Abstract
The cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S enhancer is able to confer strong constitutive expression in plants. We have previously defined two domains within this enhancer that can confer different tissue-specific expression patterns throughout development. We show here that the upstream domain (B) has a modular organization. It contains at least five subdomains that are able to confer distinct expression patterns when fused to the downstream domain (A). When fused to a minimal promoter only three of the five subdomains give any expression in the early stages of plant development. Comparison of the expression patterns conferred by the subdomains alone, in combination with the downstream domain or in combination with other subdomains provides evidence for synergistic interactions among cis-elements within the 35S enhancer.
Full text
PDF
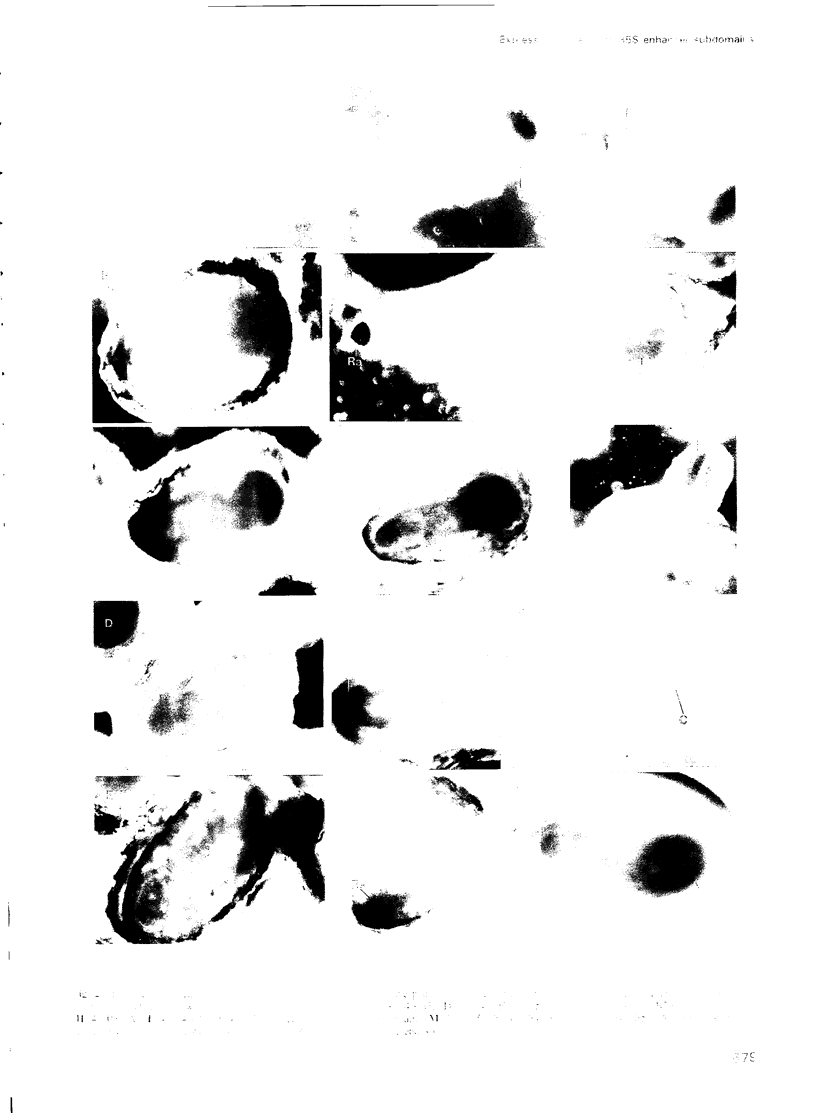




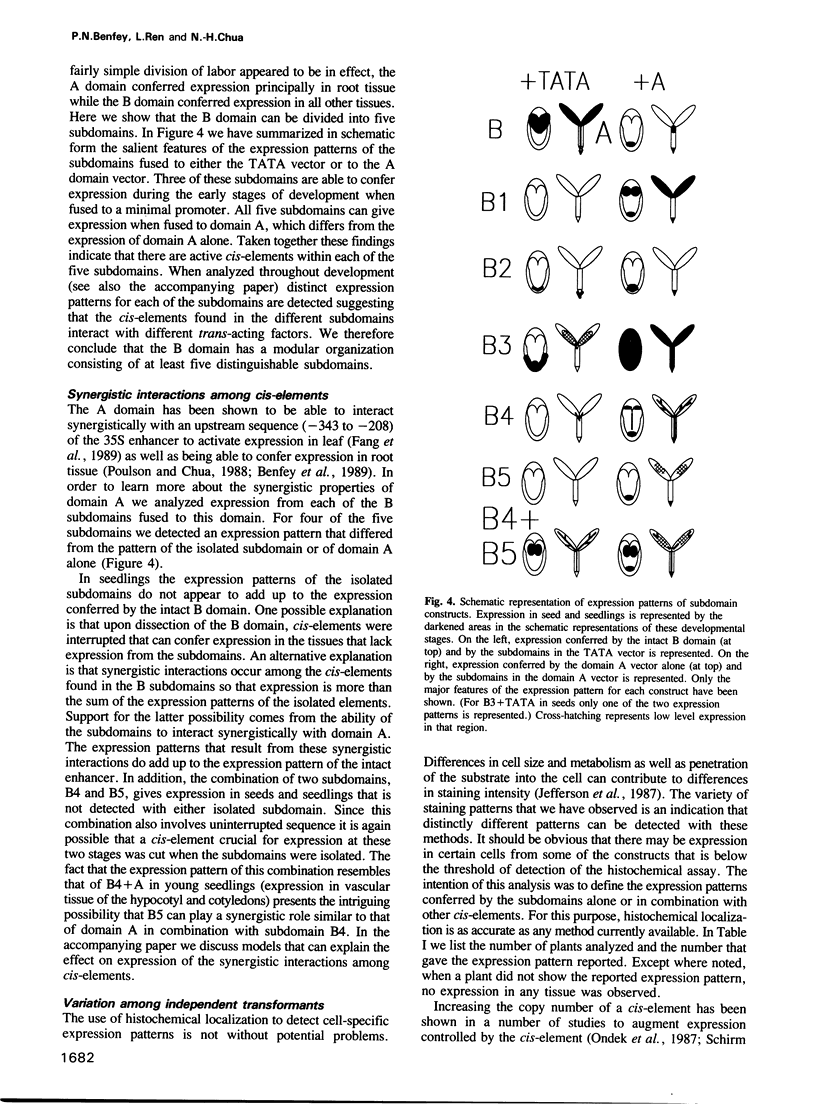

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baughman G. A., Jacobs J. D., Howell S. H. Cauliflower mosaic virus gene VI produces a symptomatic phenotype in transgenic tobacco plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):733–737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Chua N. H. Regulated genes in transgenic plants. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):174–181. doi: 10.1126/science.244.4901.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. Combinatorial and synergistic properties of CaMV 35S enhancer subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1685–1696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. The CaMV 35S enhancer contains at least two domains which can confer different developmental and tissue-specific expression patterns. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2195–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang R. X., Nagy F., Sivasubramaniam S., Chua N. H. Multiple cis regulatory elements for maximal expression of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter in transgenic plants. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):141–150. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Richards K., Geneviève-Lebeurier Cauliflower mosaic virus on its way to becoming a useful plant vector. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:194–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsch R. B., Klee H. J. Rapid assay of foreign gene expression in leaf discs transformed by Agrobacterium tumefaciens: Role of T-DNA borders in the transfer process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4428–4432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri F., Lam E., Chua N. H. Two tobacco DNA-binding proteins with homology to the nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):727–730. doi: 10.1038/340727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R., Chan A., Daly M., McPherson J. Duplication of CaMV 35S Promoter Sequences Creates a Strong Enhancer for Plant Genes. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.236.4806.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Benfey P. N., Gilmartin P. M., Fang R. X., Chua N. H. Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7890–7894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Boutry M., Hsu M. Y., Wong M., Chua N. H. The 5'-proximal region of the wheat Cab-1 gene contains a 268-bp enhancer-like sequence for phytochrome response. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Shepard A., Herr W. Discrete elements within the SV40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen C., Chua N. H. Dissection of 5' upstream sequences for selective expression of the Nicotiana plumbaginifolia rbcS-8B gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):16–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00340173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. R., Winter J. A., Barnason A. R., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T. Comparison of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S and nopaline synthase promoters in transgenic plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1543–1558. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. The SV40 enhancer can be dissected into multiple segments, each with a different cell type specificity. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoelz J., Shepherd R. J., Daubert S. Region VI of cauliflower mosaic virus encodes a host range determinant. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2632–2637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]