Abstract
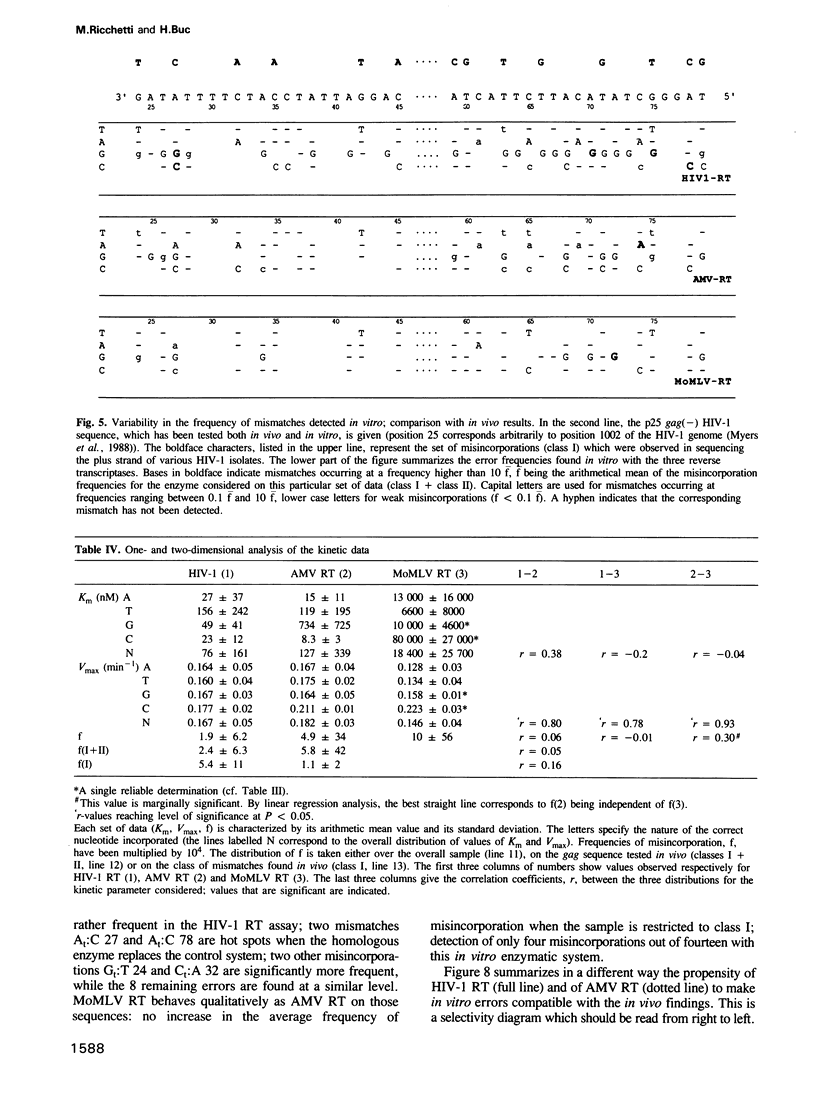
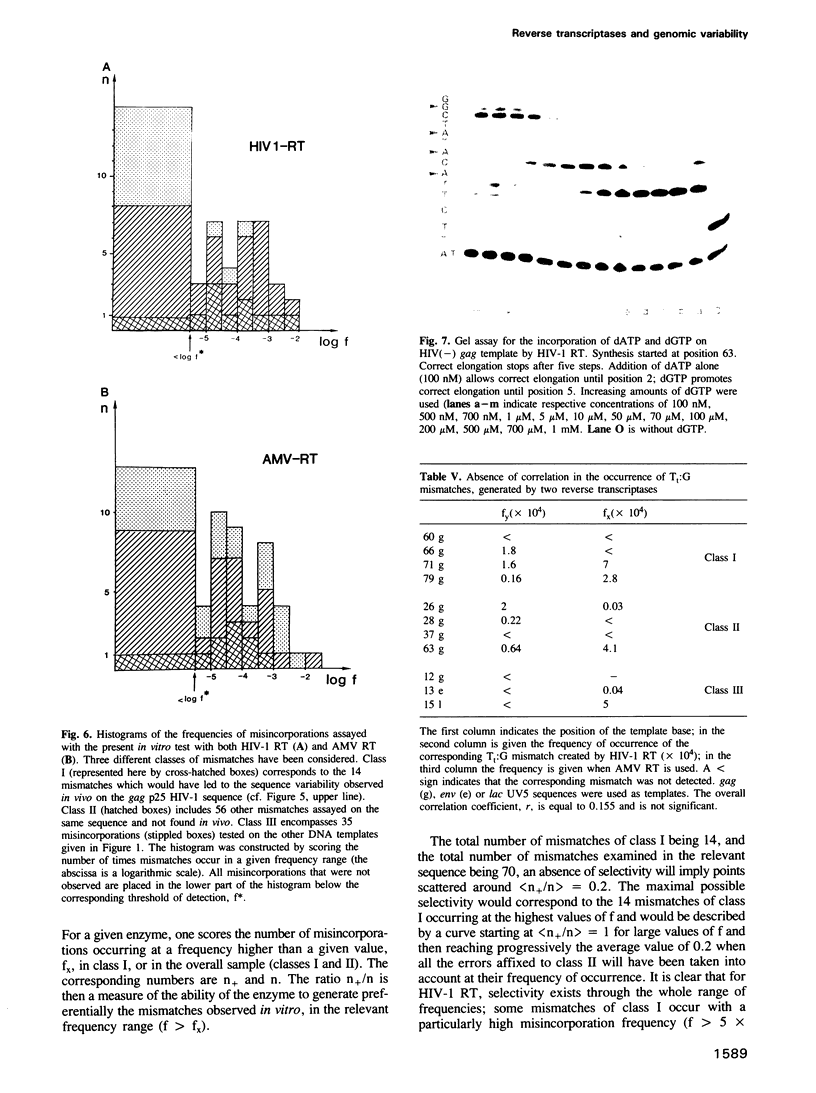
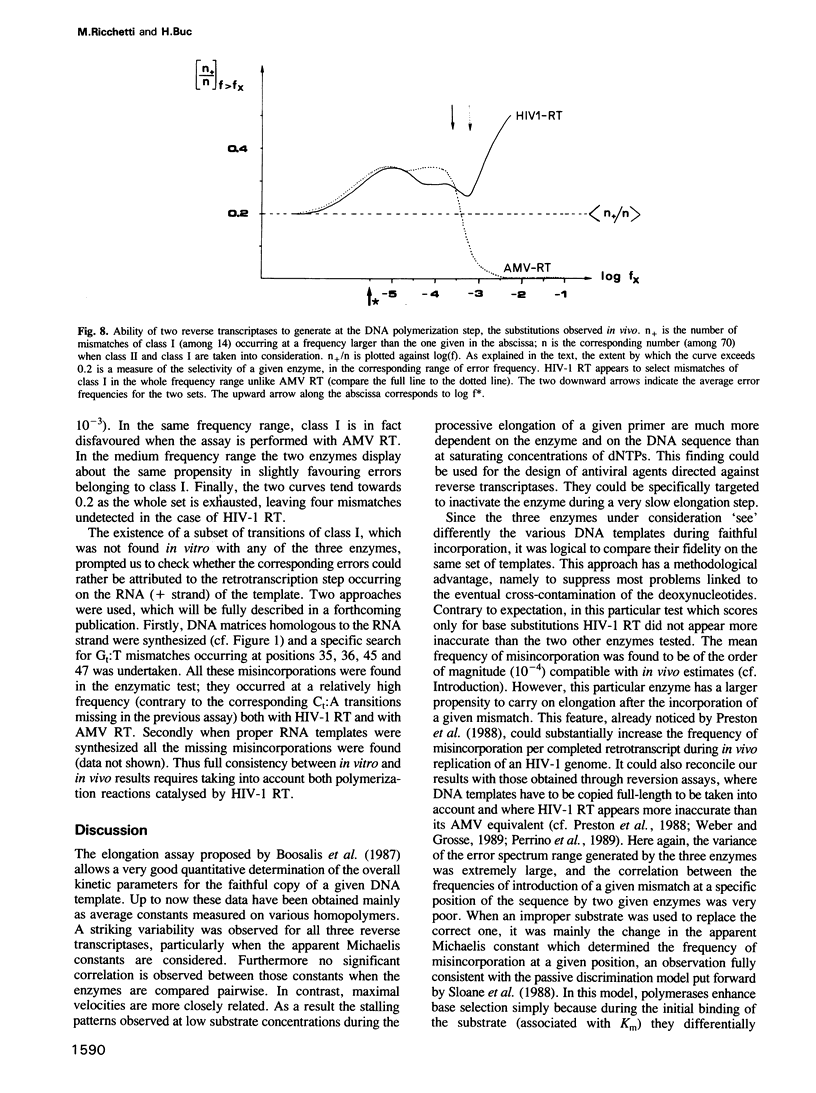
Kinetics of incorporation of correct and incorrect deoxynucleotides by three reverse transcriptases have been followed, by gel assay, on a series of DNA templates, including part of the HIV-1 gag DNA minus strand. Insertion kinetics for the properly matched nucleotide at a given place on the template vary strongly from one enzyme to the next. No significant correlation is found between the site-specific Michaelis constants, while the maximal velocities are more closely connected. For a given reverse transcriptase these parameters are strongly influenced by the DNA sequence. A systematic evaluation of the frequencies of misincorporation was then performed at 46 positions. Again great variability was found, precluding a very accurate evaluation of an average misincorporation frequency for a given enzyme and a given mismatch. Qualitatively however, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is certainly not more error-prone in this assay than the other enzymes assayed. The patterns of misincorporations were again very dependent on the enzyme used to replicate a given template. The variability of the gag sequence observed in vivo among various HIV-1 isolates was compared with the patterns of misincorporations obtained in vitro on the same sequence with HIV-1, AMV and MoMLV reverse transcriptases. A fair agreement was found with the pattern observed in the polymerization directed by the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. The correlation is less important in the two other cases. However some specific changes observed in vivo cannot be accounted for by our misincorporation assay, even when performed with the homologous enzyme, suggesting that an important class of mismatches can only be generated during reverse transcription of the RNA strand. Additional data, using a complementary DNA (positive) strand as a gag template support this hypothesis.
Full text
PDF
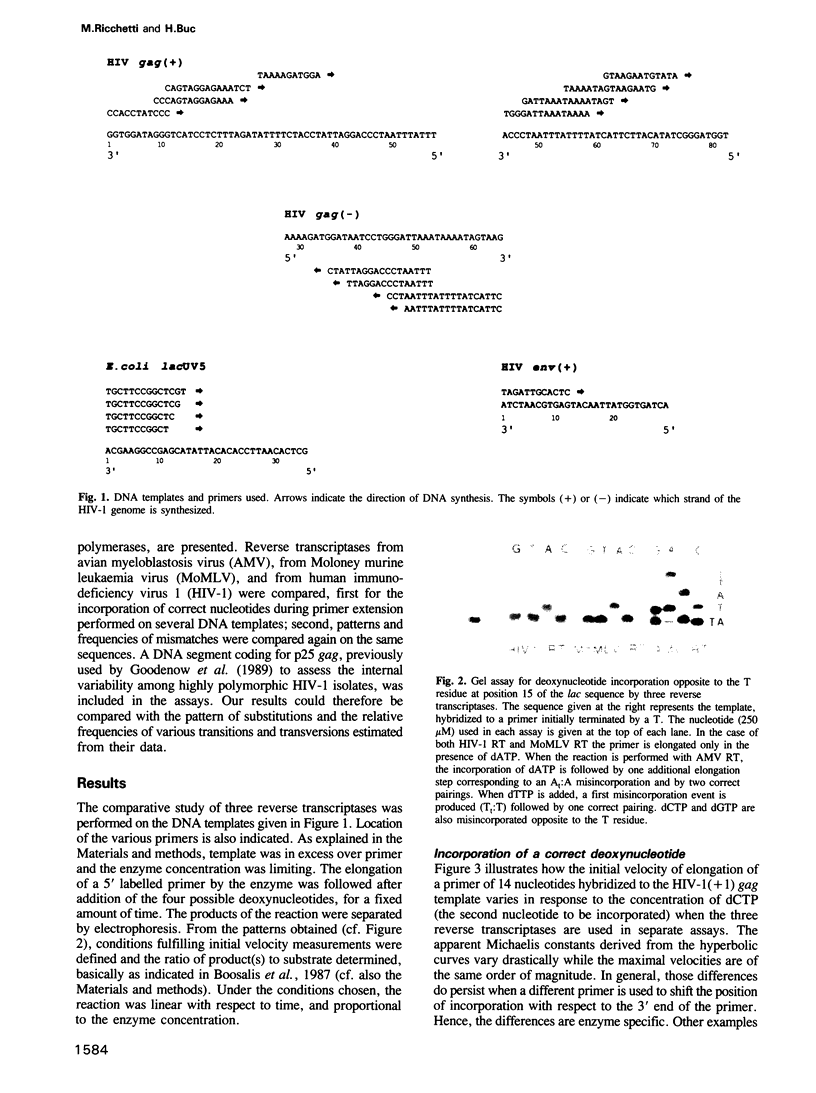

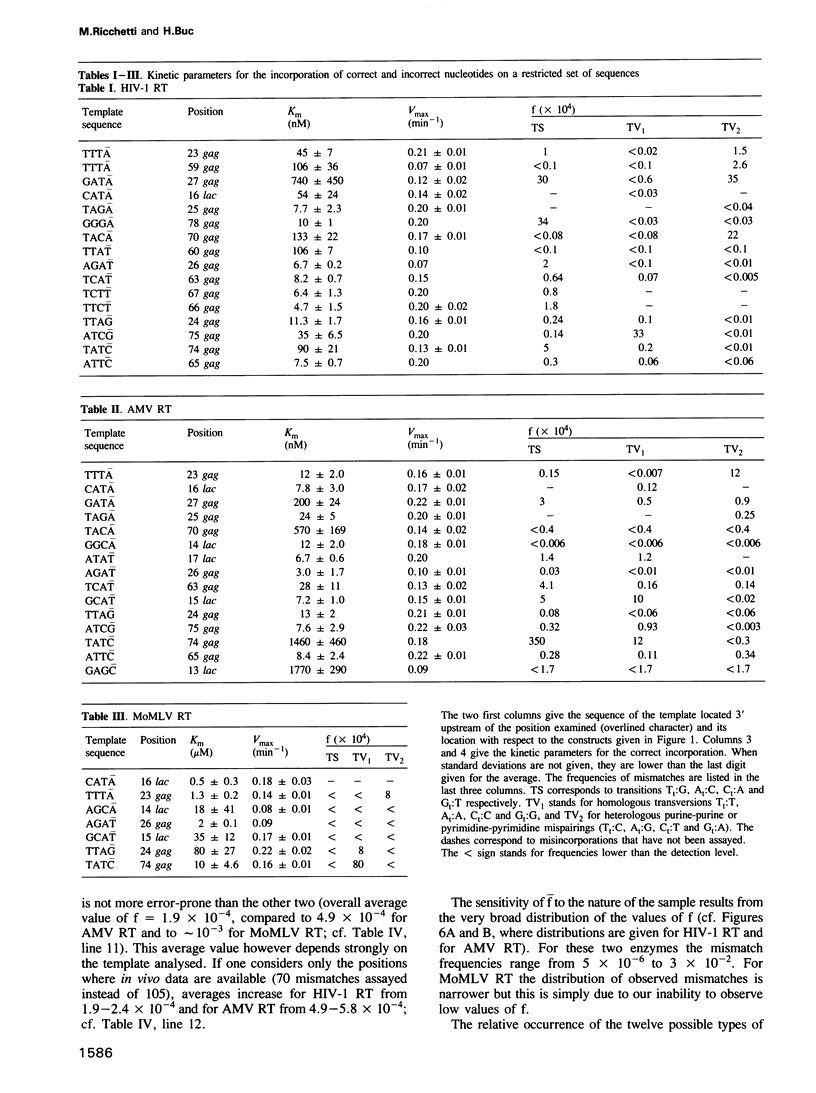




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battula N., Loeb L. A. The infidelity of avian myeloblastosis virus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase in polynucleotide replication. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4086–4093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Abbotts J., Roberts J. D., Wilson S. H., Kunkel T. A. Specificity and mechanism of error-prone replication by human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16948–16956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boosalis M. S., Petruska J., Goodman M. F. DNA polymerase insertion fidelity. Gel assay for site-specific kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14689–14696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bougueleret L., Tekaia F., Sauvaget I., Claverie J. M. Objective comparison of exon and intron sequences by means of 2-dimensional data analysis methods. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1729–1738. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. Genetic variation in AIDS viruses. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90851-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Tsichlis P. N., Barker C. S., Voynow S., Robinson H. L. Variation in avian retrovirus genomes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:410–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Temin H. M. Determination of the rate of base-pair substitution and insertion mutations in retrovirus replication. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2817–2822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2817-2822.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gojobori T., Yokoyama S. Rates of evolution of the retroviral oncogene of Moloney murine sarcoma virus and of its cellular homologues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4198–4201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow M., Huet T., Saurin W., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Wain-Hobson S. HIV-1 isolates are rapidly evolving quasispecies: evidence for viral mixtures and preferred nucleotide substitutions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):344–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Moelling K. RNase H activity associated with bacterially expressed reverse transcriptase of human T-cell lymphotropic virus III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., McGill C., Hughes S. H. Expression of soluble, enzymatically active, human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli and analysis of mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1218–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Will H. Molecular biology of viral and nonviral retroelements. Trends Genet. 1989 Nov;5(11):357–359. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Alexander P. S. The base substitution fidelity of eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Mispairing frequencies, site preferences, insertion preferences, and base substitution by dislocation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leider J. M., Palese P., Smith F. I. Determination of the mutation rate of a retrovirus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3084–3091. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3084-3091.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelman L. V., Boosalis M. S., Petruska J., Goodman M. F. Nearest neighbor influences on DNA polymerase insertion fidelity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14415–14423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrino F. W., Preston B. D., Sandell L. L., Loeb L. A. Extension of mismatched 3' termini of DNA is a major determinant of the infidelity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8343–8347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. D., Poiesz B. J., Loeb L. A. Fidelity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1168–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.2460924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Bebenek K., Kunkel T. A. The accuracy of reverse transcriptase from HIV-1. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1171–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.2460925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogerson A. C. The sequence asymmetry of the Escherichia coli chromosome appears to be independent of strand or function and may be evolutionarily conserved. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5547–5563. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloane D. L., Goodman M. F., Echols H. The fidelity of base selection by the polymerase subunit of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6465–6475. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer D. A., Holland J. J. Rapid evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:409–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Grosse F. Fidelity of human immunodeficiency virus type I reverse transcriptase in copying natural DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1379–1393. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]