Abstract
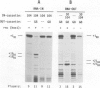
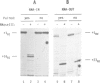
RNA stability is an important component of gene expression, and antisense RNAs have been proposed to alter target RNA stability. We show here that the IS10 transposase mRNA, RNA-IN, is rendered unstable during control by the IS10 antisense RNA, RNA-OUT. Destabilization requires RNA-OUT/RNA-IN pairing and ribonuclease III cleavage. Independent of such cleavage, RNA-OUT is rendered unstable through disruption of its secondary structure. Pairing has no other obvious effects on RNA-IN transcription or stability. Nevertheless, RNA-IN destabilization is not required for antisense control in vivo. In the accompanying paper [Ma,C. and Simons, R.W. (1990) EMBO J., 9, 1267-1274 we show that pairing blocks ribosome binding to RNA-IN. Were it not for control at this level, destabilization would play a more prominent role.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belasco J. G., Higgins C. F. Mechanisms of mRNA decay in bacteria: a perspective. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case C. C., Roels S. M., González J. E., Simons E. L., Simons R. W. Analysis of the promoters and transcripts involved in IS10 anti-sense RNA control. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):219–236. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case C. C., Roels S. M., Jensen P. D., Lee J., Kleckner N., Simons R. W. The unusual stability of the IS10 anti-sense RNA is critical for its function and is determined by the structure of its stem-domain. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4297–4305. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D. L., Subbarao M. N., Blattner F. R., Lozeron H. A. Q-mediated late gene transcription of bacteriophage lambda: RNA start point and RNase III processing sites in vivo. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):568–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey W. B. Transcript analysis of the plasmid R100 traJ and finP genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):533–544. doi: 10.1007/BF00331160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Frost L. S., Paranchych W., Willetts N. S. Nucleotide sequences of five IncF plasmid finP alleles. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):754–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.754-757.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Lundblad V., Hanley-Way S., Halling S. M., Kleckner N. Three Tn10-associated excision events: relationship to transposition and role of direct and inverted repeats. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarneros G. Retroregulation of bacteriophage lambda int gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;136:1–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-73115-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Simons R. W., Way J. C., Walsh R. B., Kleckner N. DNA sequence organization of IS10-right of Tn10 and comparison with IS10-left. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2608–2612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Meyer R. J. Copy-number of broad host-range plasmid R1162 is regulated by a small RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8027–8046. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Sirdeskmukh R., Schlessinger D. Nucleolytic processing of ribonucleic acid transcripts in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):428–451. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.428-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittle J. D., Simons R. W., Lee J., Kleckner N. Insertion sequence IS10 anti-sense pairing initiates by an interaction between the 5' end of the target RNA and a loop in the anti-sense RNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinke L., Wulff D. L. OOP RNA, produced from multicopy plasmids, inhibits lambda cII gene expression through an RNase III-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):1005–1013. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. M., Wu T. H., Chiang C. H., Susskind M. M., McClure W. R. Control of gene expression in bacteriophage P22 by a small antisense RNA. I. Characterization in vitro of the Psar promoter and the sar RNA transcript. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):197–203. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C., Simons R. W. The IS10 antisense RNA blocks ribosome binding at the transposase translation initiation site. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1267–1274. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A unique mechanism regulating gene expression: translational inhibition by a complementary RNA transcript (micRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1966–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Iordanescu S., Projan S. J., Kornblum J., Edelman I. pT181 plasmid replication is regulated by a countertranscript-driven transcriptional attenuator. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D., Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R., Kleckner N. IS10 transposition is regulated by DNA adenine methylation. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D. Escherichia coli ribonuclease III cleavage sites. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):669–672. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schollmeier K., Hillen W. Transposon Tn10 contains two structural genes with opposite polarity between tetA and IS10R. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):499–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.499-503.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Blume J. E., Nielsen D. A. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in eukaryotic cells. Bioessays. 1987 May;6(5):221–226. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R., Kleckner N. Three promoters near the termini of IS10: pIN, pOUT, and pIII. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Biological regulation by antisense RNA in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:567–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W. Naturally occurring antisense RNA control--a brief review. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiff H. E., Chen S. M., Court D. L. Genetic analysis of the rnc operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2581–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2581-2590.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. H., Liao S. M., McClure W. R., Susskind M. M. Control of gene expression in bacteriophage P22 by a small antisense RNA. II. Characterization of mutants defective in repression. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):204–212. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]