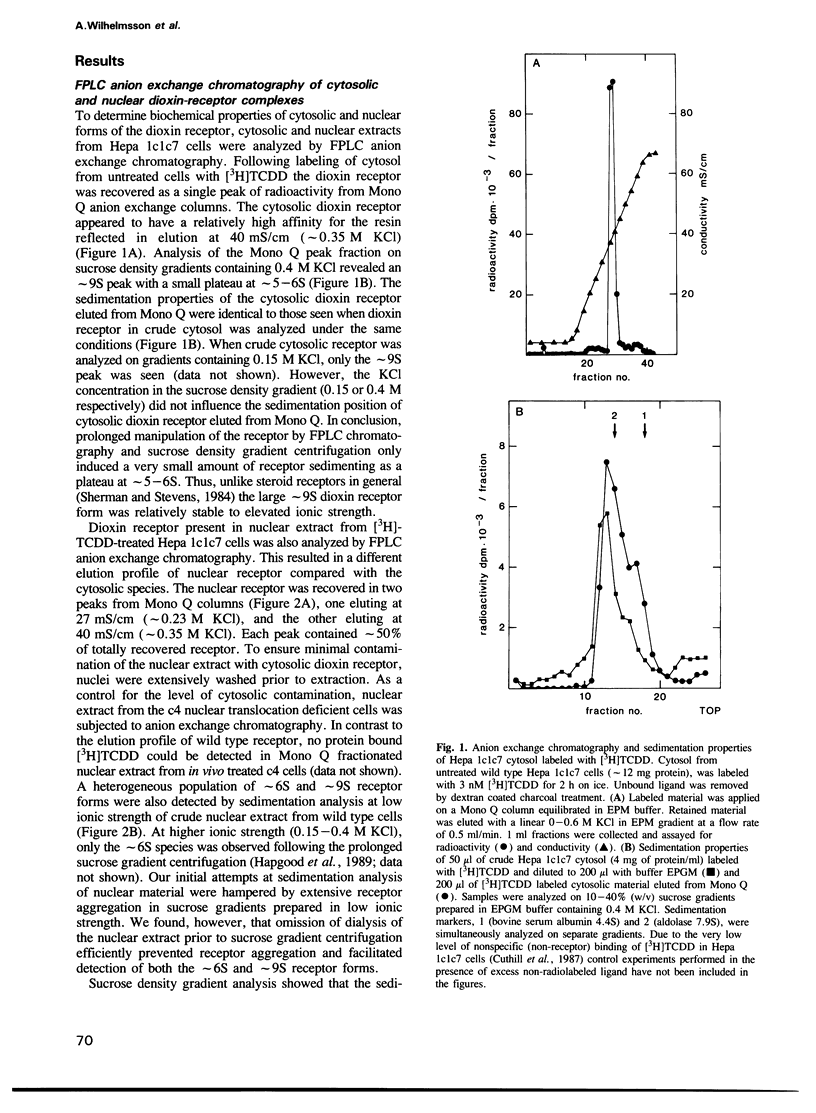
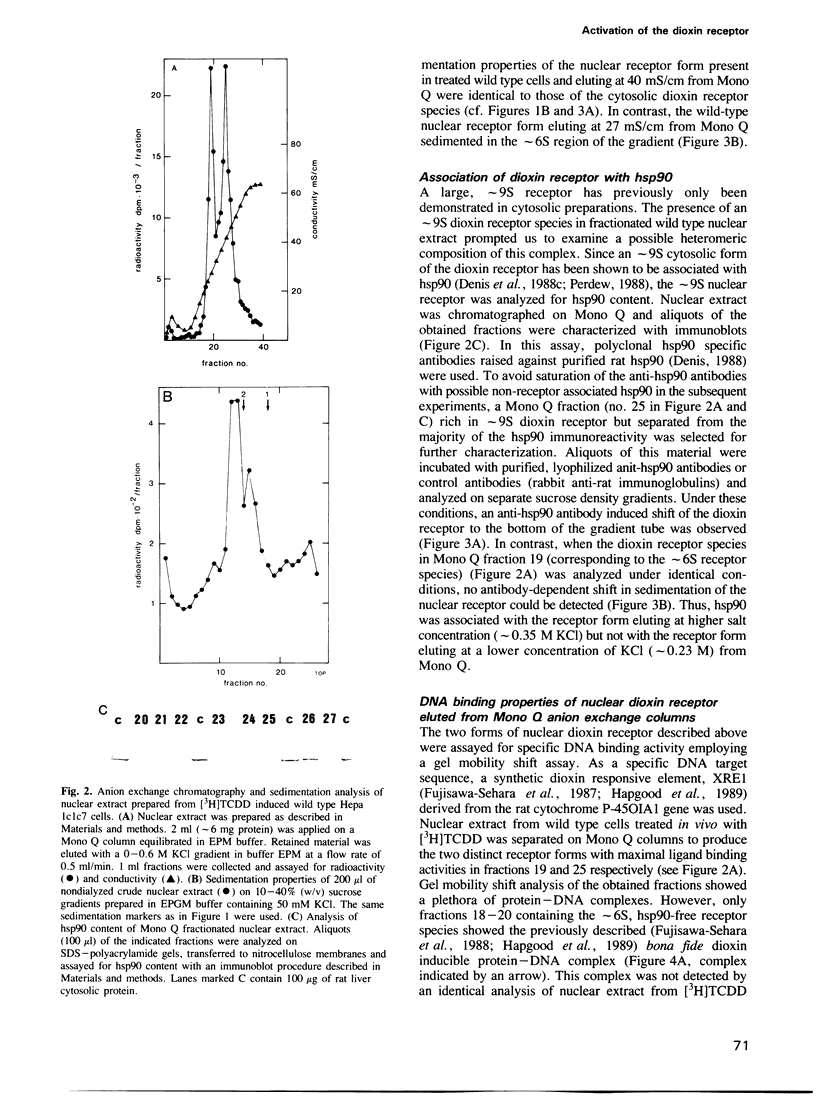
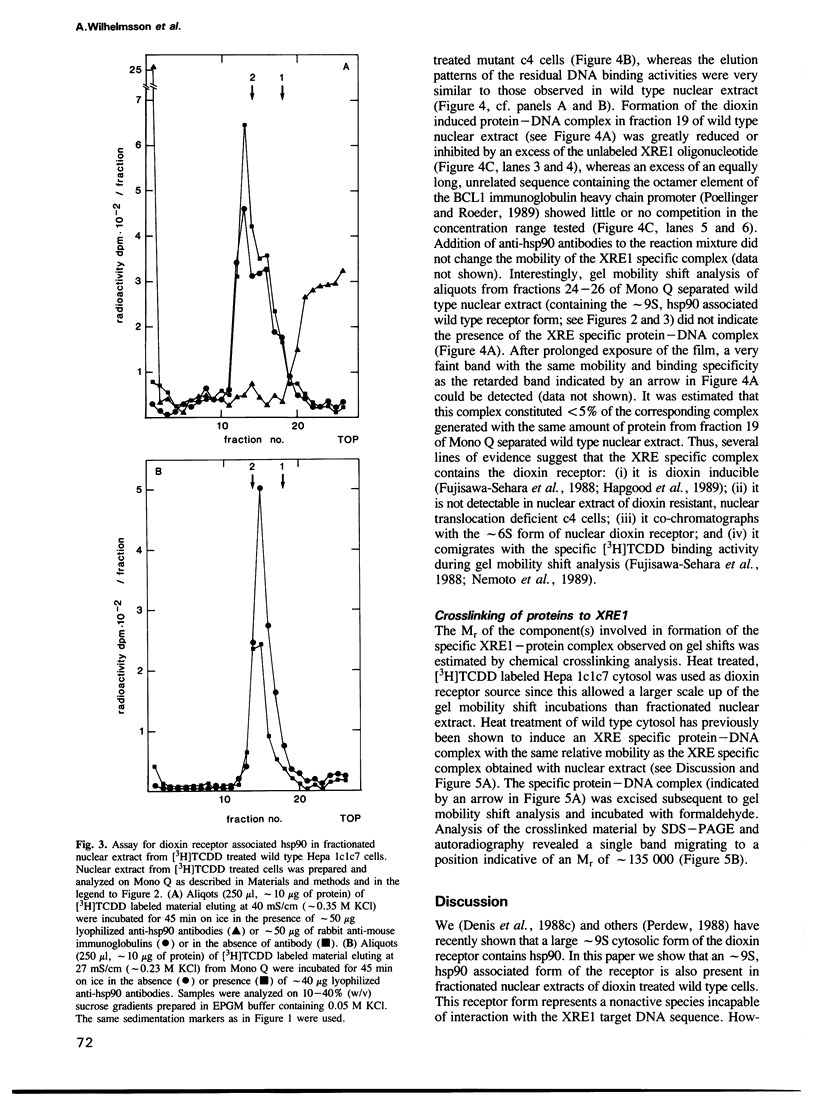
Abstract
The dioxin receptor is a gene regulatory protein which exhibits many structural and functional similarities to steroid hormone receptors. In this study we compare the subunit composition of two forms of the dioxin receptor, sedimenting at approximately 9S and approximately 6S respectively, which are present in nuclear extract from wild-type Hepa 1c1c7 mouse hepatoma cells following treatment in vivo with dioxin. The nuclear approximately 9S receptor form contained the 90 kd heat shock protein, hsp90. As assessed by a gel mobility shift assay, this receptor form did not bind to the xenobiotic response element (XRE) of the target gene cytochrome P-450 IA1. In contrast, the smaller approximately 6S receptor form did not contain any immunochemically detectable hsp90. Moreover, this receptor form specifically bound to the XRE recognition sequence. Thus, the specific DNA binding activity of the dioxin receptor was inhibited by association with hsp90, and the approximately 9S dioxin receptor species could be regarded as a nonactive receptor form. Neither the approximately 9S nor the approximately 6S receptor forms were detected in nuclear extract from a dioxin treated mutant clone of Hepa 1 that expresses a nuclear translocation deficient receptor phenotype. We conclude that activation of the dioxin receptor is, at least, a two step process involving binding of the ligand and dissociation of hsp90 from the ligand-binding receptor protein. Inhibition of the DNA binding activity of transcription factors by protein--protein interaction has also been described for several steroid hormone receptors and for the NF kappa B factor.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthill S., Poellinger L. DNA binding properties of dioxin receptors in wild-type and mutant mouse hepatoma cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2978–2982. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthill S., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A. The receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the mouse hepatoma cell line Hepa 1c1c7. A comparison with the glucocorticoid receptor and the mouse and rat hepatic dioxin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3477–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Cuthill S., Wikström A. C., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A. Association of the dioxin receptor with the Mr 90,000 heat shock protein: a structural kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):801–807. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80566-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Gustafsson J. A., Wikström A. C. Interaction of the Mr = 90,000 heat shock protein with the steroid-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18520–18523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Poellinger L., Wikstöm A. C., Gustafsson J. A. Requirement of hormone for thermal conversion of the glucocorticoid receptor to a DNA-binding state. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):686–688. doi: 10.1038/333686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Two-step purification and N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of the rat Mr 90,000 heat shock protein. Anal Biochem. 1988 Sep;173(2):405–411. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A. The molybdate-stabilized nonactivated glucocorticoid receptor contains a dimer of Mr 90,000 non-hormone-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11803–11806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Inducible, receptor-dependent protein-DNA interactions at a dioxin-responsive transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Vella L. M., Okey A. B. Structure and function of the Ah receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Species difference in molecular properties of the receptors from mouse and rat hepatic cytosols. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):3987–3995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Nishi C., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Regulatory DNA elements localized remotely upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1465–1477. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Characterization of xenobiotic responsive elements upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene: a similarity to glucocorticoid regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4179–4191. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. A DNA-binding factor specific for xenobiotic responsive elements of P-450c gene exists as a cryptic form in cytoplasm: its possible translocation to nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5859–5863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasc J. M., Delahaye F., Baulieu E. E. Compared intracellular localization of the glucocorticosteroid and progesterone receptors: an immunocytochemical study. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Apr;181(2):492–504. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Tukey R. H., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the Ah locus. Transcriptional regulation of cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 mRNA levels by 3-methylcholanthrene. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankinson O. Dominant and recessive aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase-deficient mutants of mouse hepatoma line, Hepa-1, and assignment of recessive mutants to three complementation groups. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Jul;9(4):497–514. doi: 10.1007/BF01543050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankinson O. Single-step selection of clones of a mouse hepatoma line deficient in aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):373–376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapgood J., Cuthill S., Denis M., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A. Specific protein-DNA interactions at a xenobiotic-responsive element: copurification of dioxin receptor and DNA-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Whitlock J. P., Jr Regulation of cytochrome P1-450 gene transcription by 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5400–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Radanyi C., Renoir M., Buchou T., Catelli M. G., Binart N., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Common non-hormone binding component in non-transformed chick oviduct receptors of four steroid hormones. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):850–853. doi: 10.1038/308850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klock G., Strähle U., Schütz G. Oestrogen and glucocorticoid responsive elements are closely related but distinct. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):734–736. doi: 10.1038/329734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legraverend C., Hannah R. R., Eisen H. J., Owens I. S., Nebert D. W., Hankinson O. Regulatory gene product of the Ah locus. Characterization of receptor mutants among mouse hepatoma clones. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6402–6407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B. The P450 superfamily: updated listing of all genes and recommended nomenclature for the chromosomal loci. DNA. 1989 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–13. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdew G. H. Association of the Ah receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13802–13805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Lund J., Gillner M., Hansson L. A., Gustafsson J. A. Physicochemical characterization of specific and nonspecific polyaromatic hydrocarbon binders in rat and mouse liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13535–13542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Roeder R. G. Octamer transcription factors 1 and 2 each bind to two different functional elements in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):747–756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E., Kende A. S. Stereospecific, high affinity binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by hepatic cytosol. Evidence that the binding species is receptor for induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4936–4946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. Variation in the molecular mass of the Ah receptor among vertebrate species and strains of rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1439–1449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90811-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Knutson J. C. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:517–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B., Jolly D. J., Pratt D. V., Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Cadepond F. M., Schweizer-Groyer G., Catelli M. G., Evans R. M., Baulieu E. E. A region in the steroid binding domain determines formation of the non-DNA-binding, 9 S glucocorticoid receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. R., Stevens J. Structure of mammalian steroid receptors: evolving concepts and methodological developments. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:83–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Klock G., Schütz G. A DNA sequence of 15 base pairs is sufficient to mediate both glucocorticoid and progesterone induction of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7871–7875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tienrungroj W., Meshinchi S., Sanchez E. R., Pratt S. E., Grippo J. F., Holmgren A., Pratt W. B. The role of sulfhydryl groups in permitting transformation and DNA binding of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6992–7000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Galeazzi D. R. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin receptors in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. Nuclear location and strength of nuclear binding. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):980–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsson A., Wikström A. C., Poellinger L. Polyanionic-binding properties of the receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. A comparison with the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13456–13463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Eriksson P., Perlmann T. The purified activated glucocorticoid receptor is a homodimer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5253–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]