Abstract
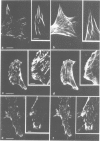
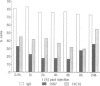
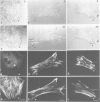
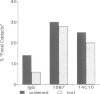
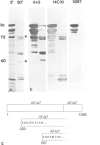
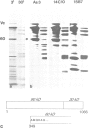
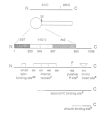
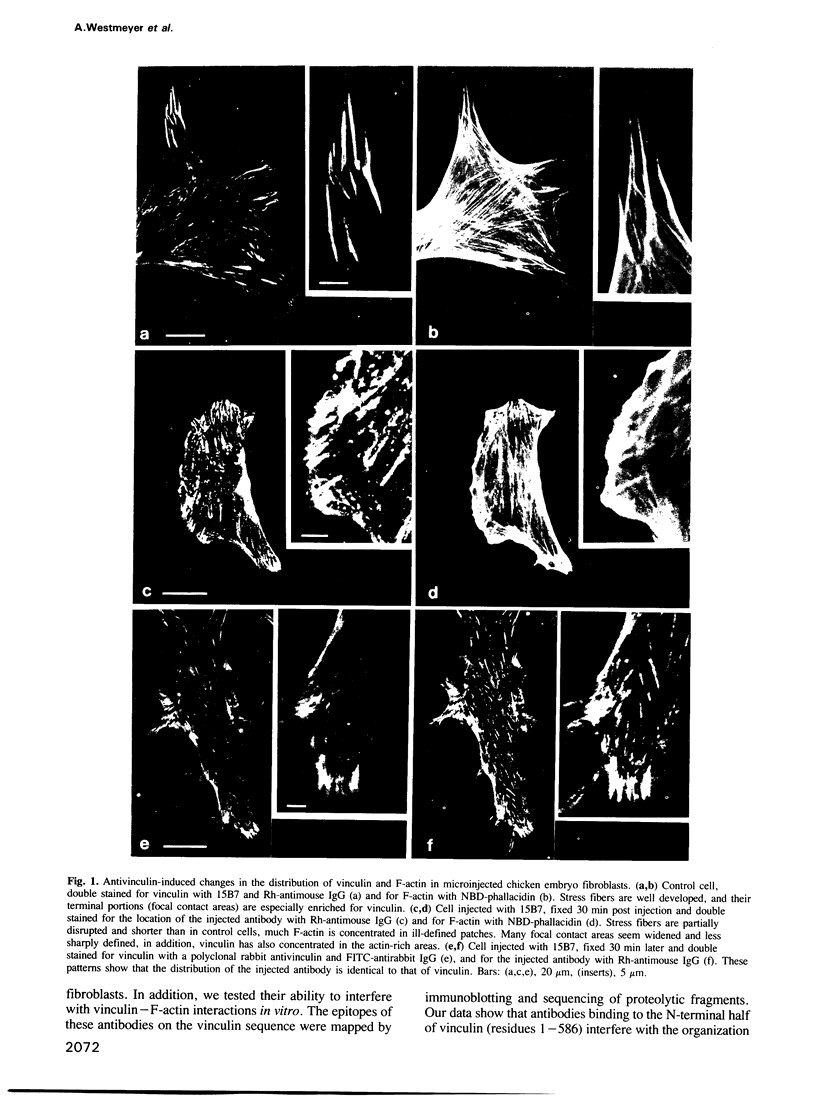
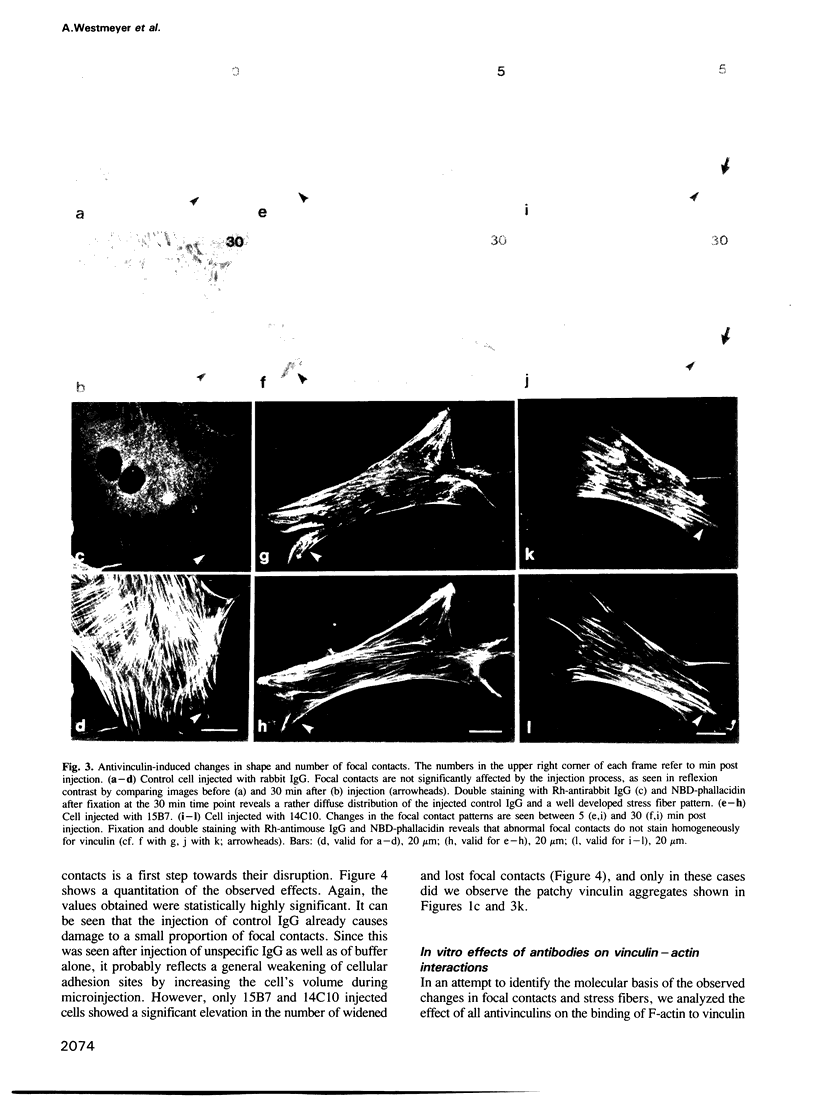
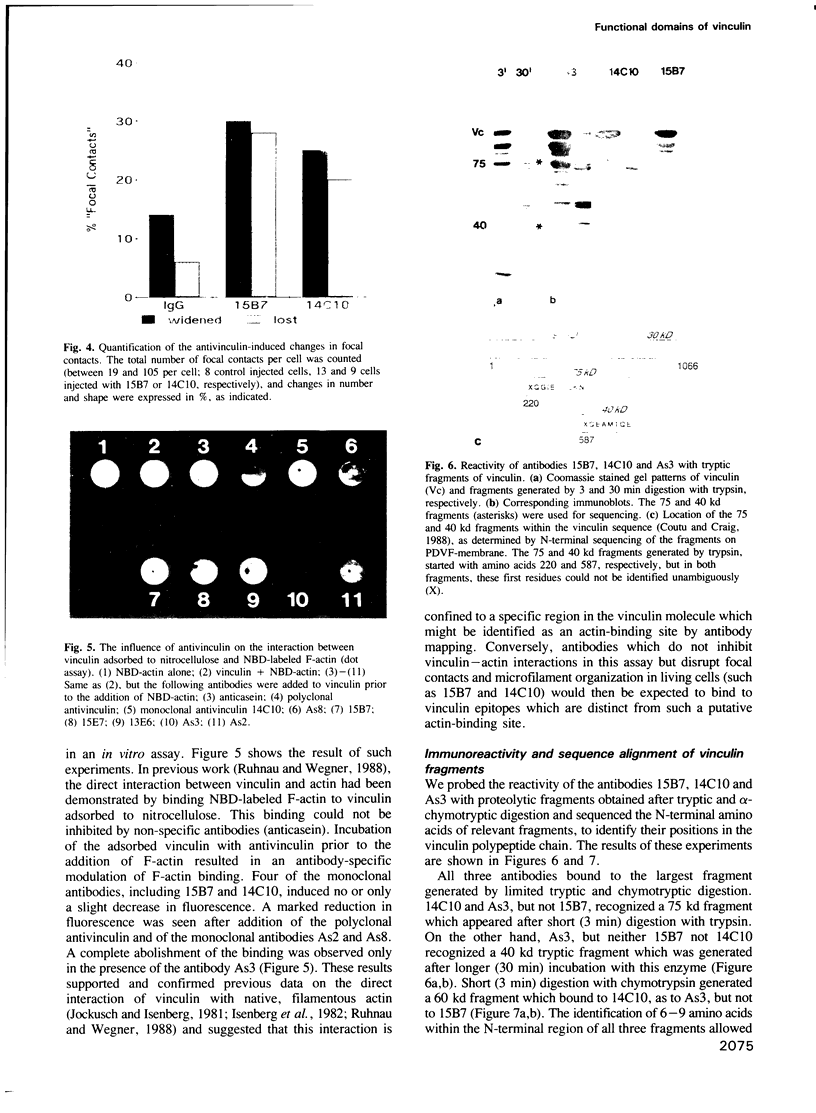
We have analyzed the functional domain structure of vinculin, a protein involved in linking microfilaments to the cytoplasmic face of cell membranes in animal cells. For this purpose, we used several monoclonal antibodies raised against chicken gizzard vinculin whose epitopes could be assigned to discrete regions in the vinculin sequence by immunoblotting of proteolytic fragments combined with N-terminal amino acid sequencing. Two of these antibodies induced the disruption of stress fibers and changed the number of morphology of focal contacts after microinjection in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Based on the location of its epitope in comparison with vinculin domains previously identified by other groups, we propose that one of these antibodies (15B7) interferes with the binding of vinculin to talin, the most peripheral of the microfilament proteins. The second antibody (14C10) binds within a region comprising three internal repeats and might therefore distort the inner architecture of vinculin. A third antibody (As3) inhibited the binding of F-actin to vinculin in an in vitro assay but had no effect on the microfilament system in cells. These data emphasize the role of vinculin as a key protein in microfilament-membrane linkage and support previous work on a direct interaction between vinculin and actin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie M., Heaysman J. E., Pegrum S. M. The locomotion of fibroblasts in culture. IV. Electron microscopy of the leading lamella. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90420-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. D., Davison M. D., Jones P., Critchley D. R. The sequence of chick alpha-actinin reveals homologies to spectrin and calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17623–17629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K. Structural model of vinculin: correlation of amino acid sequence with electron-microscopical shape. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 22;249(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belkin A. M., Koteliansky V. E. Interaction of iodinated vinculin, metavinculin and alpha-actinin with cytoskeletal proteins. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 17;220(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80832-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendori R., Salomon D., Geiger B. Identification of two distinct functional domains on vinculin involved in its association with focal contacts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2383–2393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier W., Libermann T. A., Imhof B. A., Kreis T. E. Intracellular and extracellular components involved in the formation of ventral surfaces of fibroblasts. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):755–767. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard A., Ohanian V., Critchley D. The structure and function of alpha-actinin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Aug;10(4):280–289. doi: 10.1007/BF01758424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blikstad I., Eriksson S., Carlsson L. alpha-Actinin promotes polymerization of actin from profilactin. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):317–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Mangeat P. An interaction between vinculin and talin. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):744–746. doi: 10.1038/308744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss F., Hinssen H., Jockusch B. M. Immunological and biochemical studies on the relationship between two actin-binding proteins, phosphofructokinase and gelsolin. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):251–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutu M. D., Craig S. W. cDNA-derived sequence of chicken embryo vinculin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Pfeuty T., Singer S. J. Altered distributions of the cytoskeletal proteins vinculin and alpha-actinin in cultured fibroblasts transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6687–6691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detmers P., Weber A., Elzinga M., Stephens R. E. 7-Chloro-4-nitrobenzeno-2-oxa-1,3-diazole actin as a probe for actin polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Burridge K. A rapid purification of alpha-actinin, filamin, and a 130,000-dalton protein from smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Smart J. E., Burridge K., Helfman D. M., Thomas G. P. Co-existence of vinculin and a vinculin-like protein of higher molecular weight in smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11024–11031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füchtbauer A., Jockusch B. M., Maruta H., Kilimann M. W., Isenberg G. Disruption of microfilament organization after injection of F-actin capping proteins into living tissue culture cells. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):361–364. doi: 10.1038/304361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavazzi I., Nermut M. V., Marchisio P. C. Ultrastructure and gold-immunolabelling of cell-substratum adhesions (podosomes) in RSV-transformed BHK cells. J Cell Sci. 1989 Sep;94(Pt 1):85–99. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. A 130K protein from chicken gizzard: its localization at the termini of microfilament bundles in cultured chicken cells. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. Cytoskeleton-associated cell contacts. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;1(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. Membrane-cytoskeleton interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):305–341. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Volk T., Volberg T. Molecular heterogeneity of adherens junctions. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1523–1531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimona M., Small J. V., Moeremans M., Van Damme J., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J. Porcine vinculin and metavinculin differ by a 68-residue insert located close to the carboxy-terminal part of the molecule. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2329–2334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann A., Graessmann M., Mueller C. Microinjection of early SV40 DNA fragments and T antigen. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):816–825. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A., Duggan K., Buck C., Beckerle M. C., Burridge K. Interaction of plasma membrane fibronectin receptor with talin--a transmembrane linkage. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):531–533. doi: 10.1038/320531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höner B., Citi S., Kendrick-Jones J., Jockusch B. M. Modulation of cellular morphology and locomotory activity by antibodies against myosin. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2181–2189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höner B., Jockusch B. M. Stress fiber dynamics as probed by antibodies against myosin. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;47(1):14–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Leonard K., Jockusch B. M. Structural aspects of vinculin-actin interactions. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):231–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90431-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockusch B. M., Füchtbauer A. Organization and function of structural elements in focal contacts of tissue culture cells. Cell Motil. 1983;3(5-6):391–397. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockusch B. M., Isenberg G. Interaction of alpha-actinin and vinculin with actin: opposite effects on filament network formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jockusch B. M., Isenberg G. Vinculin and alpha-actinin: interaction with actin and effect on microfilament network formation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):613–623. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P., Jackson P., Price G. J., Patel B., Ohanion V., Lear A. L., Critchley D. R. Identification of a talin binding site in the cytoskeletal protein vinculin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2917–2927. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Birchmeier W. Microinjection of fluorescently labeled proteins into living cells with emphasis on cytoskeletal proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;75:209–214. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Burridge K. Alpha-actinin: immunofluorescent localization of a muscle structural protein in nonmuscle cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchisio P. C., Cirillo D., Teti A., Zambonin-Zallone A., Tarone G. Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts and cells of monocytic origin display a peculiar dot-like organization of cytoskeletal proteins involved in microfilament-membrane interactions. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Mar;169(1):202–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90238-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milam L. M. Electron microscopy of rotary shadowed vinculin and vinculin complexes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):543–545. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90301-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimura N., Asano A. Further characterization of a conserved actin-binding 27-kDa fragment of actinogelin and alpha-actinins and mapping of their binding sites on the actin molecule by chemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4717–4723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molony L., Burridge K. Molecular shape and self-association of vinculin and metavinculin. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(1):31–36. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Witke W., Schleicher M. Calcium-sensitive non-muscle alpha-actinin contains EF-hand structures and highly conserved regions. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80962-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto J. J. Detection of vinculin-binding proteins with an 125I-vinculin gel overlay technique. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1283–1287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto J. J. The lack of interaction between vinculin and actin. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1986;6(1):48–55. doi: 10.1002/cm.970060107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price G. J., Jones P., Davison M. D., Patel B., Bendori R., Geiger B., Critchley D. R. Primary sequence and domain structure of chicken vinculin. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2590453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price G. J., Jones P., Davison M. D., Patel B., Eperon I. C., Critchley D. R. Isolation and characterization of a vinculin cDNA from chick-embryo fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):595–603. doi: 10.1042/bj2450595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhnau K., Gaertner A., Wegner A. Kinetic evidence for insertion of actin monomers between the barbed ends of actin filaments and barbed end-bound insertin, a protein purified from smooth muscle. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhnau K., Wegner A. Evidence for direct binding of vinculin to actin filaments. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80595-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano J. D., Craig S. W. Meta-vinculin--a vinculin-related protein with solubility properties of a membrane protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):533–535. doi: 10.1038/300533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsstock D. H., Wilkins J. A., Lin S. Specific interaction of vinculin with alpha-actinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):554–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90564-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehland J., Osborn M., Weber K. Cell-to-substratum contacts in living cells: a direct correlation between interference-reflexion and indirect-immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies against actin and alpha-actinin. J Cell Sci. 1979 Jun;37:257–273. doi: 10.1242/jcs.37.1.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. A., Lin S. A re-examination of the interaction of vinculin with actin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1085–1092. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. A., Lin S. High-affinity interaction of vinculin with actin filaments in vitro. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90377-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]