Abstract
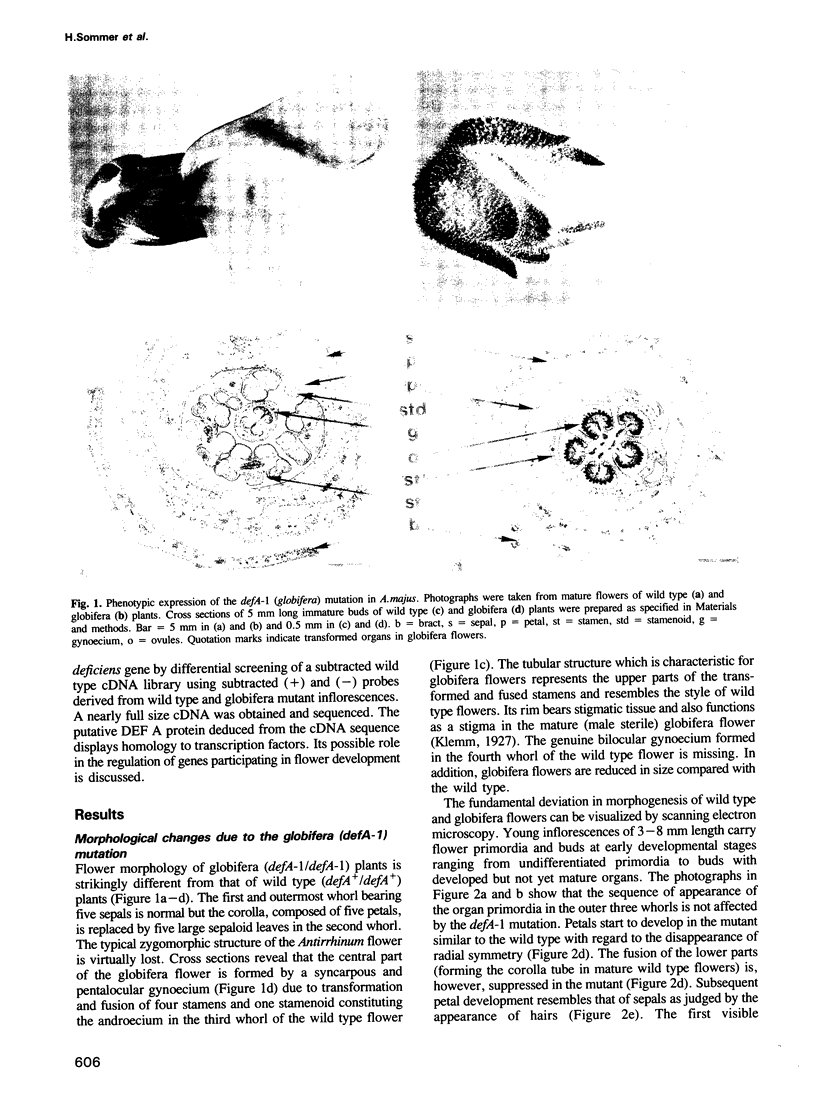
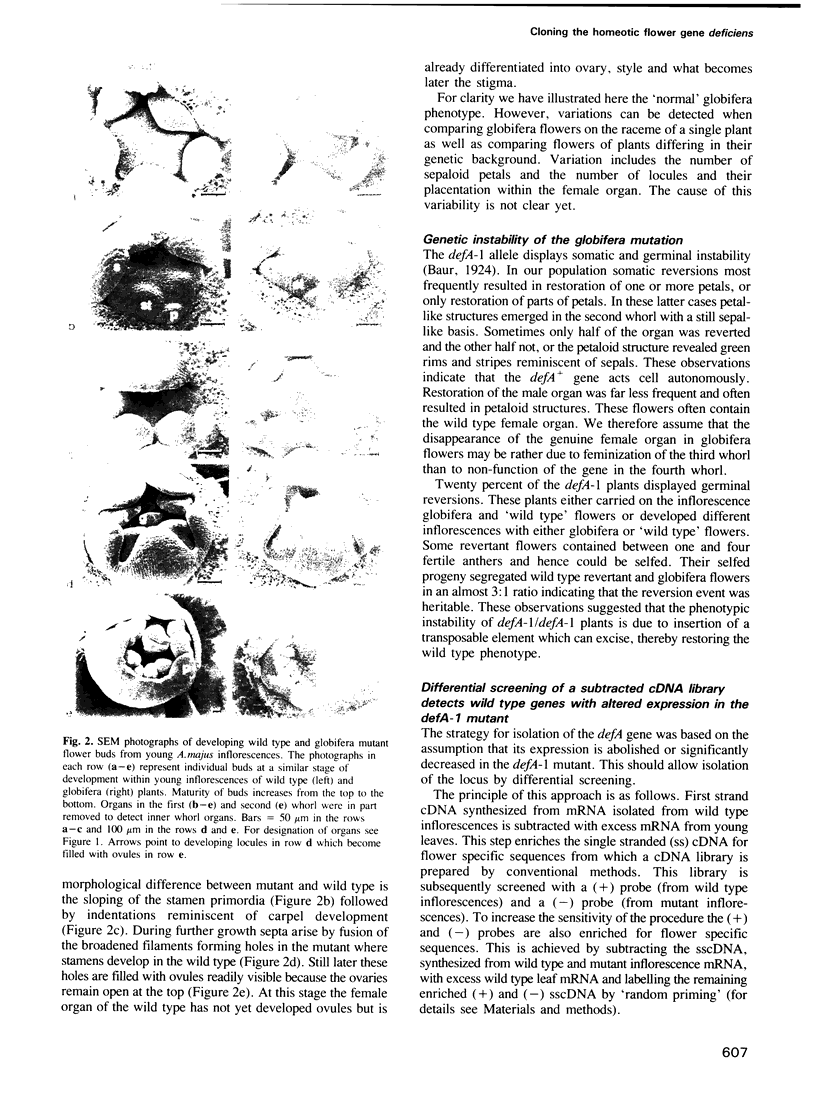
Deficiens (defA+) is a homeotic gene involved in the genetic control of Antirrhinum majus flower development. Mutation of this gene (defA-1) causes homeotic transformation of petals into sepals and of stamina into carpels in flowers displaying the 'globifera' phenotype, as shown by cross sections and scanning electronmicroscopy of developing flowers. A cDNA derived from the wild type defA+ gene has been cloned by differential screening of a subtracted 'flower specific' cDNA library. The identity of this cDNA with the defA+ gene product has been confirmed by utilizing the somatic and germinal instability of defA-1 mutants. According to Northern blot analyses the defA+ gene is expressed in flowers but not in leaves, and its expression is nearly constant during all stages of flower development. The 1.1 kb long mRNA has a 681 bp long open reading frame that can code for a putative protein of 227 amino acids (mol. wt 26.2 kd). At its N-terminus the DEF A protein reveals homology to a conserved domain of the regulatory proteins SRF (activating c-fos) in mammals and GRM/PRTF (regulating mating type) in yeast. We discuss the structure and the possible function of the DEF A protein in the control of floral organogenesis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr MAT alpha 1 protein, a yeast transcription activator, binds synergistically with a second protein to a set of cell-type-specific genes. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman J. L., Smyth D. R., Meyerowitz E. M. Genes directing flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):37–52. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline T. W. The affairs of daughterless and the promiscuity of developmental regulators. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Protein phosphorylation and hormone action. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 22;234(1275):115–144. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Bercy J., Descamps F., Messenguy F. Characterization of two new genes essential for vegetative growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence determination and chromosome mapping. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90286-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Bercy J., Messenguy F. Characterization of two genes, ARGRI and ARGRIII required for specific regulation of arginine metabolism in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):142–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00331501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Hiromi Y. Homeotic genes and the homeobox. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:147–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Hull R., Hull S., Falkow S., Freter R., Svanborg Edén C. Contribution of adhesion to bacterial persistence in the mouse urinary tract. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):265–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.265-272.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. The molecular genetics of embryonic pattern formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):25–34. doi: 10.1038/335025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis E. E., Clark K. L., Sprague G. F., Jr The yeast transcription activator PRTF, a homolog of the mammalian serum response factor, is encoded by the MCM1 gene. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):936–945. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Goutte C., Johnson A. D. The yeast cell-type-specific repressor alpha 2 acts cooperatively with a non-cell-type-specific protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J., Schell J., Willmitzer L. Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Elble R., Tye B. K. A protein involved in minichromosome maintenance in yeast binds a transcriptional enhancer conserved in eukaryotes. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):921–935. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Maine G. T., Elble R., Christ C., Tye B. K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in plasmid maintenance is necessary for mating of MAT alpha cells. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D. Isolation of differentially expressed genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:423–432. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Carroll S. B. The segmentation and homeotic gene network in early Drosophila development. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):689–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussex I. M. Developmental programming of the shoot meristem. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90895-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]