Figure 3.
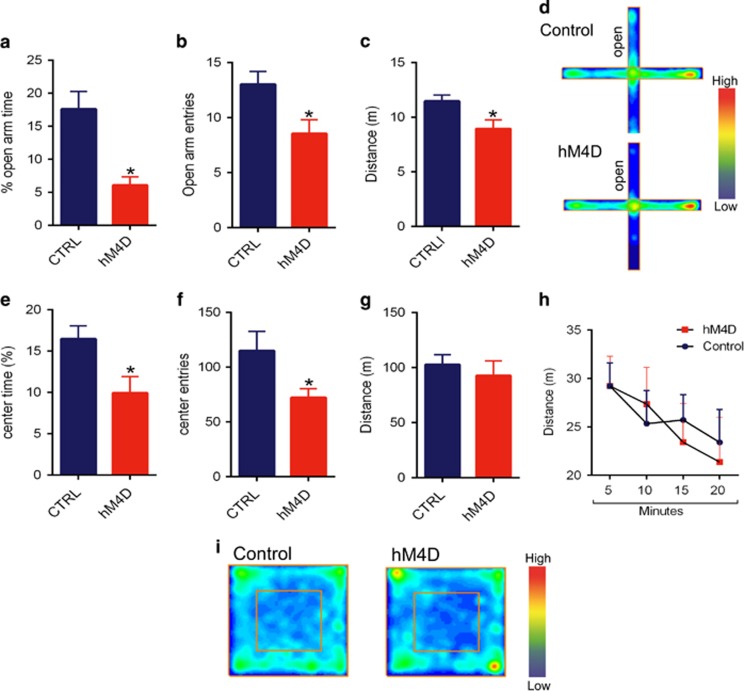
hM4D-mediated inhibition of LS-projecting vHPC cells increases anxiety. (a) hM4D-mice displayed a decreased % open arm time in the EPM after CNO injection (*p=0.0006). (b) hM4D mice displayed decreased open arm entries in the EPM after CNO injection (*p=0.001). (c) hM4D mice displayed a decreased level of locomotor activity in the EPM after CNO injection (*p=0.01). (d) Heat-map plots show the averaged cumulative time spent in different parts of the EPM. red=more time, blue=less time. (e and f) hM4D mice showed a decreased % time spent in the center (*p=0.03) and center entries in the OF after CNO injection (*p=0.03). (g) CTRL and hM3D mice showed similar levels of locomotor activity in the OF after CNO injection. (h) Examination of locomotor activity in 5 min intervals revealed no significant differences between hM4D and CTRL mice. (i) Heat-map plots show the averaged cumulative time spent in different parts of the OF. red=more time, blue=less time. n=13 for CTRL and 13 for hM3D mice.