Abstract
Analysis of acetylcholine receptor clones isolated from a human leg muscle cDNA library, revealed that the alpha-subunit existed as two isoforms. A novel exon, coding for 25 amino acids, was located in the human genomic DNA sequence; its insertion into the alpha-subunit gives the new isoform of 462 amino acids. In addition, mRNAs for the two isoforms were found in equal proportions in poly(A)+ RNA obtained from three further sources including partially denervated and innervated human muscle and the rhabdomyosarcoma cell line TE671. Both protein isoforms can be expressed in E. coli. No evidence of a sequence related to that of the new exon was found in cDNA derived from poly(A)+ RNA isolated from fetal calf or embryonic chick muscle or Torpedo marmorata electric organ.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T., Gabriel J. M., Mauron A., Hughes G. J., Roth B., Alliod C., Tzartos S. J., Ballivet M. Monoclonal antibodies to the main immunogenic region of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor bind to residues 61-76 of the alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5916–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T., Mauron A., Roth B., Alliod C., Tzartos S. J., Ballivet M. Mapping the main immunogenic region and toxin-binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.2432658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Luyten W., Evans K., Mason P., Ballivet M., Goldman D., Stengelin S., Martin G., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a clone coding for the alpha-subunit of a mouse acetylcholine receptor. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2545–2552. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Merlie J. P. Transcriptional regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes during muscle development. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11452–11455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Mudd J., Merlie J. P. Isolation and characterization of the beta and epsilon subunit genes of mouse muscle acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7611–7616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarson B., Gullick W., Conti-Tronconi B., Ellisman M., Lindstrom J. Subunit composition of bovine muscle acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5295–5302. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Boulter J., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Muscle denervation increases the levels of two mRNAs coding for the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2553–2558. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02553.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Deneris E., Luyten W., Kochhar A., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Members of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family are expressed in different regions of the mammalian central nervous system. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):965–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90705-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Tamai K. Coordinate regulation of RNAs encoding two isoforms of the rat muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor beta-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3049–3056. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotti C., Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. Mammalian muscle acetylcholine receptor purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3148–3154. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of acetylcholine receptor structure. 1. Peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2173–2180. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich F., Vincent A., Roberts A., Newsom-Davis J. Epitopes on human acetylcholine receptor defined by monoclonal antibodies and myasthenia gravis sera. Autoimmunity. 1988;1(4):285–297. doi: 10.3109/08916938809010682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarsfeld A., Changeux J. P. Activity regulates the levels of acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit mRNA in cultured chicken myotubes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4558–4562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Noda M., Takai T., Tanabe T., Kayano T., Shimizu S., Tanaka K., Takahashi H., Hirose T., Inayama S. Primary structure of delta subunit precursor of calf muscle acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 15;149(1):5–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobos E. A., Rudnick C. H., Watson M. S., Isenberg K. E. Linkage disequilibrium study of RFLPs detected at the human muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):522–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luther M. A., Schoepfer R., Whiting P., Casey B., Blatt Y., Montal M. S., Montal M., Linstrom J. A muscle acetylcholine receptor is expressed in the human cerebellar medulloblastoma cell line TE671. J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;9(3):1082–1096. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-03-01082.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momoi M. Y., Lennon V. A. Purification and biochemical characterization of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of human muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12757–12764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss S. J., Beeson D. M., Jackson J. F., Darlison M. G., Barnard E. A. Differential expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes in innervated and denervated chicken muscle. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3917–3921. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N. M., Hall Z. W. Subunit structure and peptide mapping of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors from rat muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3392–3401. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Oneyser C., Alliod C., Couturier S., Ballivet M. Genes expressed in the brain define three distinct neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):595–601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
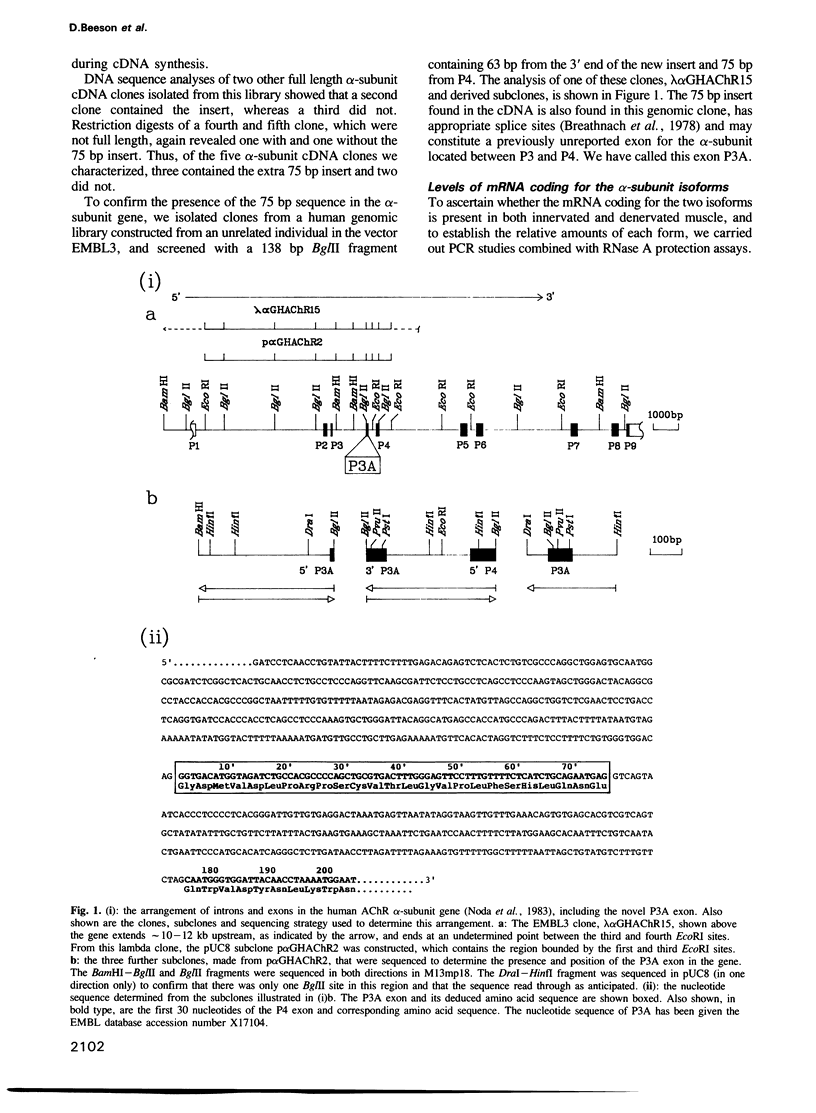
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Tanabe T., Shimizu S., Kikyotani S., Kayano T., Hirose T., Inayama S. Cloning and sequence analysis of calf cDNA and human genomic DNA encoding alpha-subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):818–823. doi: 10.1038/305818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numa S., Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Kikyotani S. Molecular structure of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):57–69. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam M., Gullick W., Spiess J., Wan K., Criado M., Lindstrom J. Structural heterogeneity of the alpha subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in relation to agonist affinity alkylation and antagonist binding. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4268–4275. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepfer R., Luther M., Lindstrom J. The human medulloblastoma cell line TE671 expresses a muscle-like acetylcholine receptor. Cloning of the alpha-subunit cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 4;226(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson F. A., Harrison R., Lunt G. G. The isolation and characterisation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from human skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):91–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Barnard E. A., Dolly J. O. Similarity of acetylcholine receptors of denervated, innervated and embryonic chicken muscles. 2. Subunit compositions. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;126(3):473–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Houghton M., Smith J. C., Bell L., Richards B. M., Barnard E. A. The molecular cloning and characterisation of cDNA coding for the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5809–5822. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Seybold M. E., Lindstrom J. M. Specificities of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors in sera from myasthenia gravis patients measured by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A. Immunology of acetylcholine receptors in relation to myasthenia gravis. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jul;60(3):756–824. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.3.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J. Acetylcholine receptor antibody as a diagnostic test for myasthenia gravis: results in 153 validated cases and 2967 diagnostic assays. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985 Dec;48(12):1246–1252. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.12.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J. Immunological and pharmacological heterogeneity of alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites extracted from TE671 cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Aug;19(1-2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]