Abstract
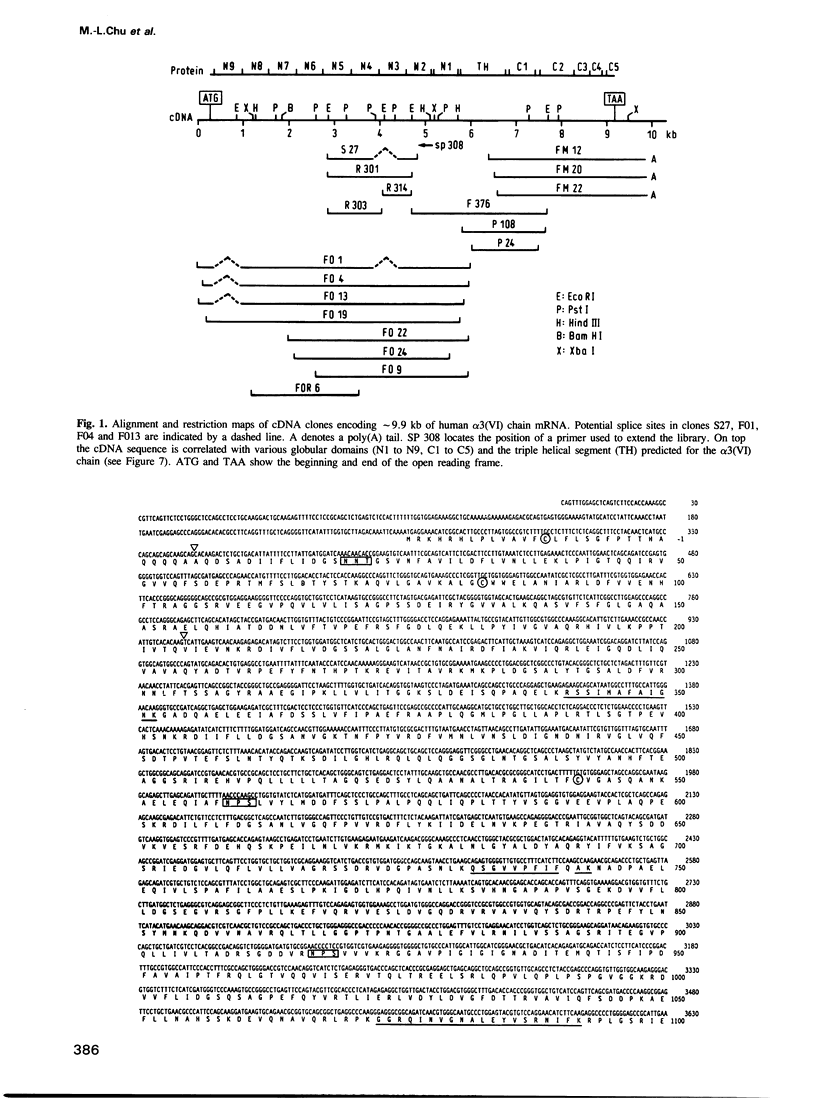
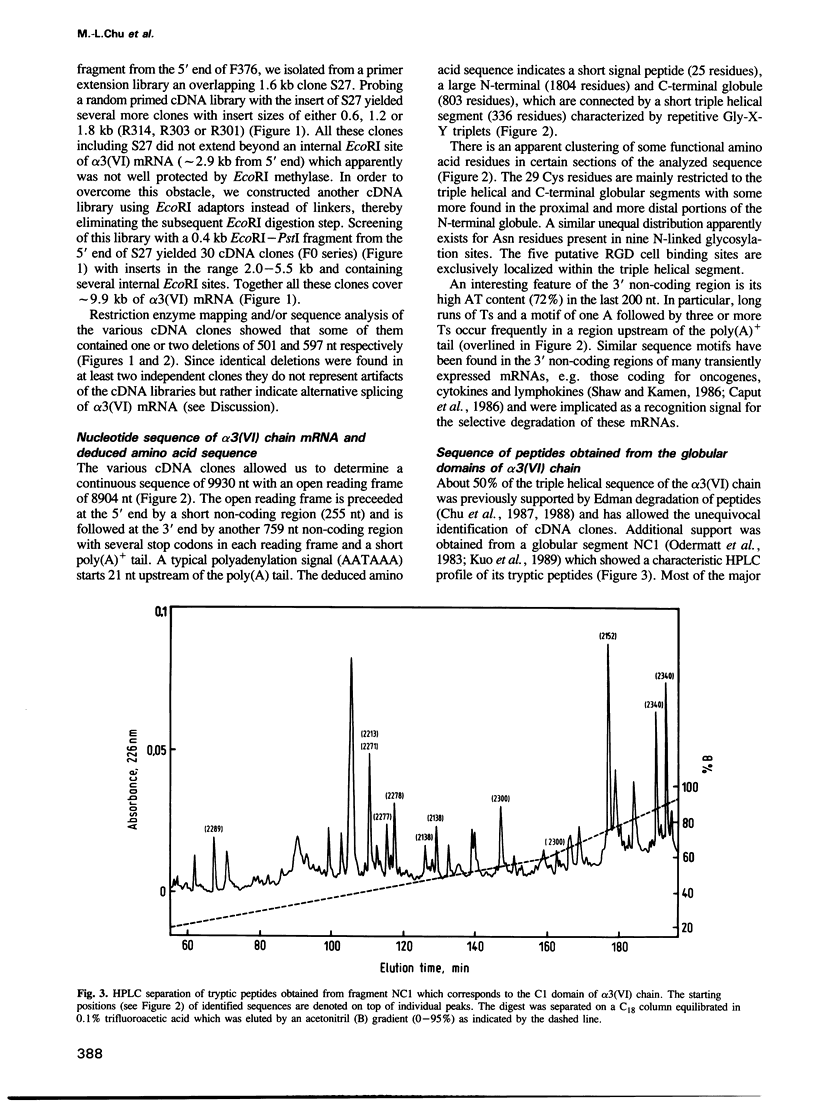
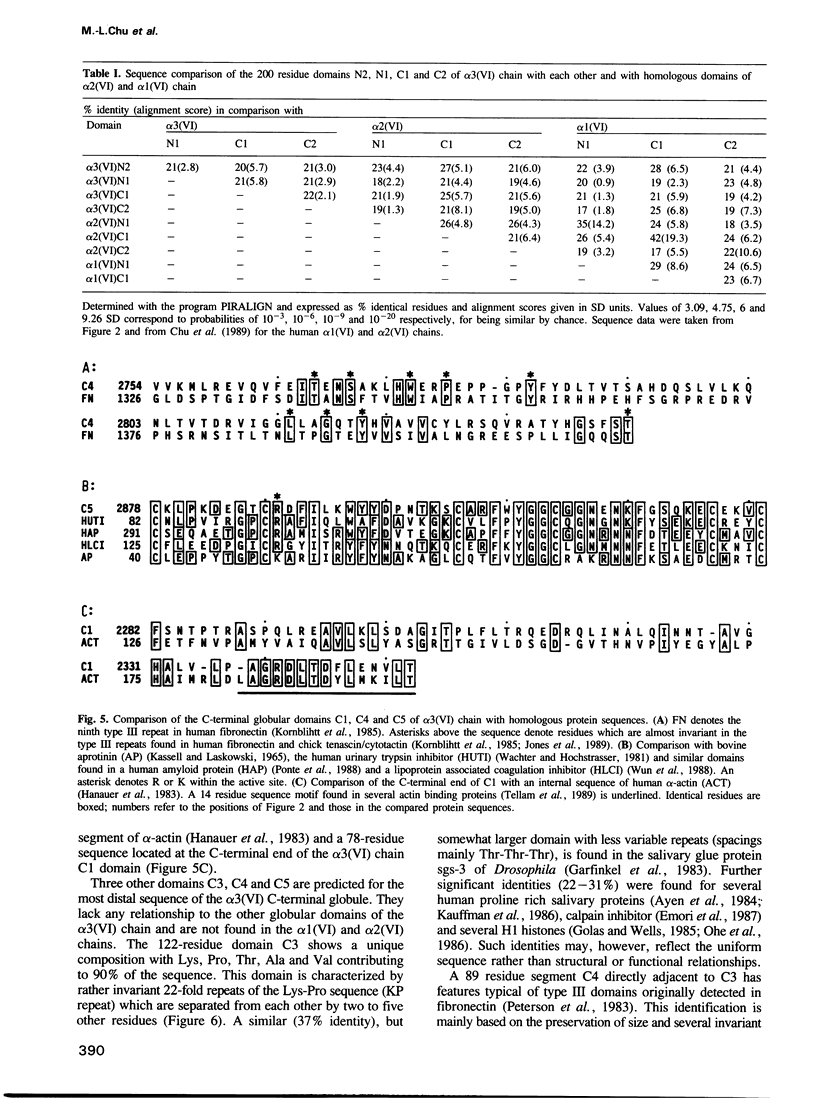
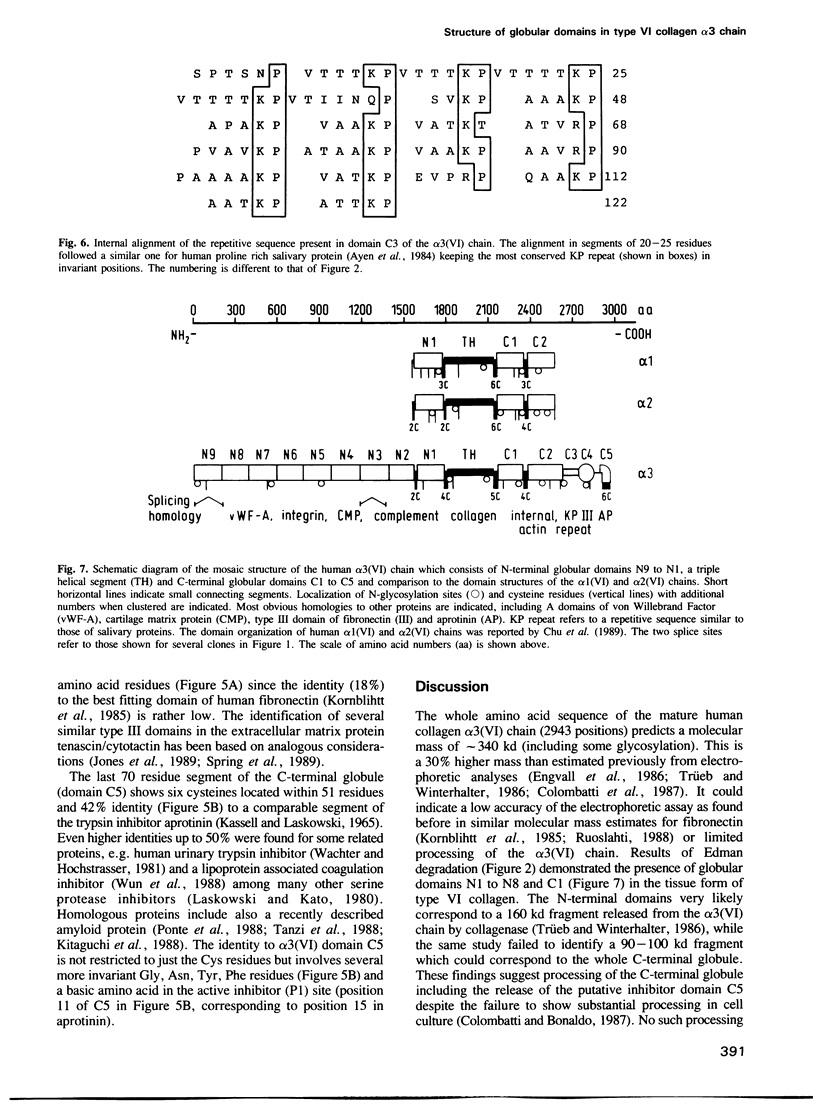
Human collagen alpha 3(VI) chain mRNA (approximately 10 kb) was cloned and shown by sequence analysis to encode a 25 residue signal peptide, a large N-terminal globule (1804 residues), a central triple helical segment (336 residues) and a C-terminal globule (803 residues). Some of the sequence was confirmed by Edman degradation of peptides. The N-terminal globular segment consists of nine consecutive 200 residue repeats (N1 to N9) showing internal homology and also significant identity (17-25%) to the A domains of von Willebrand Factor and similar domains present in some other proteins. Deletions were found in the N3 and N9 domains of several cDNA clones suggesting variation of these structures by alternative splicing. The C-terminal globule starts immediately after the triple helical segment with two domains C1 (184 residues) and C2 (248 residues) being similar to the N domains. They are followed by a proline rich, repetitive segment C3 of 122 residues, with similarity to some salivary proteins, and domain C4 (89 residues), which is similar to the type III repeats present in fibronectin and tenascin. The most C-terminal domain C5 (70 residues) shows 40-50% identity to a variety of serine protease inhibitors of the Kunitz type. The whole sequence contains 29 cysteines which are mainly clustered in short segments connecting domains N1, C1, C2 and the triple helix, and in the inhibitor domain. Five putative Arg-Gly-Asp cell-binding sequences are exclusively localized in the triple helical segment.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aumailley M., Mann K., von der Mark H., Timpl R. Cell attachment properties of collagen type VI and Arg-Gly-Asp dependent binding to its alpha 2(VI) and alpha 3(VI) chains. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Apr;181(2):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azen E., Lyons K. M., McGonigal T., Barrett N. L., Clements L. S., Maeda N., Vanin E. F., Carlson D. M., Smithies O. Clones from the human gene complex coding for salivary proline-rich proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5561–5565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckendorf S. K., Kafatos F. C. Differentiation in the salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of the glue proteins and their developmental appearance. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaldo P., Russo V., Bucciotti F., Bressan G. M., Colombatti A. Alpha 1 chain of chick type VI collagen. The complete cDNA sequence reveals a hybrid molecule made of one short collagen and three von Willebrand factor type A-like domains. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5575–5580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Conway D., Pan T. C., Baldwin C., Mann K., Deutzmann R., Timpl R. Amino acid sequence of the triple-helical domain of human collagen type VI. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18601–18606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Mann K., Deutzmann R., Pribula-Conway D., Hsu-Chen C. C., Bernard M. P., Timpl R. Characterization of three constituent chains of collagen type VI by peptide sequences and cDNA clones. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):309–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Pan T. C., Conway D., Kuo H. J., Glanville R. W., Timpl R., Mann K., Deutzmann R. Sequence analysis of alpha 1(VI) and alpha 2(VI) chains of human type VI collagen reveals internal triplication of globular domains similar to the A domains of von Willebrand factor and two alpha 2(VI) chain variants that differ in the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1939–1946. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles L. S., Wells J. R. An H1 histone gene-specific 5' element and evolution of H1 and H5 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):585–594. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombatti A., Bonaldo P., Ainger K., Bressan G. M., Volpin D. Biosynthesis of chick type VI collagen. I. Intracellular assembly and molecular structure. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14454–14460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombatti A., Bonaldo P. Biosynthesis of chick type VI collagen. II. Processing and secretion in fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14461–14466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Kawasaki H., Imajoh S., Imahori K., Suzuki K. Endogenous inhibitor for calcium-dependent cysteine protease contains four internal repeats that could be responsible for its multiple reactive sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3590–3594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Hessle H., Klier G. Molecular assembly, secretion, and matrix deposition of type VI collagen. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):703–710. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Odermatt E., Engel J. Electron-microscopical approach to a structural model of intima collagen. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):303–311. doi: 10.1042/bj2110303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel M. D., Pruitt R. E., Meyerowitz E. M. DNA sequences, gene regulation and modular protein evolution in the Drosophila 68C glue gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):765–789. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Levin M., Heilig R., Daegelen D., Kahn A., Mandel J. L. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human skeletal muscle alpha actin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3503–3516. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann M., Aumailley M., Hatamochi A., Chu M. L., Timpl R., Krieg T. Down-regulation of alpha 3(VI) chain expression by gamma-interferon decreases synthesis and deposition of collagen type VI. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 1;182(3):719–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jander R., Troyer D., Rauterberg J. A collagen-like glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix is the undegraded form of type VI collagen. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3675–3681. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. S., Hoffman S., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. A detailed structural model of cytotactin: protein homologies, alternative RNA splicing, and binding regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1905–1909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassell B., Laskowski M., Sr The basic trypsin inhibitor of bovine pancreas. V. The disulfide linkages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):463–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90601-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman D., Hofmann T., Bennick A., Keller P. Basic proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva: complete covalent structures of proteins IB-1 and IB-6. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2387–2392. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss I., Deák F., Holloway R. G., Jr, Delius H., Mebust K. A., Frimberger E., Argraves W. S., Tsonis P. A., Winterbottom N., Goetinck P. F. Structure of the gene for cartilage matrix protein, a modular protein of the extracellular matrix. Exon/intron organization, unusual splice sites, and relation to alpha chains of beta 2 integrins, von Willebrand factor, complement factors B and C2, and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8126–8134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller E., Winterhalter K. H., Trueb B. The globular domains of type VI collagen are related to the collagen-binding domains of cartilage matrix protein and von Willebrand factor. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1073–1077. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Larval saliva in Drosophila melanogaster: production, composition, and relationship to chromosome puffs. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):339–355. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Umezawa K., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Primary structure of human fibronectin: differential splicing may generate at least 10 polypeptides from a single gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1755–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo H. J., Keene D. R., Glanville R. W. Orientation of type VI collagen monomers in molecular aggregates. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3757–3762. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt E., Risteli J., van Delden V., Timpl R. Structural diversity and domain composition of a unique collagenous fragment (intima collagen) obtained from human placenta. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):295–302. doi: 10.1042/bj2110295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohe Y., Hayashi H., Iwai K. Human spleen histone H1. Isolation and amino acid sequence of a main variant, H1b. J Biochem. 1986 Aug;100(2):359–368. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen T. E., Thøgersen H. C., Skorstengaard K., Vibe-Pedersen K., Sahl P., Sottrup-Jensen L., Magnusson S. Partial primary structure of bovine plasma fibronectin: three types of internal homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring J., Beck K., Chiquet-Ehrismann R. Two contrary functions of tenascin: dissection of the active sites by recombinant tenascin fragments. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tellam R. L., Morton D. J., Clarke F. M. A common theme in the amino acid sequences of actin and many actin-binding proteins? Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Apr;14(4):130–133. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Kumar S., Takio K., Ericsson L. H., Wade R. D., Ashida K., Walsh K. A., Chopek M. W., Sadler J. E., Fujikawa K. Amino acid sequence of human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3171–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Walsh K. A. Human von Willebrand factor: the molecular glue of platelet plugs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Mar;13(3):94–97. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trüeb B., Winterhalter K. H. Type VI collagen is composed of a 200 kd subunit and two 140 kd subunits. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2815–2819. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter E., Hochstrasser K. Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitors derived by limited proteolysis of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor, IV. The amino acid sequence of the human urinary trypsin inhibitor isolated by affinity chromatography. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Oct;362(10):1351–1355. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.2.1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Mattei M. G., Passage E., N'Guyen V. C., Pribula-Conway D., Mann K., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Chu M. L. Cloning and chromosomal localization of human genes encoding the three chains of type VI collagen. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;42(3):435–445. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Kretzmer K. K., Girard T. J., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Cloning and characterization of a cDNA coding for the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor shows that it consists of three tandem Kunitz-type inhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6001–6004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark H., Aumailley M., Wick G., Fleischmajer R., Timpl R. Immunochemistry, genuine size and tissue localization of collagen VI. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;142(3):493–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


