Abstract
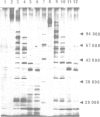
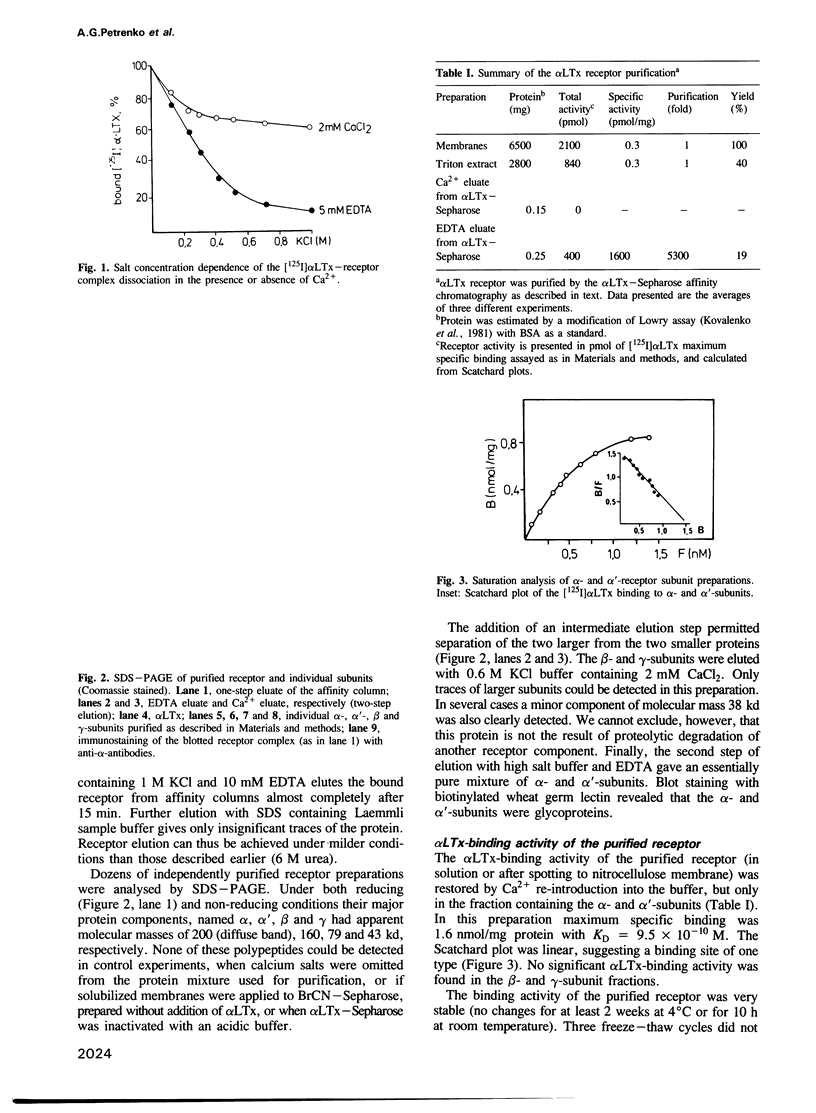
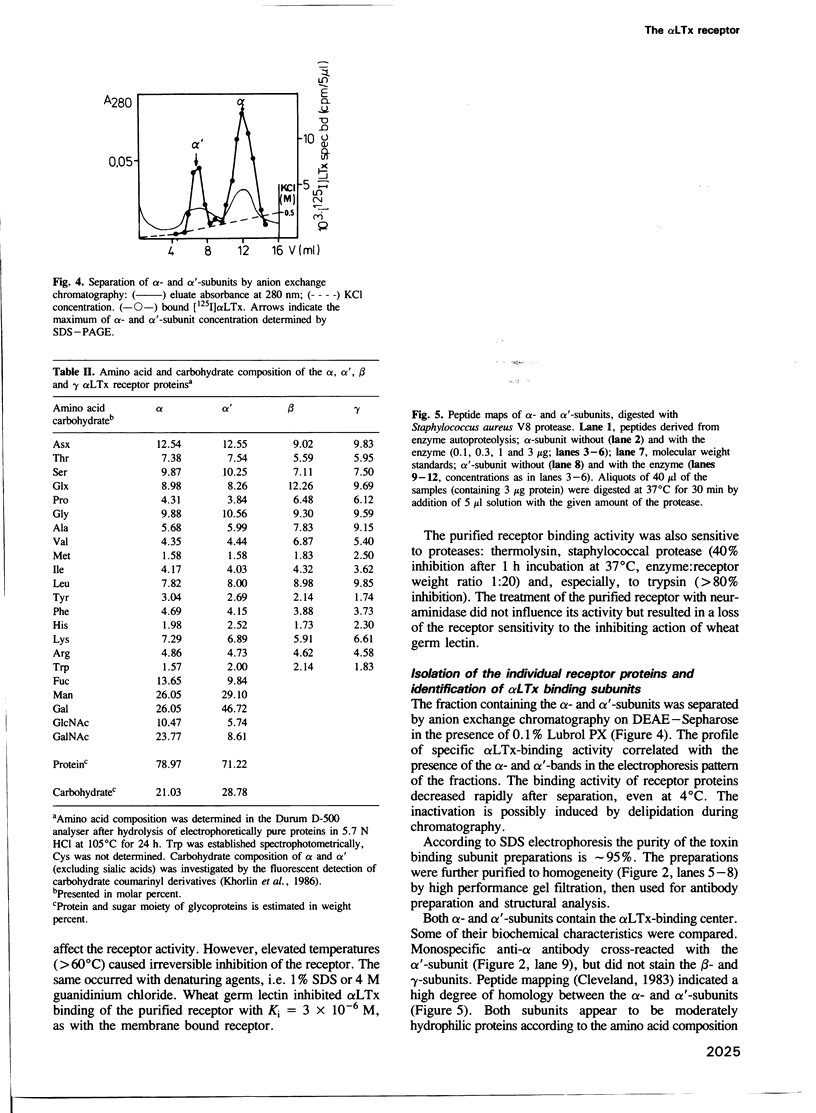
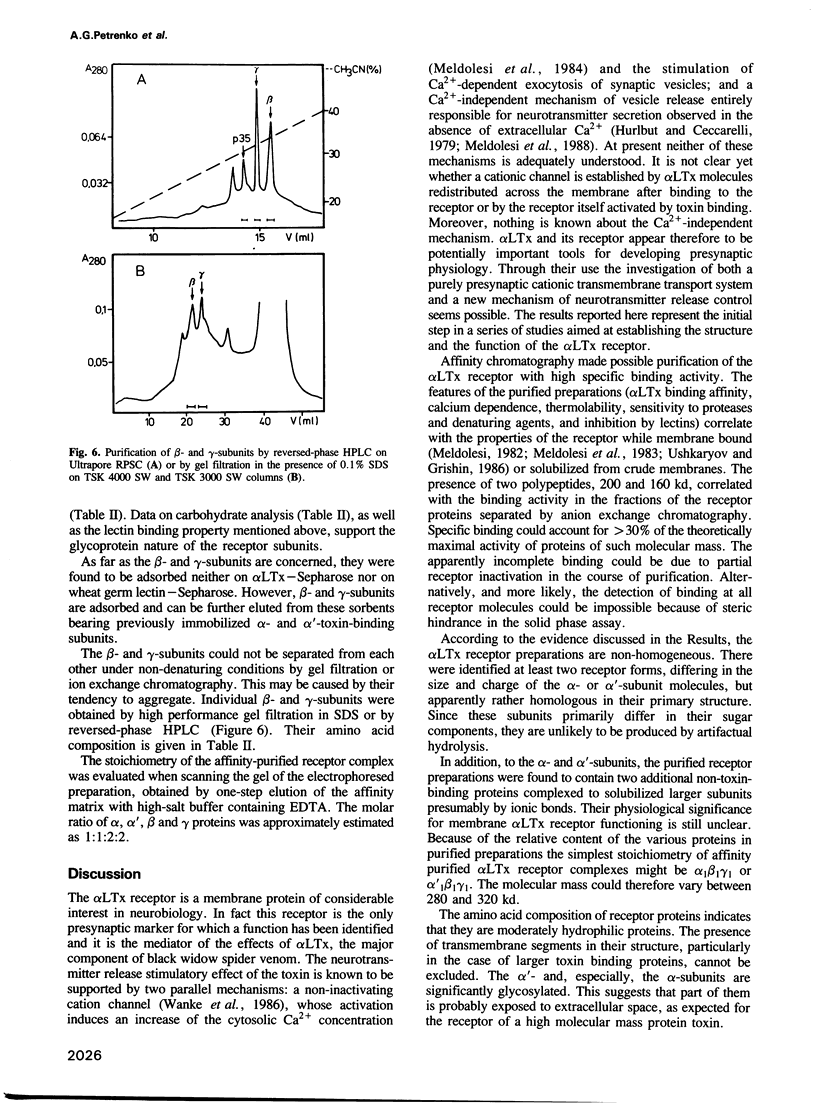
The receptor protein of alpha-latrotoxin (alpha LTx, a neurotoxin with 'pure' presynaptic action isolated from black widow spider venom), was solubilized by Triton X-100 from bovine brain membranes and purified by affinity chromatography on alpha LTx-Sepharose. The purified receptor preparation contained four major polypeptides of molecular masses 200 (alpha), 160 (alpha'), 79 (beta) and 43 (gamma) kd according to SDS electrophoresis with molecular ratio alpha 1 alpha' 1 beta 2 gamma 2. The alpha- and alpha'-subunits are glycoproteins binding to wheat germ lectin and can be separated under non-denaturing conditions by anion exchange chromatography. Purified to homogeneity, both of them, though differing in the carbohydrate composition, retain the alpha LTx-binding activity and give closely related peptide maps. Anti-alpha antibodies recognize the alpha'-subunit as well. These results suggest that alpha LTx receptor is present in purified preparations in two very close forms containing the alpha- or alpha'-subunit. Beta and gamma proteins do not specifically bind alpha LTx and their physiological role is unclear. They form a complex with solubilized alpha- and alpha'-subunits independently of alpha LTx presence. The receptor proteins were purified to homogeneity by high performance gel filtration in the presence of SDS, their amino acid composition was determined.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleveland D. W. Peptide mapping in one dimension by limited proteolysis of sodium dodecyl sulfate-solubilized proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:222–229. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frontali N., Ceccarelli B., Gorio A., Mauro A., Siekevitz P., Tzeng M. C., Hurlbut W. P. Purification from black widow spider venom of a protein factor causing the depletion of synaptic vesicles at neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):462–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. The cell biology of the nerve terminal. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90174-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Huttner W. B., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Free cytoplasmic Ca2+ and neurotransmitter release: studies on PC12 cells and synaptosomes exposed to alpha-latrotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):620–624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Madeddu L., Torda M., Gatti G., Niutta E. The effect of alpha-latrotoxin on the neurosecretory PC12 cell line: studies on toxin binding and stimulation of transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):997–1009. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J. Studies on alpha-latrotoxin receptors in rat brain synaptosomes: correlation between toxin binding and stimulation of transmitter release. J Neurochem. 1982 Jun;38(6):1559–1569. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb06633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer H., Meldolesi J. Purification of the putative alpha-latrotoxin receptor from bovine synaptosomal membranes in an active binding form. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):323–327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer H., Prestipino G., Meldolesi J. Reconstitution of the purified alpha-latrotoxin receptor in liposomes and planar lipid membranes. Clues to the mechanism of toxin action. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng M. C., Cohen R. S., Siekevitz P. Release of neurotransmitters and depletion of synaptic vesicles in cerebral cortex slices by alpha-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng M. C., Siekevitz P. The binding interaction between alpha-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom and a dog cerebral cortex synaptosomal membrane preparation. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushkarev Iu A., Grishin E. V. Neirotoksin karakurta i ego vzaimodeistvie s retseptorami iz mozga krys. Bioorg Khim. 1986 Jan;12(1):71–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtorta F., Madeddu L., Meldolesi J., Ceccarelli B. Specific localization of the alpha-latrotoxin receptor in the nerve terminal plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):124–132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke E., Ferroni A., Gattanini P., Meldolesi J. alpha Latrotoxin of the black widow spider venom opens a small, non-closing cation channel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):320–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]