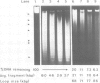
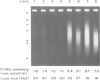
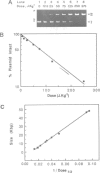
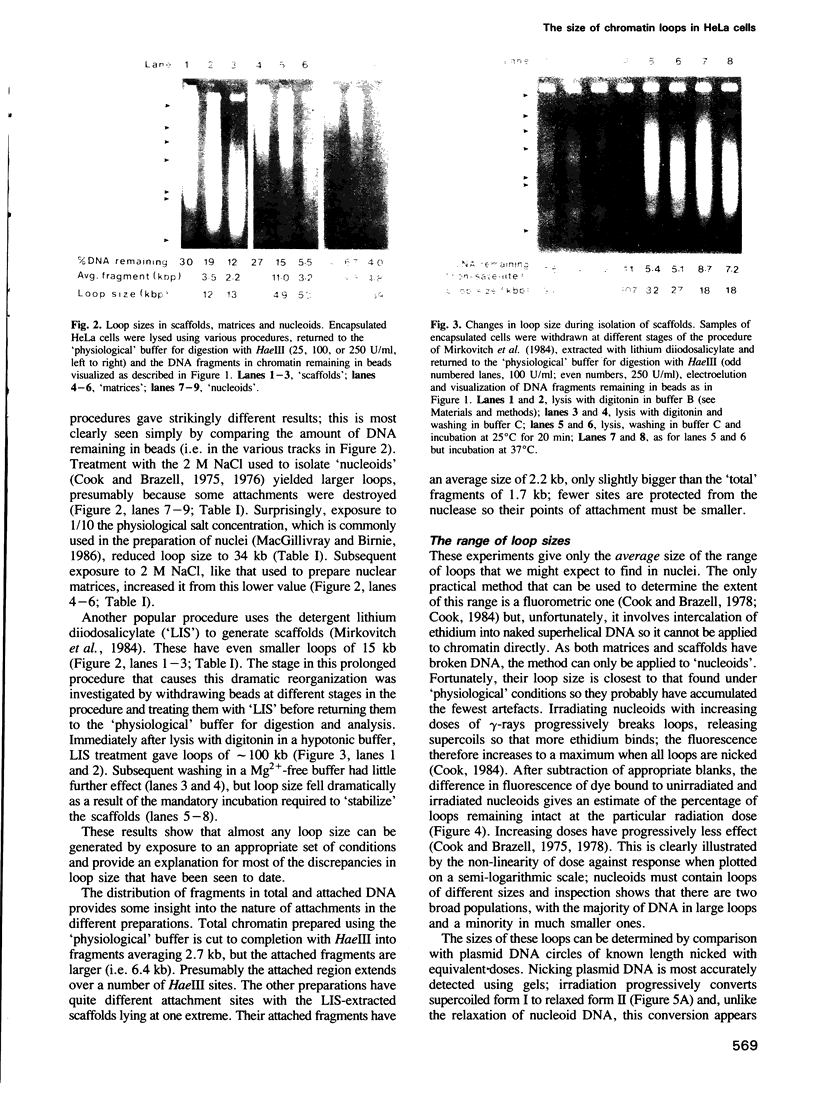
Abstract
It is widely believed that the chromatin fibre is organized into loops during interphase, with the loop being implicated as an important unit of nuclear function. However, there remains little direct evidence for looping, with estimates of loop size varying widely. This has led to the suggestion that some loops, or even all of them, arise artefactually during isolation as chromatin aggregates so easily. We have now investigated the effect of isolation procedure on loop size using HeLa cells encapsulated in agarose to allow easy manipulation. Loop size in various derivatives (i.e. nuclei, nucleoids, matrices and scaffolds) critically depended on procedure; some (or all) of their loops are artefacts. The loop size in derivatives isolated using the most 'physiological' conditions was 86 kb; this remained unchanged throughout the cell cycle. This loop size is probably an average of a range of loops of between 5 and 200 kb.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios S., Fisher P. A. Thermal stabilization of putative karyoskeletal protein-enriched fractions from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4573–4575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., McKenna G., Sharp P. A. Cleavage of mouse DNA by a restriction enzyme as a clue to the arrangement of genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:383–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G. The Croonian Lecture, 1981. Lampbrush chromosomes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Mar 22;214(1197):417–448. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. A general method for preparing intact nuclear DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1837–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Conformational constraints in nuclear DNA. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):287–302. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Mapping sequences in loops of nuclear DNA by their progressive detachment from the nuclear cage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2895–2906. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Spectrofluorometric measurement of the binding of ethidium to superhelical DNA from cell nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):465–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Supercoils in human DNA. J Cell Sci. 1975 Nov;19(2):261–279. doi: 10.1242/jcs.19.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Lang J., Hayday A., Lania L., Fried M., Chiswell D. J., Wyke J. A. Active viral genes in transformed cells lie close to the nuclear cage. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):447–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. The nucleoskeleton: artefact, passive framework or active site? J Cell Sci. 1988 May;90(Pt 1):1–6. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Hancock D. C. Studies on the interaction of the human c-myc protein with cell nuclei: p62c-myc as a member of a discrete subset of nuclear proteins. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igó-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Domains in chromatin structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):109–118. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. A cell-cycle-dependent DNA polymerase activity that replicates intact DNA in chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90464-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. A general method for preparing chromatin containing intact DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):913–918. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Replication occurs at a nucleoskeleton. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Transcription occurs at a nucleoskeleton. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):919–925. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Visualization of a filamentous nucleoskeleton with a 23 nm axial repeat. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3667–3677. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Yuan J., Cook P. R. A gentle method for preparing cyto- and nucleo-skeletons and associated chromatin. J Cell Sci. 1988 Jul;90(Pt 3):365–378. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood T. D., Hancock D. C., Evan G. I. Characterization of a heat shock-induced insoluble complex in the nuclei of cells. J Cell Sci. 1987 Aug;88(Pt 1):65–72. doi: 10.1242/jcs.88.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell M., Whalen A. M., Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Heat shock-induced changes in the structural stability of proteinaceous karyoskeletal elements in vitro and morphological effects in situ. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1087–1098. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Laemmli U. K. The structure of histone-depleted metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. I., Nelkin B. D., Vogelstein B. The ovalbumin gene is associated with the nuclear matrix of chicken oviduct cells. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen R., van Venrooij W., Ramaekers F. The nuclear matrix: structure and composition. J Cell Sci. 1988 May;90(Pt 1):11–36. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]