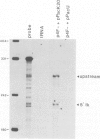
Abstract
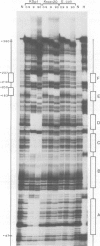
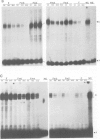
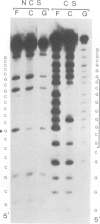
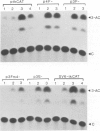
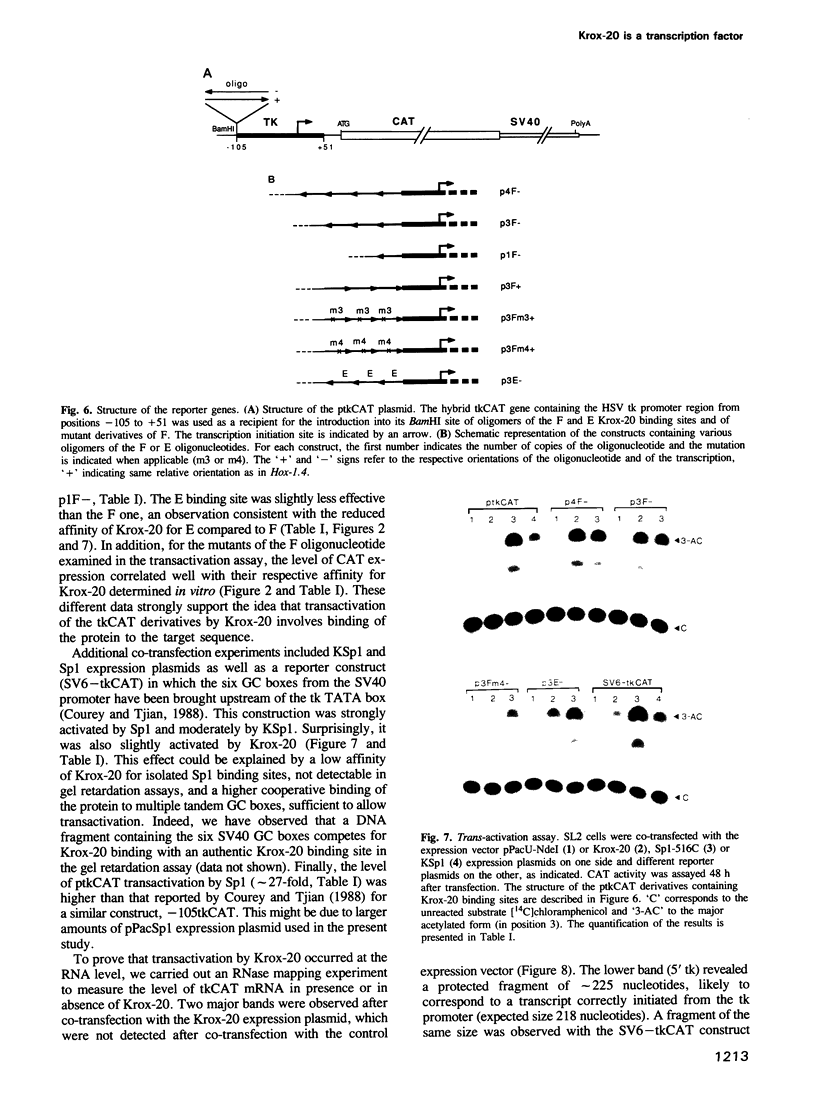
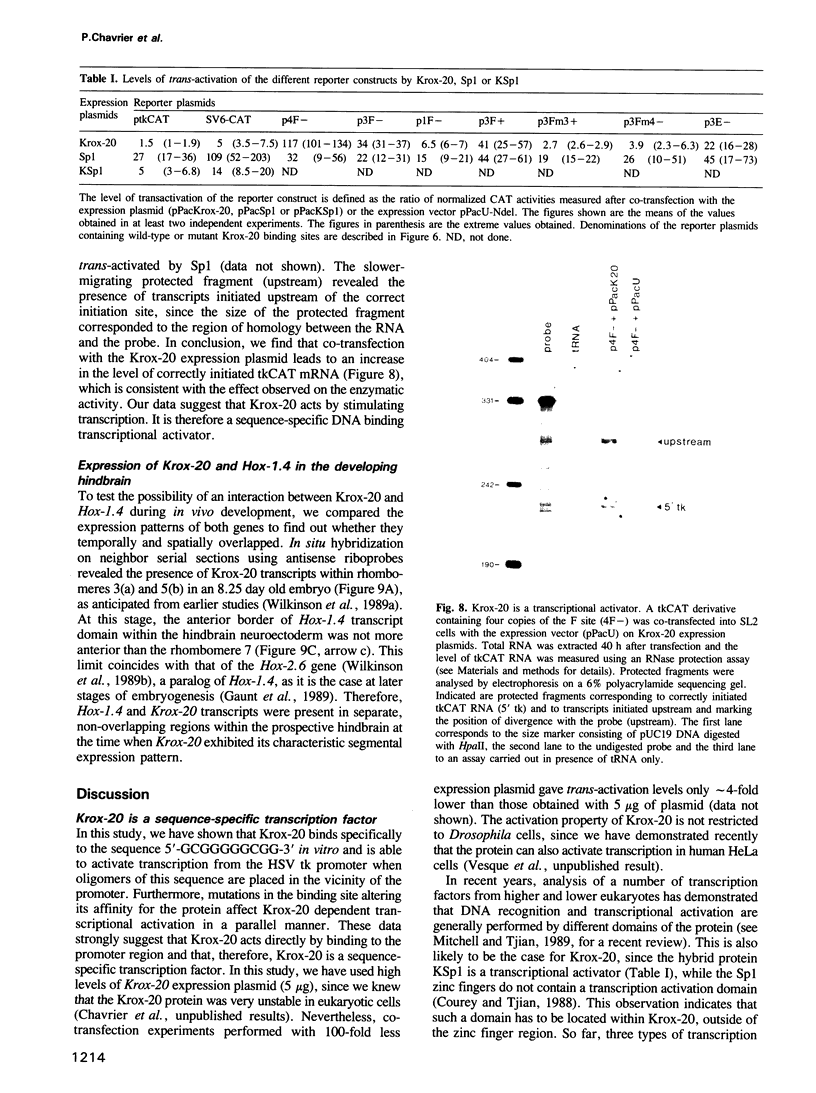
Krox-20 is a mouse zinc finger gene expressed in a segment-specific manner in the early central nervous system, which makes it a potential developmental control gene. In this report, we show that the Krox-20 protein binds in vitro to two specific DNA sites located upstream from the homeobox containing gene Hox-1.4. The nucleotide sequence recognized by Krox-20 is closely related to the Sp1 target sequence, which is consistent with the similarity existing between the zinc fingers of the two proteins. In co-transfection experiments in cultured cells, Krox-20 dramatically activates transcription from the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase promoter when an oligomer of its binding site is present in cis close to the promoter. Analysis of mutated binding sites demonstrates that the level of activation by Krox-20 correlates with the affinity of the protein for the mutant sequence. These data indicate that Krox-20 constitutes a sequence-specific DNA-binding transcription factor. Parallel analysis of the expression of Krox-20 and Hox-1.4 in the neural tube by in situ hybridization revealed no overlap, arguing against direct interactions between these two genes. The possible involvement of Krox-20 in the regulation of the transcription of other homeobox genes is discussed in view of their respective patterns of expression.
Full text
PDF
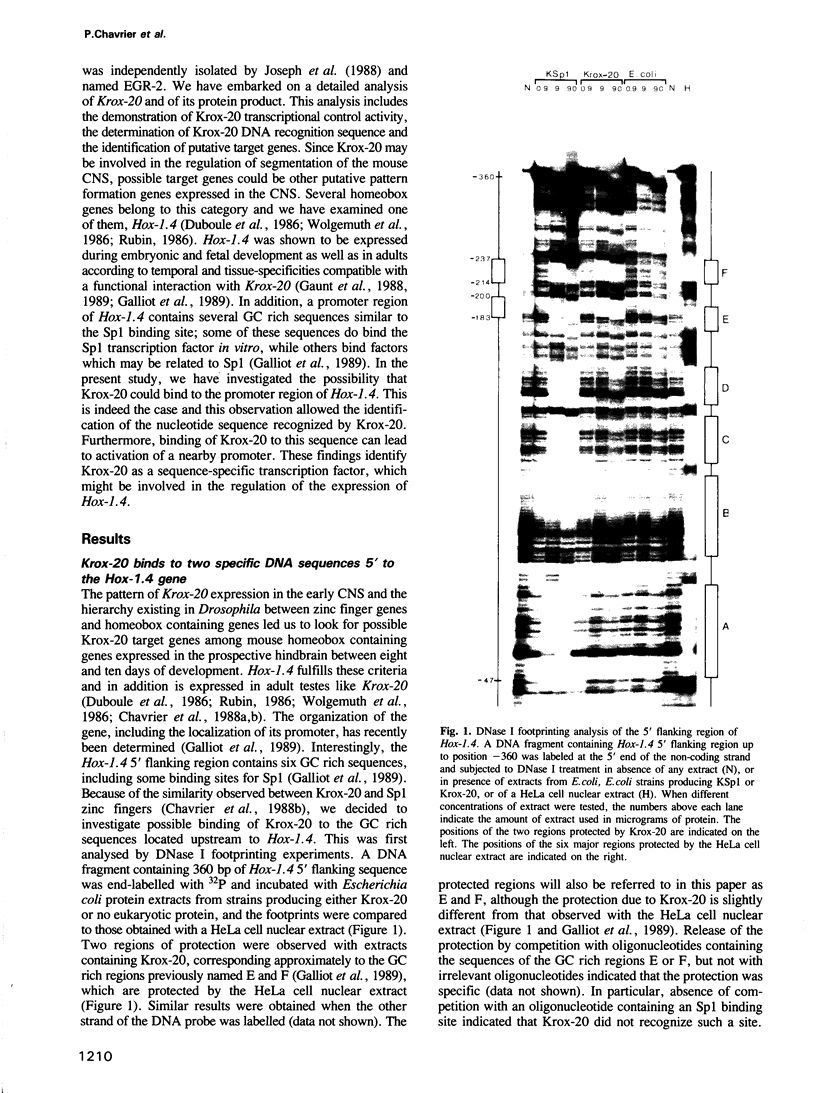
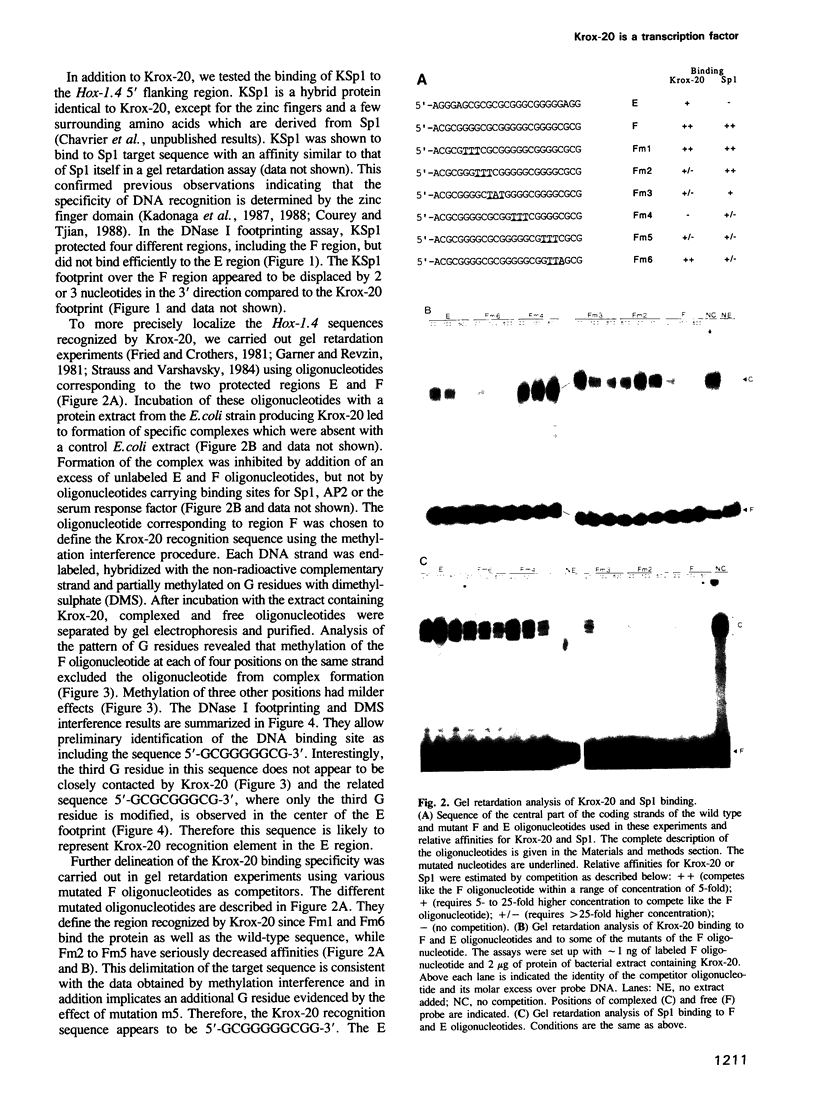





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerblom I. E., Slater E. P., Beato M., Baxter J. D., Mellon P. L. Negative regulation by glucocorticoids through interference with a cAMP responsive enhancer. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):350–353. doi: 10.1126/science.2838908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):99–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Janssen-Timmen U., Mattéi M. G., Zerial M., Bravo R., Charnay P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the mouse zinc finger gene Krox-20: multiple gene products and coregulation with the proto-oncogene c-fos. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):787–797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Characterization of a mouse multigene family that encodes zinc finger structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1319–1326. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Zerial M., Lemaire P., Almendral J., Bravo R., Charnay P. A gene encoding a protein with zinc fingers is activated during G0/G1 transition in cultured cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Deutsch U., Gruss P. A multigene family encoding several "finger" structures is present and differentially active in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):771–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Dressler G., Breier G., Deutsch U., Gruss P. The primary structure of the murine multifinger gene mKr2 and its specific expression in developing and adult neurons. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B. A., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated in mouse 3T3 cells by serum growth factors encodes a protein with "zinc finger" sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7857–7861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Duboule D. Two gene members of the murine HOX-5 complex show regional and cell-type specific expression in developing limbs and gonads. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1507–1515. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D., Baron A., Mähl P., Galliot B. A new homeo-box is present in overlapping cosmid clones which define the mouse Hox-1 locus. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D., Dollé P. The structural and functional organization of the murine HOX gene family resembles that of Drosophila homeotic genes. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1497–1505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galliot B., Dollé P., Vigneron M., Featherstone M. S., Baron A., Duboule D. The mouse Hox-1.4 gene: primary structure, evidence for promoter activity and expression during development. Development. 1989 Oct;107(2):343–359. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.2.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J., Krumlauf R., Duboule D. Mouse homeo-genes within a subfamily, Hox-1.4, -2.6 and -5.1, display similar anteroposterior domains of expression in the embryo, but show stage- and tissue-dependent differences in their regulation. Development. 1989 Sep;107(1):131–141. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J., Miller J. R., Powell D. J., Duboule D. Homoeobox gene expression in mouse embryos varies with position by the primitive streak stage. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):662–664. doi: 10.1038/324662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Postma J. P., Brown R. S., Argos P. A model for the tertiary structure of the 28 residue DNA-binding motif ('zinc finger') common to many eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Protein Eng. 1988 Sep;2(3):209–218. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. The molecular genetics of embryonic pattern formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):25–34. doi: 10.1038/335025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph L. J., Le Beau M. M., Jamieson G. A., Jr, Acharya S., Shows T. B., Rowley J. D., Sukhatme V. P. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and mapping of EGR2, a human early growth response gene encoding a protein with "zinc-binding finger" structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Courey A. J., Ladika J., Tjian R. Distinct regions of Sp1 modulate DNA binding and transcriptional activation. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1566–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.3059495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köster M., Pieler T., Pöting A., Knöchel W. The finger motif defines a multigene family represented in the maternal mRNA of Xenopus laevis oocytes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1735–1741. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Gippert G. P., Soman K. V., Case D. A., Wright P. E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):635–637. doi: 10.1126/science.2503871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Two mouse genes encoding potential transcription factors with identical DNA-binding domains are activated by growth factors in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4691–4695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hoey T. Homeobox proteins as sequence-specific transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Garber R. L., Wirz J., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. A homologous protein-coding sequence in Drosophila homeotic genes and its conservation in other metazoans. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that define a small region sufficient for enhancer activation. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.3563519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):797–799. doi: 10.1126/science.3672127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita K., Parker D. S., Mucenski M. L., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Ihle J. N. Retroviral activation of a novel gene encoding a zinc finger protein in IL-3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P., Davidson D. R., Hill R. E. Segment-specific expression of a homoeobox-containing gene in the mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):156–159. doi: 10.1038/341156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. R., Toth L. E., Patel M. D., D'Eustachio P., Nguyen-Huu M. C. A mouse homeo box gene is expressed in spermatocytes and embryos. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):663–667. doi: 10.1126/science.3726554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert J. M., Kinzler K. W., Wong A. J., Bigner S. H., Kao F. T., Law M. L., Seuanez H. N., O'Brien S. J., Vogelstein B. The GLI-Kruppel family of human genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3104–3113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The DNA-binding domains of the jun oncoprotein and the yeast GCN4 transcriptional activator protein are functionally homologous. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):841–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Cao X. M., Chang L. C., Tsai-Morris C. H., Stamenkovich D., Ferreira P. C., Cohen D. R., Edwards S. A., Shows T. B., Curran T. A zinc finger-encoding gene coregulated with c-fos during growth and differentiation, and after cellular depolarization. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Chavrier P., Bravo R., Charnay P. Segment-specific expression of a zinc-finger gene in the developing nervous system of the mouse. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):461–464. doi: 10.1038/337461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Cook M., Boncinelli E., Krumlauf R. Segmental expression of Hox-2 homoeobox-containing genes in the developing mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):405–409. doi: 10.1038/341405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Engelmyer E., Duggal R. N., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Mutter G. L., Ponzetto C., Viviano C., Zakeri Z. F. Isolation of a mouse cDNA coding for a developmentally regulated, testis-specific transcript containing homeo box homology. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1229–1235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Viviano C. M., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Frohman M. A., Joyner A. L., Martin G. R. Differential expression of the mouse homeobox-containing gene Hox-1.4 during male germ cell differentiation and embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5813–5817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]