Abstract
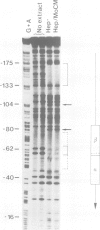
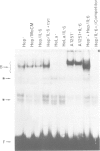
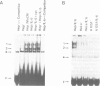
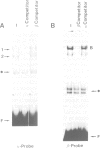
Transcription of the human C-reactive protein (CRP) gene is induced by interleukin-6 (IL-6) during acute inflammation. Important information for inducible CRP expression is located within the 90 bases preceding the transcriptional start site. We show that the CRP promoter contains two adjacent binding sites (beta and alpha) that interact with at least two hepatocyte-specific nuclear proteins, H-APF-1 and H-APF-2. Point mutations that abolish or reduce binding drastically affect the level of CRP gene expression. Binding to beta is identical when extracts from uninduced or IL-6-induced Hep3B cells are used. On the contrary, both quantitative and qualitative changes in the alpha binding can be detected with extracts from uninduced cells or from cells treated with IL-6 or IL-6 + cycloheximide. A synthetic promoter based on the multimerization of the beta-binding domain, but not of the alpha-domain, is highly inducible when transfected in hepatoma cells. These results are discussed in relation to the structure of the promoter region of other acute phase inducible genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcone R., Gualandi G., Ciliberto G. Identification of sequences responsible for acute-phase induction of human C-reactive protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3195–3207. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Onorato V., Gauldie J., Jahreis G. P. Distinct sets of acute phase plasma proteins are stimulated by separate human hepatocyte-stimulating factors and monokines in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9756–9768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Recombinant human interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2/HSF) regulates the synthesis of acute phase proteins in human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80766-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. R., Johnson T. R., Dollard C., Shuster J. R., Denis C. L. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates and inactivates the yeast transcriptional activator ADR1. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Arcone R., Wagner E. F., Rüther U. Inducible and tissue-specific expression of human C-reactive protein in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4017–4022. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E., Jr A liver-specific DNA-binding protein recognizes multiple nucleotide sites in regulatory regions of transthyretin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, albumin, and simian virus 40 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Wilson D. R., Lachman L. B. Monocyte-conditioned medium, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor stimulate the acute phase response in human hepatoma cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):787–793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Mullis N. T., Comeau C. M., Crabtree G. R. Potential basis for regulation of the coordinately expressed fibrinogen genes: homology in the 5' flanking regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2313–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., May L. T., Schultz D., Brabenec A., Weinstein J., Sehgal P. B., Kushner I. Role of interleukin-6 in regulating synthesis of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A in human hepatoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):271–277. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganter U., Arcone R., Toniatti C., Morrone G., Ciliberto G. Dual control of C-reactive protein gene expression by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3773–3779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring M. R., Shiels B. R., Northemann W., de Bruijn M. H., Kan C. C., Chain A. C., Noonan D. J., Fey G. H. Sequence of rat liver alpha 2-macroglobulin and acute phase control of its messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):446–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Yasukawa K., Harada H., Taga T., Watanabe Y., Matsuda T., Kashiwamura S., Nakajima K., Koyama K., Iwamatsu A. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):73–76. doi: 10.1038/324073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler W. K., Kovelman R., Roeder R. G. Activation of transcription factor IIIC by the adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):907–920. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Hirano T. Molecular regulation of B lymphocyte response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:485–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I. The phenomenon of the acute phase response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Bindereif A., Green M. R. A small-scale procedure for preparation of nuclear extracts that support efficient transcription and pre-mRNA splicing. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Mar-Apr;5(2):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrone G., Ciliberto G., Oliviero S., Arcone R., Dente L., Content J., Cortese R. Recombinant interleukin 6 regulates the transcriptional activation of a set of human acute phase genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12554–12558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene promoter: interleukin-6-responsive elements interact with a DNA-binding protein induced by interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Baumann H. Hepatocyte-stimulating factor, beta 2 interferon, and interleukin-1 enhance expression of the rat alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene via a distal upstream regulatory region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):42–51. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Dutta A., Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Phosphorylation of serum response factor, a factor that binds to the serum response element of the c-FOS enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7206–7210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Opdenakker G., Simpson R. J., Rubira M. R., Cayphas S., Vink A., Billiau A., Van Snick J. Identification of the human 26-kD protein, interferon beta 2 (IFN-beta 2), as a B cell hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor induced by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):914–919. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Ruggieri R., Korn J. H., Revel M. Structure and expression of cDNA and genes for human interferon-beta-2, a distinct species inducible by growth-stimulatory cytokines. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2529–2537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]