Abstract
GC-poor and GC-rich isochores, the long (greater than 300 kb) compositionally homogeneous DNA segments that form the genome of warm-blooded vertebrates, are located in G- and R-bands respectively of metaphase chromosomes. The precise correspondence between GC-rich isochores and R-band structure is still, however, an open problem, because GC-rich isochores are compositionally heterogeneous and only represent one-third of the genome, with the GC-richest family (which is by far the highest in gene concentration) corresponding to less than 5% of the genome. In order to clarify this issue and, more generally, to correlate DNA composition and chromosomal structure in an unequivocal way, we have developed a new approach, compositional mapping. This consists of assessing the base composition over 0.2-0.3 Mb (megabase) regions surrounding landmarks that were previously localized on the physical map. Compositional mapping was applied here to the long arm of human chromosome 21, using 53 probes that had already been used in physical mapping. The results obtained provide a direct demonstration that the DNA stretches of G-bands essentially correspond to GC-poor isochores, and that R-band DNA is characterized by a compositional heterogeneity that is much more striking than expected, in that it comprises isochores covering the full spectrum of GC levels. GC-poor isochores of R-bands may, however, correspond to 'thin' G-bands, as visualized at high resolution, leaving GC-rich and very GC-rich isochores as the real components of (high-resolution) R-band DNA.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros P. F., Sumner A. T. Correlation of pachytene chromomeres and metaphase bands of human chromosomes, and distinctive properties of telomeric regions. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(4):223–228. doi: 10.1159/000132375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aota S., Ikemura T. Diversity in G + C content at the third position of codons in vertebrate genes and its cause. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6345–6355. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Mouchiroud D., Gautier C., Bernardi G. Compositional patterns in vertebrate genomes: conservation and change in evolution. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02143493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G. The isochore organization of the human genome. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:637–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann H., Dattagupta N. On the binding and specificity of 3,6-bis-(acetatomercurimethyl)-dioxane to DNAs of different base composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 21;331(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Lejeune J. Sur une nouvelle technique d'analyse du caryotype humain. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 May 17;272(20):2638–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B. Nouveau système de marquage chromosomique: Les bandes. Chromosoma. 1973 Apr 27;41(4):395–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00396497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
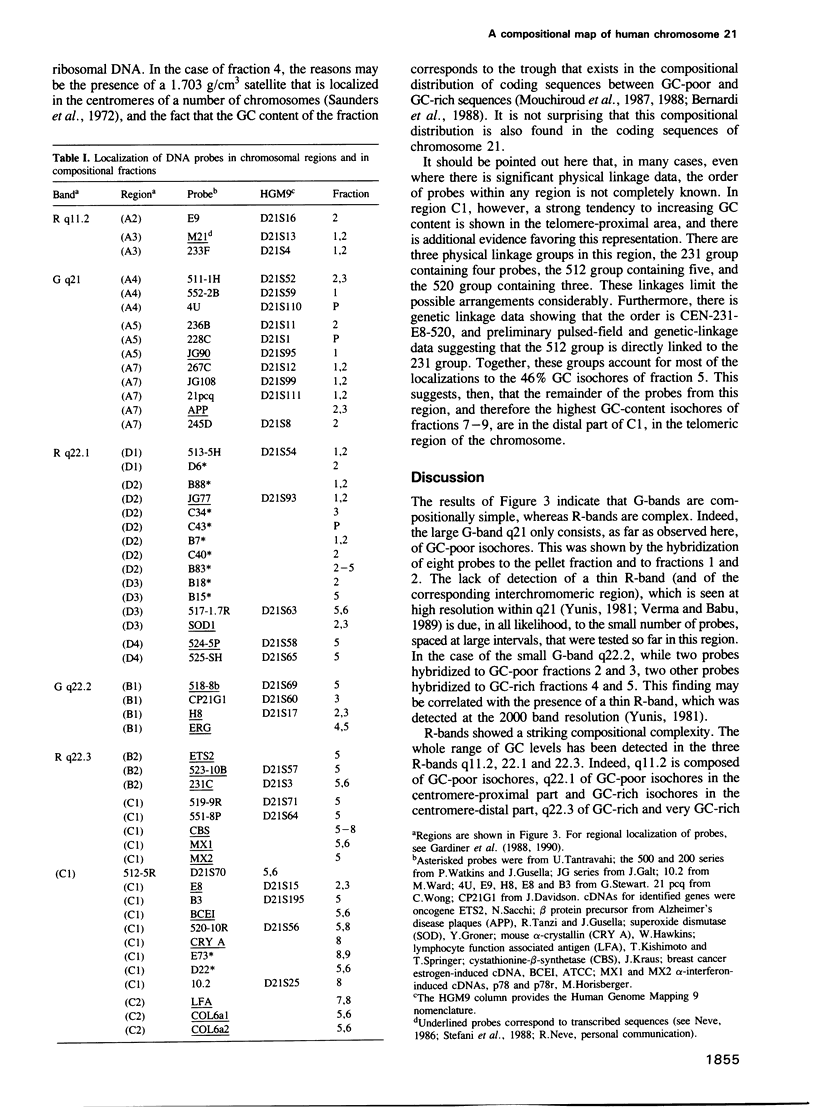
- Gardiner K., Horisberger M., Kraus J., Tantravahi U., Korenberg J., Rao V., Reddy S., Patterson D. Analysis of human chromosome 21: correlation of physical and cytogenetic maps; gene and CpG island distributions. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Watkins P., Münke M., Drabkin H., Jones C., Patterson D. Partial physical map of human chromosome 21. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Nov;14(6):623–637. doi: 10.1007/BF01535316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Aota S. Global variation in G+C content along vertebrate genome DNA. Possible correlation with chromosome band structures. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciani J. M., Morazzani M. R., Stahl A. Identification of pachytene bivalents in human male meiosis using G-banding technique. Chromosoma. 1975 Oct 14;52(3):275–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00332116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouchiroud D., Fichant G., Bernardi G. Compositional compartmentalization and gene composition in the genome of vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(3):198–204. doi: 10.1007/BF02099852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouchiroud D., Gautier C., Bernardi G. The compositional distribution of coding sequences and DNA molecules in humans and murids. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(4):311–320. doi: 10.1007/BF02101193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Stewart G. D., Newcomb P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Drabkin H. A., Kurnit D. M. Human chromosome 21-encoded cDNA clones. Gene. 1986;49(3):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada T. A., Comings D. E. Mechanisms of chromosome banding. III. Similarity between G-bands of mitotic chromosomes and chromomeres of meiotic chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1974;48(1):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00284867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., James L. A., Hardy J. A., Williamson R., Goate A. M. Physical mapping around the Alzheimer disease locus on the proximal long arm of chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):316–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinas J., Zerial M., Filipski J., Bernardi G. Gene distribution and nucleotide sequence organization in the mouse genome. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):469–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani L., Galt J., Palmer A., Affara N., Ferguson-Smith M., Nevin N. C. Expression of chromosome 21 specific sequences in normal and Down's syndrome tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2885–2896. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. An analysis of eukaryotic genomes by density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):219–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. High resolution of human chromosomes. Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1268–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.1257746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Salinas J., Filipski J., Bernardi G. Gene distribution and nucleotide sequence organization in the human genome. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):479–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]