Abstract
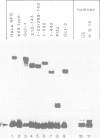
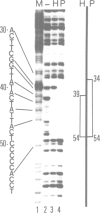
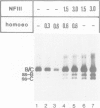
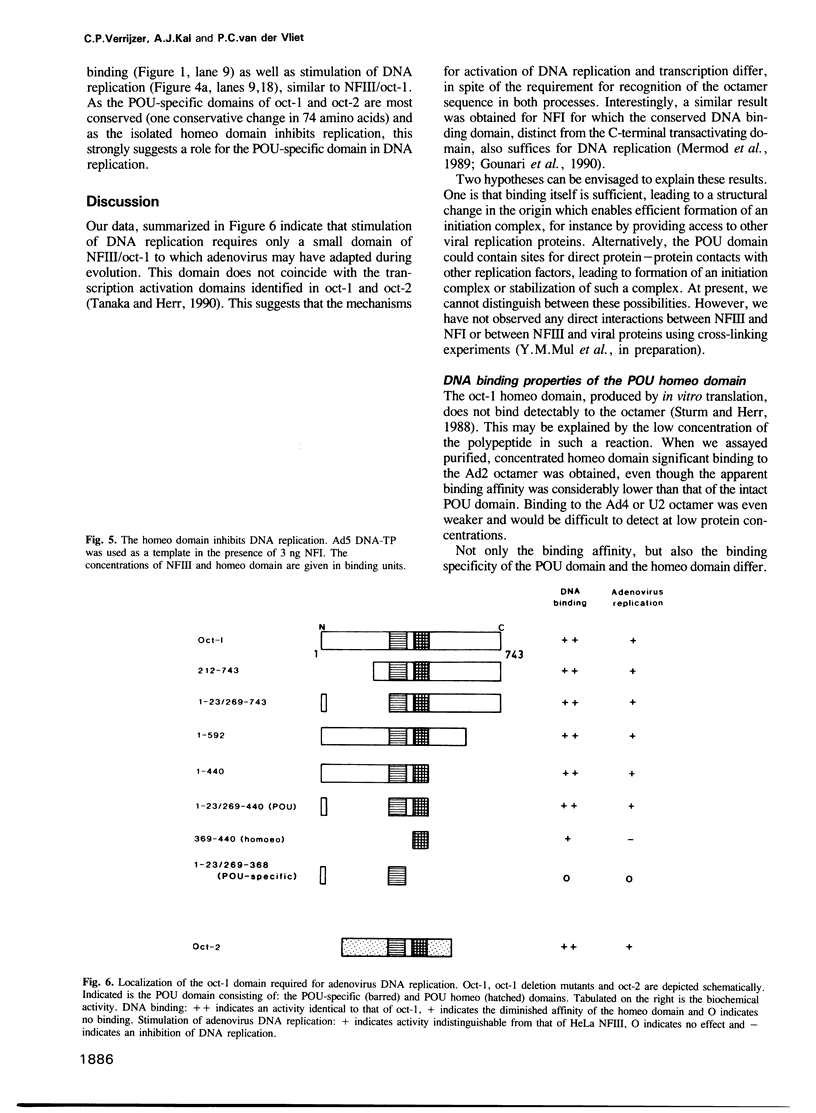
Oct-1, also referred to as NFIII, OTF-1, OBP100 or NF-A1, is a ubiquitous sequence-specific DNA binding protein that activates transcription and adenovirus DNA replication. The protein contains a conserved DNA binding domain (POU domain) present in several transcription factors. We have overproduced oct-1, the related oct-2 and several oct-1 deletion mutants in a vaccinia expression system to identify the domains important for activation of DNA replication in vitro. Both oct-1 and oct-2 stimulate adenovirus DNA replication in an octamer-dependent manner. From deletion studies it appears that the 160 amino acid long POU domain suffices for stimulation. This domain consists of two subdomains, a POU-specific and a homeo domain. Deletion of the POU-specific domain revealed that the homeo domain has an intrinsic, but weak DNA binding activity and surprisingly, inhibits DNA replication. As the POU domain does not coincide with the transcription activation domain, these results indicate that, although oct-1 functions both in DNA replication and transcription, the mechanisms underlying these processes are probably distinct.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Blanco M. A., Clerc R. G., Sharp P. A. The DNA-binding homeo domain of the Oct-2 protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):739–745. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounari F., De Francesco R., Schmitt J., van der Vliet P., Cortese R., Stunnenberg H. Amino-terminal domain of NF1 binds to DNA as a dimer and activates adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):559–566. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T. Origin of adenovirus DNA replication. Role of the nuclear factor I binding site in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90263-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., Russell W. C. Recognition mechanisms in the synthesis of animal virus DNA. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2580003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Kobayashi T., Staudt L., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Octamer-binding proteins from B or HeLa cells stimulate transcription of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1227–1237. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leegwater P. A., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Recognition site of nuclear factor I, a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells that stimulates adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1515–1521. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Staudt L., Robbins P., Kuang A., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Repression of the IgH enhancer in teratocarcinoma cells associated with a novel octamer factor. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):544–546. doi: 10.1126/science.2536195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Gander I., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L. A quantitative analysis of nuclear factor I/DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4419–4435. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mul Y. M., van Miltenburg R. T., De Clercq E., van der Vliet P. C. Mechanism of inhibition of adenovirus DNA replication by the acyclic nucleoside triphosphate analogue (S)-HPMPApp: influence of the adenovirus DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):8917–8929. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Enomoto T., Lichy J. H., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: identification of a host factor that stimulates synthesis of the preterminal protein-dCMP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Fletcher C., Burrow C. R., Heintz N., Roeder R. G., Kelly T. J. Transcription factor OTF-1 is functionally identical to the DNA replication factor NF-III. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.3413485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van Miltenburg R. T., van der Vliet P. C. Promoter and enhancer elements containing a conserved sequence motif are recognized by nuclear factor III, a protein stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3771–3778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Miltenburg R. T., Claessens J. A., van der Vliet P. C. Interaction between the octamer-binding protein nuclear factor III and the adenovirus origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3092–3102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3092-3102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn J. M., van der Vliet P. C., Dathan N. A., Mattaj I. W. Anti-OTF-1 antibodies inhibit NFIII stimulation of in vitro adenovirus DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1845–1863. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., O'Neill E. A., Wides R. J., Kelly T. J. Sequence-specific interactions between cellular DNA-binding proteins and the adenovirus origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):875–886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G., Lange H., Philipson L., van Miltenburg R. T., van der Vliet P. C. High expression of functional adenovirus DNA polymerase and precursor terminal protein using recombinant vaccinia virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2431–2444. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Das G., Herr W. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1582–1599. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R. A., Herr W. The POU domain is a bipartite DNA-binding structure. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):601–604. doi: 10.1038/336601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Castrillo J. L., Wu D., Karin M. Dissection of functional domains of the pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):945–948. doi: 10.1038/342945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries E., van Driel W., Bergsma W. G., Arnberg A. C., van der Vliet P. C. HeLa nuclear protein recognizing DNA termini and translocating on DNA forming a regular DNA-multimeric protein complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]