Abstract
Background
Guidelines for assessing methodological and reporting quality of systematic reviews (SRs) were developed to contribute to implementing evidence-based health care and the reduction of research waste. As SRs assessing a cohort of SRs is becoming more prevalent in the literature and with the increased uptake of SR evidence for decision-making, methodological quality and standard of reporting of SRs is of interest. The objective of this study is to evaluate SR adherence to the Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses (QUOROM) and PRISMA reporting guidelines and the A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR) and Overview Quality Assessment Questionnaire (OQAQ) quality assessment tools as evaluated in methodological overviews.
Methods
The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE®, and EMBASE® databases were searched from January 1990 to October 2014. Title and abstract screening and full-text screening were conducted independently by two reviewers. Reports assessing the quality or reporting of a cohort of SRs of interventions using PRISMA, QUOROM, OQAQ, or AMSTAR were included. All results are reported as frequencies and percentages of reports and SRs respectively.
Results
Of the 20,765 independent records retrieved from electronic searching, 1189 reports were reviewed for eligibility at full text, of which 56 reports (5371 SRs in total) evaluating the PRISMA, QUOROM, AMSTAR, and/or OQAQ tools were included. Notable items include the following: of the SRs using PRISMA, over 85% (1532/1741) provided a rationale for the review and less than 6% (102/1741) provided protocol information. For reports using QUOROM, only 9% (40/449) of SRs provided a trial flow diagram. However, 90% (402/449) described the explicit clinical problem and review rationale in the introduction section. Of reports using AMSTAR, 30% (534/1794) used duplicate study selection and data extraction. Conversely, 80% (1439/1794) of SRs provided study characteristics of included studies. In terms of OQAQ, 37% (499/1367) of the SRs assessed risk of bias (validity) in the included studies, while 80% (1112/1387) reported the criteria for study selection.
Conclusions
Although reporting guidelines and quality assessment tools exist, reporting and methodological quality of SRs are inconsistent. Mechanisms to improve adherence to established reporting guidelines and methodological assessment tools are needed to improve the quality of SRs.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13643-017-0527-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Reporting quality, Methodological quality, Systematic reviews, Guideline adherence
Background
Systematic reviews (SRs) are considered the gold standard for evidence used to evaluate the benefits and harms of healthcare interventions. They are powerful tools used to assess treatment effectiveness which can subsequently improve patient care [1]. SR evidence has become increasingly important in clinical decision-making and for informing clinical guidelines and health policy [2, 3].
Often, the quality of both methodology and reporting of SRs is flawed due to deficiencies in the design, conduct, and reporting. Poorly conducted SRs can lead to inaccurate estimates of treatment effectiveness, misleading conclusions, and reduced applicability, all of which are a waste of limited resources [4]. Unfortunately, poorly conducted or reported SRs may be associated with bias, limiting their usefulness [5]. When SRs comply with established methodology, report findings transparently, and are free of bias, they provide relevant information for practice guideline developers and other stakeholders such as policy makers [5]. As such, SR methodologists have proposed and developed various methodological and reporting guidelines over the years to assist in improving the methodological rigor and reporting of SRs.
With the rise of evidence-based medicine, criteria for assessing quality began to emerge, such as Mulrow [6] and Sacks [7]. In 1991, Oxman and Guyatt developed the Overview Quality Assessment Questionnaire (OQAQ) [8], a validated tool to assess methodological quality for SRs of intervention studies. Since then, SR methodologists have suggested several other methodological quality (MQ) items, such as potential sources of bias, as important in improving quality of conduct. A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR) [9] tool was developed in 2007 for SRs for intervention studies to include these additional items. In 2010, a revised tool (R-AMSTAR) was developed to provide a quantitative scoring method to assess quality [10]. The accurate reporting of methods and SR findings was established in the late 1990s. In 1999, the Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses (QUOROM) Statement was developed to evaluate the completeness of reporting of meta-analyses of randomized trials [11]. A decade later, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement was developed as an update of QUOROM to address several conceptual and methodological advances in the conduct and reporting of SRs of randomized trial [12]. In 2011, Cochrane developed the Methodological Expectations of Cochrane Intervention Reviews (MECIR) guidelines to specify the methodological and reporting standards for Cochrane intervention protocols and reviews [13, 14]. These guidelines drew criteria from AMSTAR, PRISMA, and other guidelines from organizations such as the US Institute of Medicine [13, 14].
Little was known about how quality or reporting of SRs was assessed in methodological reports. In a separate manuscript, we mapped the methods used to assess SR quality (e.g., use of quality assessment tools) or reporting of SRs (e.g., reporting guidelines) in methodological reports [15]. We found that the criteria used to assess MQ and reporting quality (RQ) of SRs varied considerably. These findings raised an important issue regarding how well SR authors used published reporting guidelines and MQ assessment tools.
Although methodological studies of SRs assessing the MQ or RQ have been published, adherence of SRs to established MQ and RQ assessment tools is unknown. We will address this aspect by examining existing methodological overviews.
Objectives
The objective of this study was to determine SR adherence to the QUOROM and PRISMA reporting guidelines and the AMSTAR and OQAQ quality assessment tools as evaluated in methodological overviews.
Methods
Definitions and important concepts
SRs and meta-analyses were defined based on the guidelines provided by the Cochrane Collaboration and the PRISMA Statement [12, 16]. We adopted the term overview to mean a summary of evidence from more than one SR at a variety of different levels, including the combination of different interventions, different outcomes, different conditions, problems or populations, or the provision of a summary of evidence on the adverse events of an intervention [17, 18]. Other terminology used to describe overviews includes systematic review of systematic reviews, reviews of reviews, or an umbrella review. We included publications that are “methodological overviews,” meaning research that has assessed the MQ or RQ of a cohort of SRs and refer to these publications simply as “reports.”
Methodological quality and completeness of reporting
There is an important distinction between SR quality of methods and quality of reporting. MQ is concerned with how well a SR was designed and conducted (e.g., literature search, selection criteria, pooling of data). RQ refers to how well methodology and findings were described in the SR report(s) [19]. This critical difference should be reflected in the choice of quality assessment tools and reporting guidelines.
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria
This work stems from a parallel investigation where any methodological report published between January 1990 and October 2014 with a primary objective to assess the quality of methodology, reporting, or other quality characteristics of SRs was included [15]. We included only those methodological reports that evaluated SRs addressing the comparative effectiveness of interventions as most quality tools have been developed for intervention reviews. For this paper, however, we include only those reports using the most frequently employed published MQ (AMSTAR and OQAQ) and RQ (PRISMA and QUOROM) tools, as determined from the parallel investigation [15].
Exclusion criteria
We excluded reports of clinical interventions, where the intent was to summarize the evidence for use in healthcare decision-making; reports assessing the quality of diagnostic, screening, etiological, or prognostic studies; and other publication types, such as editorials, narrative reviews, rapid reviews, and network meta-analyses. Reviews that include study designs other than randomized controlled trials were also excluded. Reports in languages other than English were not included. Reports including fewer than 10 SRs, assessing the reliability of an assessment tool, evaluating only one methodological characteristic (e.g., search strategy), or those assessing only SRs with pooled estimates of effect were also excluded.
Search methods
An experienced information specialist developed and conducted an extensive search of the Cochrane Library, EMBASE®, and MEDLINE® to identify methodological reports published between January 1990 and October 16, 2014. Potentially eligible titles and/or abstracts were identified using a combination of subject headings (e.g., “Meta-Analysis as Topic,” “Quality Control,” “Checklist”) and key words (e.g., “umbrella review,” scoring, compliance) (see Additional File 1). The search strategy was peer-reviewed prior to execution [20]. Additional reports eligible for inclusion were identified by members of the research team prior to the start of the project [2, 21, 22]. These articles were used as “seed” articles when developing the electronic search strategy.
Screening
Titles and abstracts were screened for potentially relevant articles using a liberal accelerated approach (i.e., any potentially relevant citations were identified by one reviewer; a second person verified potential excludes). Full-text screening was completed independently and in duplicate by a team of reviewers with experience in methodological reviews; a 5% pilot testing was conducted at both screening levels. All screening disagreements were discussed among pairs of reviewers, with any outstanding disagreements resolved by an independent third reviewer (DM). A data management software, DistillerSR® [23], was used to manage retrieved records, screen citations/reports, record reasons for exclusion, and store extracted data.
Data extraction
We developed standardized forms for data extraction of items of interest from the included reports. Basic characteristics and findings relating to the SRs that were reviewed were extracted from each included report by two of four reviewers; a 10% random sample of reports was assessed for accuracy. A pre-extraction meeting was held for all extraction levels along with pilot testing to ensure consistency across reviewers. The following basic characteristics of the included overviews were extracted: year of publication, number of included SRs, specified medical area, number of databases searched, language restrictions, SR definition, types of publishing journals, Cochrane or non-Cochrane review, reporting of availability of study protocol, and source of funding. Additional items pertaining to the evaluated reviews were extracted: intent of assessment (whether MQ or RQ), the method(s) used to assess MQ or RQ, and details of adherence of SRs to individual items included in OQAQ, AMSTAR, QUOROM, or PRISMA guidelines.
Analyses
Summary statistics are reported as frequency and percentage of reports for report characteristics or frequency and percentage of compliant SRs. No formal inferential statistical analyses were conducted. In some cases, reports would allocate points, or scores, to MQ or RQ items. In these cases, we considered full points or a complete score to be optimal; any meeting partial scores would be considered non-adherent. A post hoc decision was made to look at publications by their intent to assess MQ only, RQ only, or both MQ and RQ. This decision was made without prior examination of the data by the senior investigator (DM). Due to the limited number of Cochrane reviews, the data did not allow for comparison of reports, including Cochrane versus non-Cochrane reviews, as planned. This study was not registered in PROSPERO or elsewhere as no known repositories take methodological protocols. However, the study protocol is available upon request.
Results
Of the 20,765 independent records retrieved from electronic searching, 1189 reports were reviewed in relation to a subset of the eligibility at full text, of which 935 were excluded for either not assessing a cohort of SRs or the primary intent was not to assess MQ or RQ. A secondary full-text review of the remaining 254 reports was carried out to determine whether exclusion criteria were met; 178 reports were excluded, leaving 76 potentially eligible reports. Once it was determined by the parallel investigation [15] which quality tools were used most often (OQAQ, AMSTAR, QUOROM, or PRISMA), 20 of the 76 reports were excluded for not using one of those tools. The tools or criteria used by the 20 reports were reported in a separate manuscript [15]. A total of 56 reports [21–77] evaluating 5371 SRs were included (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
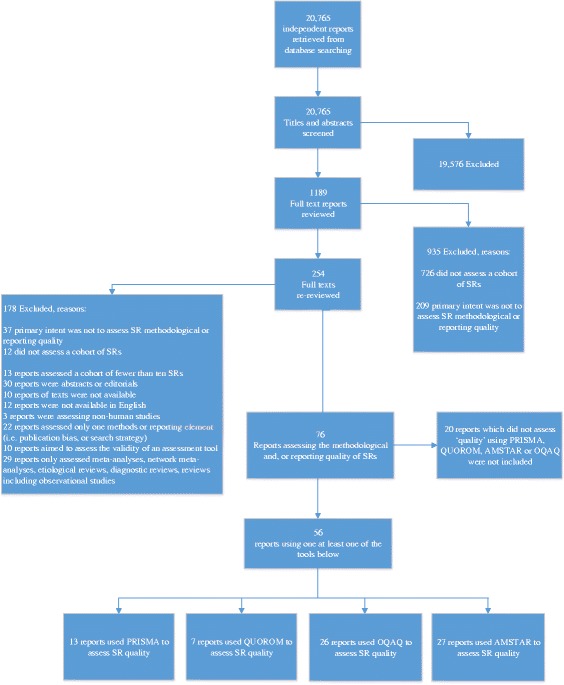
Flow of study reports
Report characteristics
The report characteristics are listed in Table 1. The majority of reports were conducted with the intent to assess MQ or RQ using an appropriate tool; 61% (34/56) of reports had a primary intent to assess MQ only, 7% (4/56) reported having a primary intent to assess RQ, and 27% (15/56) had a primary intent to assess both MQ and RQ. The remaining reports did not use the tools according to their intended use: one report used OQAQ for RQ assessment, one used PRISMA for both RQ and MQ assessments, and two reports used MQ tools to assess both MQ and RQ. Regardless of intent, 27 reports used AMSTAR, 26 reports used OQAQ, 13 reports used PRISMA, and seven reports used QUOROM.
Table 1.
Table of characteristics by mechanism for assessing “quality”
| Characteristic | Reports using PRISMA N = 13 |
Reports using QUOROM N = 7 |
Reports using OQAQ N = 26 |
Reports using AMSTAR N = 27 |
All reports N = 56 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Year of publication of methodological report | 1996–2010 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 100 | 20 | 77 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 38 |
| 2010–2014 | 13 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 23 | 27 | 100 | 35 | 63 | |
| Number of assessed SRs across reports | Median (IQR) | 88 (37, 134) | 61 (53, 107) | 59 (31, 109) | 46 (22, 106) | 57 (30, 109) | |||||
| Range | 10–487 | 10–161 | 10–200 | 10–369 | 10–487 | ||||||
| Were SRs of particular medical field? | No | 1 | 8 | 2 | 29 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 9 |
| Yes | 12 | 92 | 5 | 71 | 24 | 92 | 26 | 96 | 51 | 91 | |
| Intent of assessment | MQ tool for MQ assessment | – | – | – | – | 16 | 62 | 18 | 67 | 34 | 61 |
| RQ tool for RQ assessment | 2 | 15 | 2a | 29 | – | – | – | – | 4 | 7 | |
| Both MQ and RQ (and appropriate use of tool, accordingly) | 10 | 77 | 5 | 71 | 7 | 27 | 8 | 30 | 15 | 27 | |
| Used MQ tool for RQ assessment | – | – | – | – | 1a | 4 | – | – | 1 | 2 | |
| Used MQ tool for both MQ and RQ assessment | – | – | – | – | 1 | 4 | – | – | 1 | 2 | |
| Used MQ tools plus other criteria; both MQ and RQ assessedb | – | – | – | – | 1c | 4 | 1c | 4 | 1 | 2 | |
| Used RQ tool for both MQ and RQ assessment | 1 | 8 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 | 2 | |
| Cohort of Cochrane SRs | Cochrane only | 0 | 0 | 3 | 43 | 4 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 7 |
| Sample of reviews | 6 | 46 | 3 | 43 | 11 | 42 | 13 | 48 | 28 | 50 | |
| Specific journal sample or other | 7 | 54 | 1 | 14 | 11 | 42 | 14 | 52 | 24 | 43 | |
| Number of databases searched | 1 | 2 | 15 | 4 | 57 | 4 | 15 | 4 | 15 | 10 | 18 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 11 | 5 | 9 | |
| 3 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 23 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 13 | |
| 4 | 4 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 4 | 15 | 10 | 18 | |
| 5 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 19 | 4 | 15 | 8 | 14 | |
| 6 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 5 | |
| 7 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 5 | |
| 8+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 15 | 3 | 5 | |
| Not reported | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 4 | |
| Not applicable (select journals) | 3 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 15 | 5 | 9 | |
| Reports restricted SRs by language | No restrictions | 2 | 15 | 2 | 29 | 12 | 46 | 4 | 15 | 15 | 27 |
| Not reported | 7 | 54 | 4 | 57 | 10 | 39 | 13 | 48 | 22 | 39 | |
| Restricted to English | 1 | 8 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 23 | 7 | 26 | 13 | 23 | |
| Restricted to English and other specified languages | 3 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 11 | 6 | 11 | |
| SR defined for inclusion criteria | Not reported | 2 | 15 | 1 | 14 | 7 | 27 | 6 | 22 | 12 | 21 |
| Yes, but no reference given | 4 | 31 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 19 | 5 | 19 | 10 | 18 | |
| “Systematic review” reported as a search term | 5 | 39 | 4 | 57 | 13 | 50 | 9 | 33 | 24 | 43 | |
| Cochrane Collaboration and PRISMA Statement | 2 | 15 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 8 | 5 | 19 | 7 | 13 | |
| Other reference | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 5 | |
| Was a study protocol reported as available for this report? | No or not reported | 11 | 85 | 6 | 86 | 24 | 92 | 24 | 89 | 49 | 88 |
| Yes, link reported | 2 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 4 | |
| Yes, upon request | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 3 | 12 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 9 | |
| Report source of funding | Industry Funded | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Non-profit Funding | 7 | 54 | 3 | 43 | 13 | 50 | 10 | 37 | 26 | 46 | |
| Reported no funding | 1 | 8 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 19 | 6 | 22 | 8 | 14 | |
| Not reported | 5 | 39 | 3 | 43 | 10 | 39 | 10 | 37 | 21 | 38 | |
Note: columns are not mutually exclusive
aOne study evaluated both QUOROM and OQAQ for RQ
bUnclear from the study description whether MQ tools and/or additional criteria were used to assess the RQ aspect of the study
cSame report
Reports spanned an 18-year period, of which 63% (35/56) were published between 2010 and 2014, indicating a marked increase in recent years. A median of 57 SRs (interquartile range 30 to 109) were assessed in reports. Almost all reports (91%) addressed SRs of a topic within a specific medical field. Forty-three percent (24/56) of reports include SRs limited to specific journals, half (28/56) included SRs from a general sample of reviews across medical journals, and only 7% (4/56) evaluated a cohort of Cochrane reviews (i.e., from one specific source). Accordingly, the majority of reports provided details for the source of SRs, whether it was databases or specific journals. Information as to whether language restrictions were used was provided in 61% (34/56) of reports. In relation to specifying a definition for SR, 21% (12/56) did not report this information. The majority of reports (88%) did not state whether a protocol was available. Thirty-eight percent (21/56) of reports did not state the source of funding for their research. Table 1 also details these characteristics according to reports using a particular tool.
Adherence to MQ and RQ items in methodological reports
The reports assessed adherence to items for the most frequently used MQ and RQ tools (i.e., AMSTAR, OQAQ, QUOROM, PRISMA). These data have been collated across the samples of SRs (Tables 2, 3, 4, and 5). Data pertaining to adherence to quality or reporting criteria by item were obtainable from most methodological reports: 100% (13/13) using PRISMA, 71% or more (5–6 out of 7, depending on the item) using QUOROM, 85% or more (22–23 out of 27, depending on the item) using AMSTAR, and 85% (22/26) using OQAQ.
Table 2.
Summary across reports of systematic reviews adhering to PRISMA reporting guidelines (N = 13)
| Item assessed | Item description | No. of reports reporting adherence by item | Adhering SRs | Total SRs | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Title | Identify the report as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both | 13 | 1480 | 1741 | 85 |
| 2. Abstract: structured summary | Provide a structured summary including the following as applicable: background; objectives; data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, and interventions; study appraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions and implications of key findings; systematic review registration number | 13 | 885 | 1741 | 51 |
| 3. Introduction: rationale | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known | 13 | 1532 | 1741 | 88 |
| 4. Objectives | Provide an explicit statement of questions being addressed with reference to participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design (PICOS) | 13 | 1039 | 1741 | 60 |
| 5. Methods: protocol and registration | Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (e.g., web address), and, if available, provide registration information including registration number | 13 | 102 | 1741 | 6 |
| 6. Eligibility criteria | Specify study characteristics (e.g., PICOS, length of follow-up) and report characteristics (e.g., years considered, language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale | 13 | 1342 | 1741 | 77 |
| 7. Information sources | Describe all information sources (e.g., databases with dates of coverage, contact with study authors to identify additional studies) in the search and date last searched | 13 | 1530 | 1741 | 88 |
| 8. Search | Present full electronic search strategy for at least one database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated | 13 | 923 | 1741 | 53 |
| 9. Study selection | State the process for selecting studies (i.e., screening, eligibility, included in systematic review, and, if applicable, included in the meta-analysis) | 13 | 1048 | 1741 | 60 |
| 10. Data collection process | Describe method of data extraction from reports (e.g., piloted forms, independently, in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators | 13 | 1059 | 1741 | 61 |
| 11. Data items | List and define all variables for which data were sought (e.g., PICOS, funding sources) and any assumptions and simplifications made | 13 | 865 | 1741 | 50 |
| 12. Risk of bias in individual studies | Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias of individual studies (including specification of whether this was done at the study or outcome level) and how this information is to be used in any data synthesis | 13 | 1251 | 1741 | 72 |
| 13. Summary measures | State the principal summary measures (e.g., risk ratio, difference in means) | 13 | 1353 | 1741 | 78 |
| 14. Synthesis of results | Describe the methods of handling data and combining results of studies, if done, including measures of consistency (e.g., I 2) for each meta-analysis | 13 | 1129 | 1736 | 65 |
| 15. Risk of bias across studies | Specify any assessment of risk of bias that may affect the cumulative evidence (e.g., publication bias, selective reporting within studies) | 13 | 657 | 1741 | 38 |
| 16. Additional analyses | Describe methods of additional analyses (e.g., sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done, indicating which were pre-specified | 13 | 879 | 1738 | 51 |
| 17. Results: study selection | Give numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram | 13 | 1094 | 1740 | 63 |
| 18. Study characteristics | For each study, present characteristics for which data were extracted (e.g., study size, PICOS, follow-up period) and provide the citations | 13 | 1324 | 1741 | 76 |
| 19. Risk of bias within studies | Present data on risk of bias of each study and, if available, any outcome level assessment (see item 12) | 13 | 1199 | 1738 | 69 |
| 20. Results of individual studies | For all outcomes considered (benefits or harms) present for each study: (a) simple summary data for each intervention group and (b) effect estimates and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest plot | 13 | 1399 | 1737 | 81 |
| 21. Synthesis of results | Present results of each meta-analysis done, including confidence intervals and measures of consistency | 13 | 1150 | 1687 | 68 |
| 22. Risk of bias across studies | Present results of any assessment of risk of bias across studies (see item 15) | 13 | 527 | 1736 | 30 |
| 23. Additional analysis | Give results of additional analyses, if done (e.g., sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression [see item 16]) | 13 | 631 | 1658 | 38 |
| 24. Discussion: summary of evidence | Summarize the main findings including the strength of evidence for each main outcome; consider their relevance to key groups (e.g., healthcare providers, users, and policy makers) | 13 | 1085 | 1741 | 62 |
| 25. Limitations | Discuss limitations at study and outcome level (e.g., risk of bias) and at review-level (e.g., incomplete retrieval of identified research, reporting bias) | 13 | 1358 | 1741 | 78 |
| 26. Conclusions | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence and implications for future research | 13 | 1480 | 1741 | 85 |
| 27. Funding | Describe sources of funding for the systematic review and other support (e.g., supply of data) and role of funders for the systematic review | 13 | 647 | 1741 | 37 |
Table 3.
Summary across reports of systematic reviews adhering to QUOROM reporting guideline (N = 7)
| Item assessed | Item description | No. of reports reporting adherence by item | Adhering SRs | Total SRs | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Identify the report as a systematic review | 6 | 133 | 449 | 30 |
| Abstract | Use a structured format | 6 | 402 | 449 | 90 |
| Describe the clinical question explicitly | 6 | 341 | 449 | 76 | |
| Describe the databases (i.e., list) and other information sources | 6 | 335 | 449 | 75 | |
| Describe the selection criteria (i.e., population, intervention, outcome, and study design), methods for validity assessment, data abstraction, and study characteristics, and quantitative data synthesis in sufficient detail to permit replication | 5 | 177 | 388 | 46 | |
| Describe characteristics of the RCTs included and excluded; qualitative and quantitative findings (i.e., point estimates and confidence intervals); and subgroup analyses | 5 | 180 | 388 | 46 | |
| Describe the main results | 6 | 425 | 449 | 95 | |
| Introduction: rationale | Describe the explicit clinical problem, biological rationale for the intervention, and rationale for review | 6 | 382 | 449 | 85 |
| Search | Describe the information sources, in detail (e.g., databases, registers, personal files, expert informants, agencies, hand-searching), and any restrictions (years considered, publication status, language of publication) | 5 | 274 | 388 | 71 |
| Study selection | Describe the inclusion and exclusion criteria (defining population, intervention, principal outcomes, and study design) | 6 | 417 | 449 | 93 |
| Data collection process | Data extraction: describe the process or processes used (e.g., completed independently, in duplicate) | 6 | 363 | 449 | 81 |
| Data items | Describe the type of study design, participants’ characteristics, details of intervention, outcome definitions, and how clinical heterogeneity was assessed | 6 | 316 | 449 | 70 |
| Risk of bias in individual studies | Validity assessment: describe the criteria and process used (e.g., masked conditions, quality assessment, and their findings) | 6 | 240 | 449 | 54 |
| Synthesis of results | Describe the principal measures of effect (e.g., relative risk), method of combining results (statistical testing and confidence intervals), handling of missing data; how statistical heterogeneity was assessed; a rationale for any a priori sensitivity and subgroup analyses; and any assessment of publication bias | 5 | 219 | 388 | 56 |
| Results: study selection | Provide a meta-analysis profile summarizing trial flow | 6 | 40 | 449 | 9 |
| Study characteristics | Present descriptive data for each trial (e.g., age, sample size, intervention, dose, duration, follow-up period) | 6 | 384 | 449 | 86 |
| Results of individual studies | Report agreement on the selection and validity assessment; present simple summary results (for each treatment group in each trial, for each primary outcome); present data needed to calculate effect sizes and confidence intervals in intention-to-treat analyses (e.g., 2 × 2 tables of counts, means and SDs, proportions) | 5 | 213 | 388 | 55 |
| Discussion: summary of evidence | Summarize key findings; discuss clinical inferences based on internal and external validity; interpret the results in light of the totality of available evidence; describe potential biases in the review process (e.g., publication bias); and suggest a future research agenda | 5 | 265 | 388 | 68 |
Table 4.
Summary across reports of systematic reviews meeting AMSTAR quality assessment criteria (N = 27)
| Item assessed | Item Description | No. of reports reporting adherence by item | Adhering SRs | Total SRs | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Methods: Protocol and registration | Was an 'a priori' design provided? | 23 | 820 | 1794 | 46 |
| 2. Information sources | Was the status of publication (i.e. grey literature) used as an inclusion criterion? | 23 | 1013 | 1794 | 57 |
| 3. Search | Was a comprehensive literature search performed? | 23 | 1149 | 1794 | 64 |
| 4. Data collection process | Was there duplicate study selection and data extraction? | 23 | 534 | 1794 | 30 |
| 5. Results: Study selection | Was a list of studies (included and excluded) provided? | 22 | 537 | 1779 | 30 |
| 6. Study characteristics | Were the characteristics of the included studies provided? | 23 | 1439 | 1794 | 80 |
| 7. Risk of bias within studies | Was the scientific quality of the included studies assessed and documented? | 23 | 1200 | 1794 | 67 |
| 8. Synthesis of results | Were the methods used to combine the findings of studies appropriate? | 23 | 1169 | 1794 | 65 |
| 9. Risk of bias across studies | Was the likelihood of publication bias assessed? | 23 | 995 | 1794 | 56 |
| 10. Limitations | Was the scientific quality of the included studies used appropriately in formulating conclusions? | 23 | 590 | 1794 | 33 |
| 11. Funding | Was the conflict of interest stated? | 22 | 685 | 1779 | 39 |
Table 5.
Summary across reports of systematic reviews adhering to OQAQ items (N = 26)
| Item assessed | Item description | No. of reports reporting adherence by item | Adhering SRs | Total SRs | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Information sources | Were the search methods used to find evidence reported? | 22 | 1027 | 1387 | 74 |
| 2. Search | Was the search strategy for evidence reasonably comprehensive? | 22 | 754 | 1370 | 55 |
| 3. Study selection | Were the criteria used for deciding which studies to include in the overview reported? | 22 | 1112 | 1387 | 80 |
| 4. Risk of bias in individual studies | Were criteria used for assessing validity of the included studies reported? | 22 | 499 | 1367 | 37 |
| 5. Synthesis of results | Were findings of the relevant studies combined appropriately relative to the primary question addressed? | 22 | 830 | 1387 | 60 |
| 6. Results: study selection | Was bias in the selection of studies avoided? | 22 | 740 | 1351 | 55 |
| 7. Synthesis of results | Were methods used to combine the findings of relevant studies (to reach a conclusion) reported? | 22 | 1005 | 1387 | 73 |
| 8. Limitations | Was the validity of all studies referred to in the text assessed using appropriate criteria (either in selecting studies for inclusion or in analyzing studies that are cited)? | 22 | 898 | 1363 | 66 |
| 9. Conclusions | Were the conclusions made by the author (s) supported by the data and/or analysis reported in the overview? | 22 | 1076 | 1387 | 78 |
Adherence to reporting guidelines (RQ)
A total of 1741 SRs were included in the 13 reports that used PRISMA (Table 2). Over 85% of SRs fully reported their title, provided a rationale for the review, described all information sources, and provided a general interpretation of the results. However, compliance was poor for several items, with only 38% (657/1741) of SRs specifying any assessment of risk of bias methods across studies, 30% (527/1736) presenting results of risk of bias assessments across studies, and 37% (647/1741) describing sources of funding. Less than 6% (102/1741) provide protocol information in their SR report.
Six reports evaluating 449 SRs used QUOROM (Table 3). One additional report did not provide any information by item and is excluded from the analysis. Thirty percent (133/449) identified the report as a systematic review, and 9% (40/449) of SRs provided a figure summarizing trial flow. Included SRs adhered well to several QUOROM items. Over 85% of SRs used a structured format in the abstract, described the main results in the abstract, provided an explicit clinical question and rationale in the introduction/background section, described the study selection criteria, and presented descriptive data for each trial.
Adherence according to methodological quality
A total of 1794 SRs were included in the 23 reports that provided AMSTAR assessments by item (Table 4). Eighty percent (1439/1794) of SRs provided the characteristics of included studies. Just over half (995/1794) assessed publication bias. Thirty-nine percent (685/1779) stated a conflict of interest, and a third (590/1794) of SRs reported limitations. In addition, 30% (534/1794) of SRs used duplicate study selection and data extraction during the data collection process and 30% (537/1779) provided a list of included and excluded studies.
Twenty-two reports evaluating 1387 SRs used the OQAQ criteria (Table 5). Thirty-seven percent (499/1367) of the SRs assessed risk of bias (validity) in the included studies. Comparatively, 80% (1112/1387) of the SRs reported the criteria for study selection, 75% (1027/1387) of SRs reported search methods used to find the evidence, 73% (1005/1387) described the methods used to combine the findings, and 78% (1076/1387) of SRs determined whether the conclusions were supported by the data.
Discussion
Previously, we identified that the most commonly used tools or guidelines for critical appraisal and RQ assessment were QUOROM, PRISMA, AMSTAR, and OQAQ [15]. In this study, we evaluated SR, MQ, or RQ adherence to these quality assessments or reporting guidelines tools across methodological reports published between 1990 and 2014.
Our results indicate that SR adherence to reporting items was variable. Over 85% provided a rationale for the review when assessed using PRISMA, yet less than 6% gave protocol information in their SR report. Our study, like others, shows that reporting of review protocols is poorly reported [2, 24]. Review protocols are important to reduce duplication of research, allow researchers to plan and anticipate potential issues, assess validity of methods and replication of the review if desired, and prevent arbitrary decision-making [78, 79]. In addition, risk of bias across individual studies within reviews, additional analyses, and funding source were also poorly reported. These findings are consistent with other research [24]. We note that compliance to some reporting criteria has improved over time. Nine percent provided a trial flow diagram as reported using the QUOROM guidelines, compared to 63% using the PRISMA guidelines. This observed improvement in reporting could be partly due to journal endorsement of the reporting guideline but also due to authors’ exposure to the published tools or their general awareness to the issues of reporting in health research over time. For the few items that are similar between PRISMA and QUOROM and show a lower compliance with PRISMA, these results are possibly attributed to differences in operationalization of the criteria or simply as chance findings.
Adherence to methodological quality items was also variable. Overall, SRs using OQAQ adhered quite well to all methodological items in the tool. OQAQ was validated and is well accepted, but it was developed and validated over two decades ago [8]. The OQAQ criteria do not include assessment of issues such as a priori design, assessment of publication bias, and conflict of interest. As such, OQAQ differs from AMSTAR, which was published and validated more recently [80, 81]. For the 27 reports using AMSTAR to assess quality of SRs, the percentage of SRs meeting AMSTAR criteria was mediocre. One third or less of SRs used duplicate study selection and data extraction, provided a list of included and excluded studies within their review, or reported limitations. One small study has also shown the need for better adherence to AMSTAR [82]. We would expect that future research will include an evaluation of the recently published risk of bias in systematic reviews (ROBIS) tool [83].
SR evidence is used by decision-makers, policy makers, and other stakeholders. They should expect consistent and high-quality standards for reporting and conduct. Guidelines and tools have been developed over the years to improve RQ and MQ of SRs. Our findings suggest that for several items in MQ or RQ tools, SR authors comply well with the guidelines, but some items require major improvement. Other studies have also found that methodological and reporting quality is suboptimal [2, 84, 85]. In addition, evidence is emerging that biases within SRs could influence results and quality of overviews [86]. Effort should be directed towards improving the quality and reporting of SRs, wherever possible.
Journal endorsement and implementation of the use of reporting guidelines and critical appraisal tools during the editorial process is one mechanism to facilitate better quality. There is insufficient evidence to date in relation to systematic reviews but some information in relation to trials. One recent methodological review found insufficient evidence to determine a relationship between endorsement and completeness of reporting: Of 101 reporting guidelines, only seven had evaluable data from only a few evaluations each [87]. One small study found that reporting and methodological quality (adherence to both AMSTAR and PRISMA) significantly increased after journal endorsement of the PRISMA guidelines [25]. Readers may also be curious as to whether reporting differs when examining the influence of publication of the tools, such as a before and after publication comparison; none of the included methodological reviews assessed this. Further, in thinking about publication and then journal endorsement as potential interventions, we would agree with previously published work that journal endorsement might serve as a “stronger” intervention [87].
One unexplored hypothesis is whether the endorsement and use of reporting tools at the protocol phase of a SR paves the way for better reporting and methodological quality for the SR report. Review protocols allow researchers to plan and anticipate potential issues, assess validity of methods, and prevent arbitrary decision-making [78, 79]. The reporting of protocols can be guided and assessed by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis for Protocols 2015 (PRISMA-P 2015) [78, 79]. Further, Moher et al. [2] suggested that granting agencies and journals require full compliance with established reporting and methodological guidelines, such as a requirement to include SR protocols with the submission of a SR.
Our review was limited exclusively to SRs included by authors of methodological reports. Each overview had their own selection criteria and quality thresholds; therefore, we did not seek out the publication of the individual SRs but relied on the data reported in each overview. As such, there is inherent heterogeneity that may be causing some of the observed variation in MQ and RQ. In addition, we relied on how the authors assessed and reported adherence. Variability in how strictly review authors assessed adherence to items in MQ and RQ tools could result in additional heterogeneity. Nevertheless, this report provides some insight into the adherence to quality assessment and reporting guideline items.
A rigorous development of tools for MQ and RQ is important and should involve several steps and appropriate consideration of stakeholders and methodological experts’ participation [88]. Despite considerable effort, the delivery of fit-for-purpose tools may not always be optimally achieved if items are not completely reflective of intent. For example, it could be reasonable to note that some MQ items in both AMSTAR and OQAQ are written in language that reflects more of reporting than conduct. We encourage developers to carefully consider the wording of items. Further, any tool could potentially be subject to content modifications as the science of health research methodology continues to evolve.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the methodological and reporting quality of SRs varied considerably across items in four well-known tools. Mechanisms to improve adherence to established reporting guidelines and methodological assessment tools are needed to improve the quality of SRs.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Michelle Fiander for peer-reviewing the search strategy. We would also like to thank Raymond Daniel for his support in running the search, identifying duplicates, and identifying studies for screening. We would like to thank Sophia Tsouros, Alexander Tsertsvadze, and Kavita Singh for their screening support.
Funding
This project was completed on behalf of the Cochrane Bias Methods Group, funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR reference no.: CON-105529). The funder had no role in the design, conduct, and reporting of the project.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. The original datasets used or analyzed are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors’ contributions
DM and DGA conceived the project. IB, LB, CG, LT, AS, DGA, and DM developed the protocol for the project. BS developed the search strategy. LT, KP, AM, and RO screened the studies and extracted the data. LT compiled the data and drafted the first version of the report. All authors commented on the data and edited and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
DM is a co-editor in chief of systematic reviews and also received funding from BioMed Central for a separate project. AS is an associate editor of systematic reviews. DGA is on the Editorial Board of systematic reviews. AM worked for the Cochrane Methods Bias Group from September 2013 to September 2015 when he worked on this paper; the group was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR funding reference no.: CON-105529).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- AMSTAR
A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews
- MECIR
Methodological Expectations of Cochrane Intervention Reviews
- MQ
Methodological quality
- OQAQ
Overview Quality Assessment Questionnaire
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PRISMA-P
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis for Protocols
- QUOROM
Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses
- R-AMSTAR
Revised-A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews
- RQ
Reporting quality
- SR
Systematic review
Additional file
Search strategy. (DOCX 16 kb)
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13643-017-0527-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Kusala Pussegoda, Email: kpussegoda@ohri.ca.
Lucy Turner, Email: lturner@htai.org.
Chantelle Garritty, Email: cgarritty@ohri.ca.
Alain Mayhew, Email: AMayhew@bruyere.org.
Becky Skidmore, Email: bskidmore@rogers.com.
Adrienne Stevens, Email: adstevens@ohri.ca.
Isabelle Boutron, Email: isabelle.boutron@aphp.fr.
Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, Email: rafaelonofre@gmail.com.
Lise M. Bjerre, Email: lbjerre@bruyere.org
Asbjørn Hróbjartsson, Email: ah@cochrane.dk.
Douglas G. Altman, Email: doug.altman@csm.ox.ac.uk
David Moher, Email: dmoher@ohri.ca.
References
- 1.Ernst E, Pittler MH. Assessment of therapeutic safety in systematic reviews: literature review. BMJ. 2001;323:546. doi: 10.1136/bmj.323.7312.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moher D, Tetzlaff J, Tricco AC, Sampson M, Altman DG. Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e78. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Page MJ, Shamseer L, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Sampson M, Tricco AC, et al. Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews of biomedical research: a cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 2016;13:e1002028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chalmers I, Glasziou P. Avoidable waste in the production and reporting of research evidence. Lancet. 2009;374:86–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cook DJ, Mulrow CD, Haynes RB. Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126:376–80. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-5-199703010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mulrow CD. The medical review article: state of the science. Ann Intern Med. 1987;106:485–8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-3-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sacks HS, Berrier J, Reitman D, Ancona-Berk VA, Chalmers TC. Meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:450–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702193160806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Oxman AD, Guyatt GH. Validation of an index of the quality of review articles. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991;44:1271–8. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(91)90160-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shea BJ, Grimshaw JM, Wells GA, Boers M, Andersson N, Hamel C, et al. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7:10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-7-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kung J, Chiappelli F, Cajulis OO, Avezova R, Kossan G, Chew L, et al. From systematic reviews to clinical recommendations for evidence-based health care: validation of Revised Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews (R-AMSTAR) for grading of clinical relevance. Open Dent J. 2010;4:84–91. doi: 10.2174/1874210601004020084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses. Lancet. 1999;354:1896–900. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)04149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:W65–W94. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cochrane Methods Group MECIR. Standards for Cochrane new reviews of interventions and their updates. [Internet]. [http://methods.cochrane.org/mecir]. Accessed: 7 Mar 2017.
- 14.Lasserson T, Churchill R, Higgins J, Chandler J, Tovey D. Development of methodological standards for the conduct of intervention reviews. [Internet]. [http://editorial-unit.cochrane.org/sites/editorial-unit.cochrane.org/files/public/uploads/Development_of_conduct_%20standards_0.pdf]. Accessed 7 Mar 2017.
- 15.Pussegoda K, Turner L, Garritty C, Mayhew A, Skidmore B, Stevens A, Boutron I, Sarkis-Onofre R, Bjerre LM, Hróbjartsson A, Altman DG, Moher D. Identifying approaches for assessing methodological and reporting quality of systematic reviews: a descriptive study. Syst Rev. 2017 jun 19;6(1):117. doi:10.1186/s13643-017-0507-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Green S, Higgins JPT, Alderson P, Clarke M, Mulrow CD, Oxman AD. Chapter 1: Introduction. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. [Internet]. [http://training.cochrane.org/handbook]. Accessed 27 Jan 2016.
- 17.Smith V, Devane D, Begley CM, Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-11-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Becker LA, Oxman AD. Chapter 22: Overviews of reviews. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011 [Internet]. [http://training.cochrane.org/handbook]. Accessed 14 Jan 2016.
- 19.PRISMA: Transparent reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. [Internet]. [http://www.prisma-statement.org/]. Accessed: 14 Jan 2016.
- 20.Sampson M, McGowan J, Cogo E, Grimshaw J, Moher D, Lefebvre C. An evidence-based practice guideline for the peer review of electronic search strategies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:944–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wen J, Ren Y, Wang L, Li Y, Liu Y, Zhou M, et al. The reporting quality of meta-analyses improves: a random sampling study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61:770–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ma B, Guo J, Qi G, Li H, Peng J, Zhang Y, et al. Epidemiology, quality and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews of traditional Chinese medicine interventions published in Chinese journals. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Evidence Partners DistillerSR [Internet]. [https://www.evidencepartners.com/]. Accessed 27 Jan 2016.
- 24.Li JL, Ge L, Ma JC, Zeng QL, Yao L, An N, et al. Quality of reporting of systematic reviews published in “evidence-based” Chinese journals. Syst Rev. 2014;3:58. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-3-58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Panic N, Leoncini E, de Belvis G, Ricciardi W, Boccia S. Evaluation of the endorsement of the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) statement on the quality of published systematic review and meta-analyses. PLoS One. 2013;8:e83138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Al FK, Al-Omran M. Reporting and methodologic quality of Cochrane Neonatal review group systematic reviews. BMC Pediatr. 2009;9:38. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-9-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Anttila H, Samuelsson K, Salminen A, Brandt A. Quality of evidence of assistive technology interventions for people with disability: an overview of systematic reviews. Technol Disability. 2012;24:9–48. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Aziz T, Compton S, Nassar U, Matthews D, Ansari K, Flores-Mir C. Methodological quality and descriptive characteristics of prosthodontic-related systematic reviews. J Oral Rehabil. 2013;40:263–78. doi: 10.1111/joor.12028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Barbosa FT, Castro AA, de Miranda CT. Neuraxial anesthesia compared to general anesthesia for procedures on the lower half of the body: systematic review of systematic reviews. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2012;62:235–43. doi: 10.1016/S0034-7094(12)70121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Biondi-Zoccai GG, Lotrionte M, Abbate A, Testa L, Remigi E, Burzotta F, et al. Compliance with QUOROM and quality of reporting of overlapping meta-analyses on the role of acetylcysteine in the prevention of contrast associated nephropathy: case study. BMJ. 2006;332:202–9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38693.516782.7C. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Boluyt N, van der Lee JH, Moyer VA, Brand PL, Offringa M. State of the evidence on acute asthma management in children: a critical appraisal of systematic reviews. Pediatrics. 2007;120:1334–43. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-3381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Braga LH, Pemberton J, Demaria J, Lorenzo AJ. Methodological concerns and quality appraisal of contemporary systematic reviews and meta-analyses in pediatric urology. J Urol. 2011;186:266–71. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.03.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brito JP, Tsapas A, Griebeler ML, Wang Z, Prutsky GJ, Domecq JP, et al. Systematic reviews supporting practice guideline recommendations lack protection against bias. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013;66:633–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Choi PT, Halpern SH, Malik N, Jadad AR, Tramer MR, Walder B. Examining the evidence in anesthesia literature: a critical appraisal of systematic reviews. Anesth Analg. 2001;92:700–9. doi: 10.1213/00000539-200103000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Collier A, Heilig L, Schilling L, Williams H, Dellavalle RP. Cochrane Skin Group systematic reviews are more methodologically rigorous than other systematic reviews in dermatology. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:1230–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Conway A, Inglis SC, Chang AM, Horton-Breshears M, Cleland JG, Clark RA. Not all systematic reviews are systematic: a meta-review of the quality of systematic reviews for non-invasive remote monitoring in heart failure. J Telemed Telecare. 2013;19:326–37. doi: 10.1177/1357633X13503427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.de Bot CM, Moed H, Berger MY, Roder E, van Wijk RG, van der Wouden JC. Sublingual immunotherapy in children with allergic rhinitis: quality of systematic reviews. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011;22:548–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2011.01165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Delaney A, Bagshaw SM, Ferland A, Laupland K, Manns B, Doig C. The quality of reports of critical care meta-analyses in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews: an independent appraisal. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:589–94. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000253394.15628.FD. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Elangovan S, Avila-Ortiz G, Johnson GK, Karimbux N, Allareddy V. Quality assessment of systematic reviews on periodontal regeneration in humans. J Periodontol. 2013;84:176–85. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.120021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fleming PS, Koletsi D, Seehra J, Pandis N. Systematic reviews published in higher impact clinical journals were of higher quality. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67:754–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fleming PS, Seehra J, Polychronopoulou A, Fedorowicz Z, Pandis N. A PRISMA assessment of the reporting quality of systematic reviews in orthodontics. Angle Orthod. 2013;83:158–63. doi: 10.2319/032612-251.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fleming PS, Seehra J, Polychronopoulou A, Fedorowicz Z, Pandis N. Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews in leading orthodontic journals: a quality paradigm? Eur J Orthod. 2013;35:244–8. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjs016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gagnier JJ, Kellam PJ. Reporting and methodological quality of systematic reviews in the orthopaedic literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:e771–e777. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.L.00597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gebel K, Bauman AE, Petticrew M. The physical environment and physical activity: a critical appraisal of review articles. Am J Prev Med. 2007;32:361–9. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2007.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hu J, Zhang J, Zhao W, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Shang H. Cochrane systematic reviews of Chinese herbal medicines: an overview. PLoS One. 2011;6:e28696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jadad AR, Moher M, Browman GP, Booker L, Sigouin C, Fuentes M, et al. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses on treatment of asthma: critical evaluation. BMJ. 2000;320:537–40. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7234.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Junhua Z, Hongcai S, Xiumei G, Boli Z, Yaozu X, Hongbo C, et al. Methodology and reporting quality of systematic review/meta-analysis of traditional Chinese medicine. J Altern Complement Med. 2007;13:797–805. doi: 10.1089/acm.2007.7195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kelly KD, Travers A, Dorgan M, Slater L, Rowe BH. Evaluating the quality of systematic reviews in the emergency medicine literature. Ann Emerg Med. 2001;38:518–26. doi: 10.1067/mem.2001.115881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kuukasjarvi P, Malmivaara A, Halinen M, Hartikainen J, Keto PE, Talvensaari T, et al. Overview of systematic reviews on invasive treatment of stable coronary artery disease. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2006;22:219–34. doi: 10.1017/S026646230605104X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lawson ML, Pham B, Klassen TP, Moher D. Systematic reviews involving complementary and alternative medicine interventions had higher quality of reporting than conventional medicine reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58:777–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lee MS, Oh B, Ernst E. Qigong for healthcare: an overview of systematic reviews. JRSM Short Rep. 2011;2:7. doi: 10.1258/shorts.2010.010091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Linde K, ter RG, Hondras M, Melchart D, Willich SN. Characteristics and quality of systematic reviews of acupuncture, herbal medicines, and homeopathy. Forsch Komplementarmed Klass Naturheilkd. 2003;10:88–94. doi: 10.1159/000071668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lundh A, Knijnenburg SL, Jorgensen AW, van Dalen EC, Kremer LC. Quality of systematic reviews in pediatric oncology—a systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009;35:645–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2009.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Luo J, Xu H, Yang G, Qiu Y, Liu J, Chen K. Oral Chinese proprietary medicine for angina pectoris: an overview of systematic reviews/meta-analyses. Complement Ther Med. 2014;22:787–800. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2014.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ma B, Qi GQ, Lin XT, Wang T, Chen ZM, Yang KH. Epidemiology, quality, and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews of acupuncture interventions published in Chinese journals. J Altern Complement Med. 2012;18:813–7. doi: 10.1089/acm.2011.0274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.MacDonald SL, Canfield SE, Fesperman SF, Dahm P. Assessment of the methodological quality of systematic reviews published in the urological literature from 1998 to 2008. J Urol. 2010;184:648–53. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.03.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.McGee RG, Craig JC, Rogerson TE, Webster AC. Systematic reviews of surgical procedures in children: quantity, coverage and quality. J Paediatr Child Health. 2013;49:319–24. doi: 10.1111/jpc.12156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Melchiors AC, Correr CJ, Venson R, Pontarolo R. An analysis of quality of systematic reviews on pharmacist health interventions. Int J Clin Pharm. 2012;34:32–42. doi: 10.1007/s11096-011-9592-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Moher D, Soeken K, Sampson M, Ben-Porat L, Berman B. Assessing the quality of reports of systematic reviews in pediatric complementary and alternative medicine. BMC Pediatr. 2002;2:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-2-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Momeni A, Lee GK, Talley JR. The quality of systematic reviews in hand surgery: an analysis using AMSTAR. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131:831–7. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182818d24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Moseley AM, Elkins MR, Herbert RD, Maher CG, Sherrington C. Cochrane reviews used more rigorous methods than non-Cochrane reviews: survey of systematic reviews in physiotherapy. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:1021–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mrkobrada M, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Haynes RB, Iansavichus AV, Rehman F, Garg AX. Need for quality improvement in renal systematic reviews. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:1102–14. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04401007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Nicolau I, Ling D, Tian L, Lienhardt C, Pai M. Methodological and reporting quality of systematic reviews on tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013;17:1160–9. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.13.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Padula RS, Pires RS, Alouche SR, Chiavegato LD, Lopes AD, Costa LO. Analysis of reporting of systematic reviews in physical therapy published in Portuguese. Rev Bras Fisioter. 2012;16:381–8. doi: 10.1590/S1413-35552012005000040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Papageorgiou SN, Papadopoulos MA, Athanasiou AE. Evaluation of methodology and quality characteristics of systematic reviews in orthodontics. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2011;14:116–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-6343.2011.01522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pieper D, Mathes T, Eikermann M. Impact of choice of quality appraisal tool for systematic reviews in overviews. J Evid Based Med. 2014;7:72–8. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Pieper D, Mathes T, Neugebauer E, Eikermann M. State of evidence on the relationship between high-volume hospitals and outcomes in surgery: a systematic review of systematic reviews. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216:1015–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.12.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Remschmidt C, Wichmann O, Harder T. Methodological quality of systematic reviews on influenza vaccination. Vaccine. 2014;32:1678–84. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Santaguida P, Oremus M, Walker K, Wishart LR, Siegel KL, Raina P. Systematic reviews identify important methodological flaws in stroke rehabilitation therapy primary studies: review of reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2012;65:358–67. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2011.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Seo HJ, Kim KU. Quality assessment of systematic reviews or meta-analyses of nursing interventions conducted by Korean reviewers. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012;12:129. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Shea B, Boers M, Grimshaw JM, Hamel C, Bouter LM. Does updating improve the methodological and reporting quality of systematic reviews? BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6:27. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-6-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Shea B, Bouter LM, Grimshaw JM, Francis D, Ortiz Z, Wells GA, et al. Scope for improvement in the quality of reporting of systematic reviews. From the Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Shea B, Moher D, Graham I, Pham B, Tugwell P. A comparison of the quality of Cochrane reviews and systematic reviews published in paper-based journals. Eval Health Prof. 2002;25:116–29. doi: 10.1177/0163278702025001008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Tunis AS, McInnes MD, Hanna R, Esmail K. Association of study quality with completeness of reporting: have completeness of reporting and quality of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in major radiology journals changed since publication of the PRISMA statement? Radiology. 2013;269:413–26. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13130273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Weed DL, Althuis MD, Mink PJ. Quality of reviews on sugar-sweetened beverages and health outcomes: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94:1340–7. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.111.015875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Windsor B, Popovich I, Jordan V, Showell M, Shea B, Farquhar C. Methodological quality of systematic reviews in subfertility: a comparison of Cochrane and non-Cochrane systematic reviews in assisted reproductive technologies. Hum Reprod. 2012;27:3460–6. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Xu F, Xiao Z, Zhang Y, Wang Y. Quality assessment for systematic review/meta-analysis on antidepressant therapy published in chinese journals. Int J Pharmacol. 2012;8:614–20. doi: 10.3923/ijp.2012.614.620. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;349:g7647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4:1. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-4-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Shea BJ, Hamel C, Wells GA, Bouter LM, Kristjansson E, Grimshaw J, et al. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:1013–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Parmelli E, Banzi R, Fernandez DR, Minozzi S, Moja L, Pecoraro V et al. Using AMSTAR to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews: an external validation study. Poster presentation at the 19th Cochrane Colloquium; 2011 Oct 19-22; Madrid, Spain [abstract]. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Supplement 2011, Suppl:139.
- 82.Sequeira-Byron P, Fedorowicz Z, Jagannath VA, Sharif MO. An AMSTAR assessment of the methodological quality of systematic reviews of oral healthcare interventions published in the Journal of Applied Oral Science (JAOS) J Appl Oral Sci. 2011;19:440–7. doi: 10.1590/S1678-77572011000500002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Whiting P, Savovic J, Higgins JP, Caldwell DM, Reeves BC, Shea B, et al. ROBIS: a new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;69:225–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.06.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ma IW, Khan NA, Kang A, Zalunardo N, Palepu A. Systematic review identified suboptimal reporting and use of race/ethnicity in general medical journals. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60:572–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Brugha TS, Matthews R, Morgan Z, Hill T, Alonso J, Jones DR. Methodology and reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies in psychiatric epidemiology: systematic review. Br J Psychiatry. 2012;200:446–53. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.111.098103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Kirkham J, Dwan K, Kramer S, Green S, et al. Bias due to selective inclusion and reporting of outcomes and analyses in systematic reviews of randomised trials of healthcare interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;10:MR000035. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000035.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Stevens A, Shamseer L, Weinstein E, Yazdi F, Turner L, Thielman J, et al. Relation of completeness of reporting of health research to journals’ endorsement of reporting guidelines: systematic review. BMJ. 2014;348:g3804. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g3804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Moher D, Altman DG, Schulz KF, Simera I. How to develop a reporting guideline. In: Moher D, Altman D, Schulz K, Simera I, Wager E, editors. Guidelines for reporting health research: a user's manual. Oxford: John Wiley & Sons; 2014. pp. 14–21. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. The original datasets used or analyzed are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


