Abstract
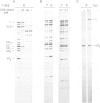
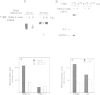
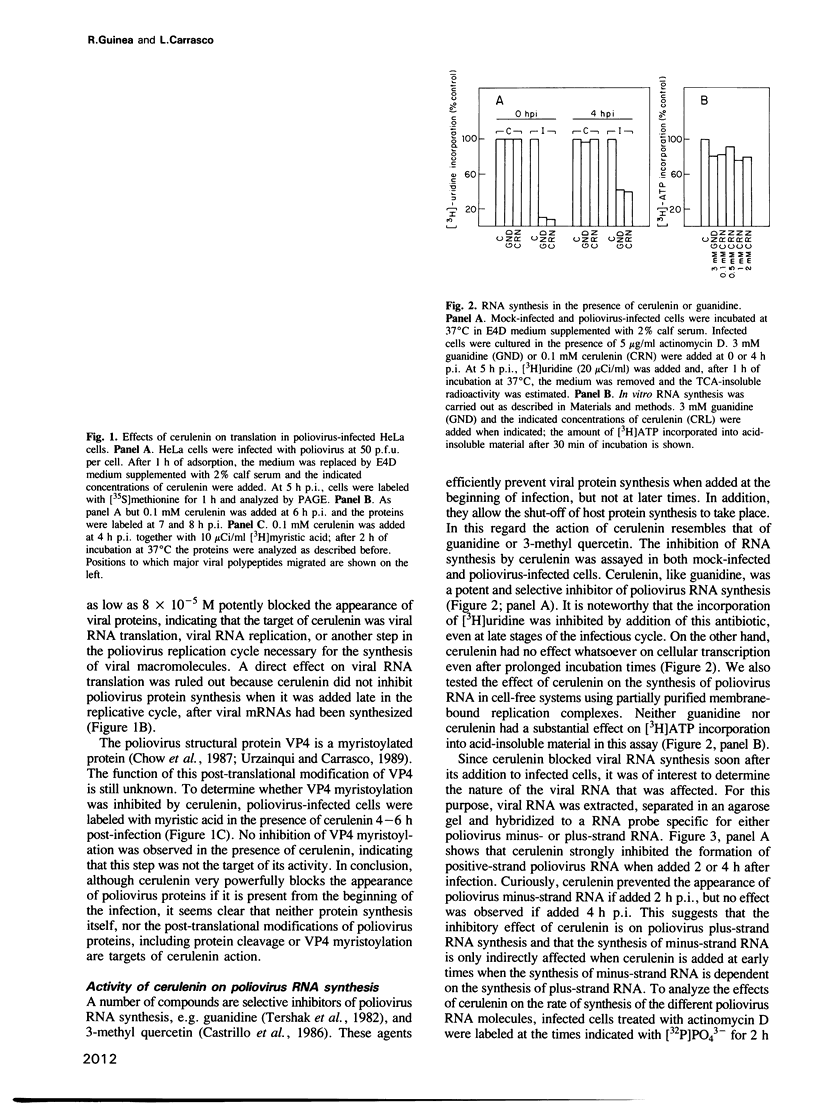
Poliovirus infection leads to an increase of phospholipid synthesis and the proliferation of new membranes, giving rise to a great number of cytoplasmic vesicles in the infected cells. Viral RNA replication is physically associated with these newly-synthesized membranes. Cerulenin, an inhibitor of lipid biosynthesis, effectively blocks the growth of poliovirus in HeLa cells. The presence of cerulenin after virus entry prevents the synthesis of poliovirus proteins. However, if this antibiotic is added at later stages of the virus replication cycle, it has no effect on viral translation itself, nor on the proteolytic processing and myristoylation of poliovirus proteins. The synthesis of viral, but not cellular RNA is selectively inhibited by cerulenin. Analysis of the viral RNA made in poliovirus-infected cells by specific minus-or plus-stranded RNA probes suggests a selective blockade by cerulenin of plus-strand RNA synthesis. Finally, the synthesis of phospholipids and the proliferation of membranes does not take place if cerulenin is added to the culture medium. These findings indicate that continuous phospholipid synthesis is required for efficient poliovirus genome replication and provide new insights towards the understanding of the molecular events that occur during poliovirus growth.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienz K., Egger D., Pasamontes L. Association of polioviral proteins of the P2 genomic region with the viral replication complex and virus-induced membrane synthesis as visualized by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry and autoradiography. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Shimshick E. J., Yin F. H. Association of the polioviral RNA polymerase complex with phospholipid membranes. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):457–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.457-466.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Characterization of poliovirus-specific structures associated with cytoplasmic membranes. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):112–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Otero M. J., Castrillo J. L. Modification of membrane permeability by animal viruses. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;40(2):171–212. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo J. L., Vanden Berghe D., Carrasco L. 3-Methylquercetin is a potent and selective inhibitor of poliovirus RNA synthesis. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S., EGGERS H. J., TAMM I., PALADE G. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF POLIOVIRUS. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. G., Kusano T., Yamaki H., Balakrishnan R., King M., Murchie J., Schaechter M. Binding of the origin of replication of Escherichia coli to the outer membrane. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):915–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser A. G., Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Incorporation of lipid precursors into cytoplasmic membranes of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura S. The antibiotic cerulenin, a novel tool for biochemistry as an inhibitor of fatty acid synthesis. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):681–697. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.681-697.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENMAN S., BECKER Y., DARNELL J. E. A CYTOPLASMIC STRUCTURE INVOLVED IN THE SYNTHESIS AND ASSEMBLY OF POLIOVIRUS COMPONENTS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:541–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierucci O., Rickert M. Duplication of Escherichia coli during inhibition of net phospholipid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):374–382. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.374-382.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel H., Traub P. The effect of mengovirus infection on lipid synthesis in cultured Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Lipids. 1987 Feb;22(2):95–103. doi: 10.1007/BF02534860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Kornberg A. Cardiolipin activation of dnaA protein, the initiation protein of replication in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7131–7135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda N., Kuhn R. J., Yang C. F., Takegami T., Wimmer E. Initiation of poliovirus plus-strand RNA synthesis in a membrane complex of infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):43–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.43-53.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tershak D. R. Association of poliovirus proteins with the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):777–783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.777-783.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urzainqui A., Carrasco L. Post-translational modifications of poliovirus proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):263–271. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D. E., Trip E. M., Paddon H. B. Poliovirus increases phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in HeLa cells by stimulation of the rate-limiting reaction catalyzed by CTP: phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1064–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Kuhn R. J., Pincus S., Yang C. F., Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Takeda N. Molecular events leading to picornavirus genome replication. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:251–276. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]