Abstract
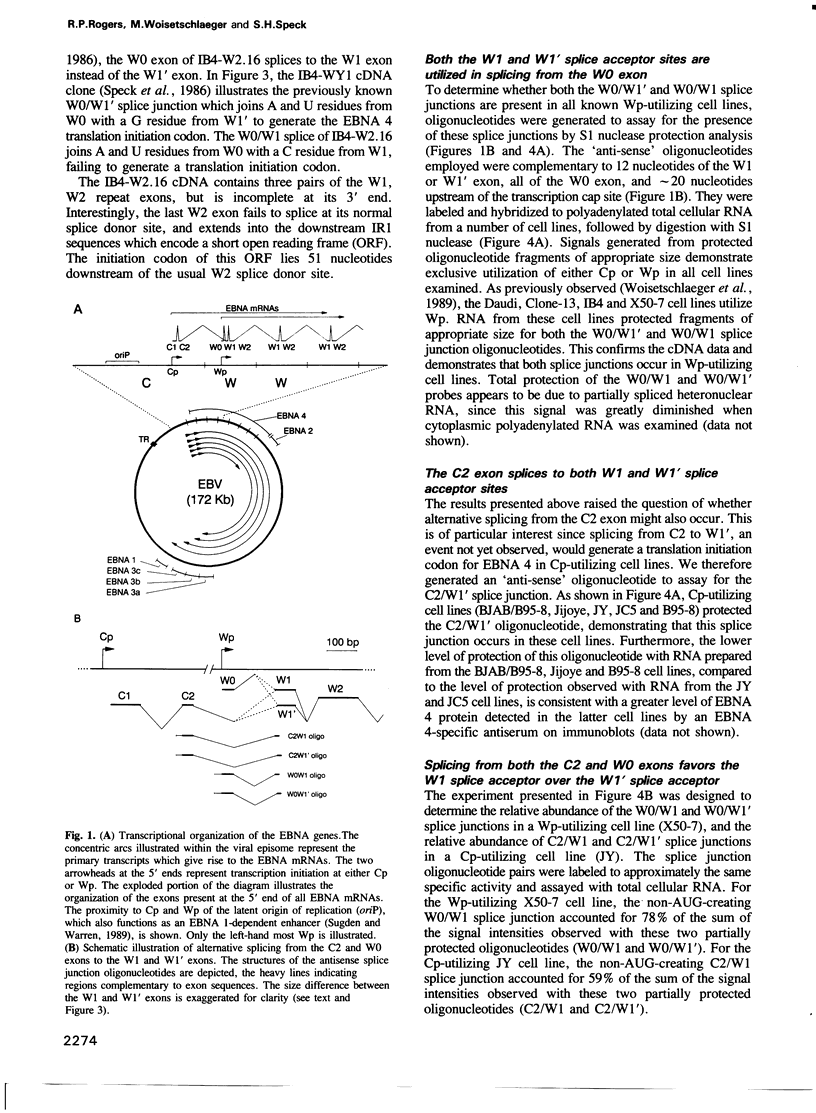
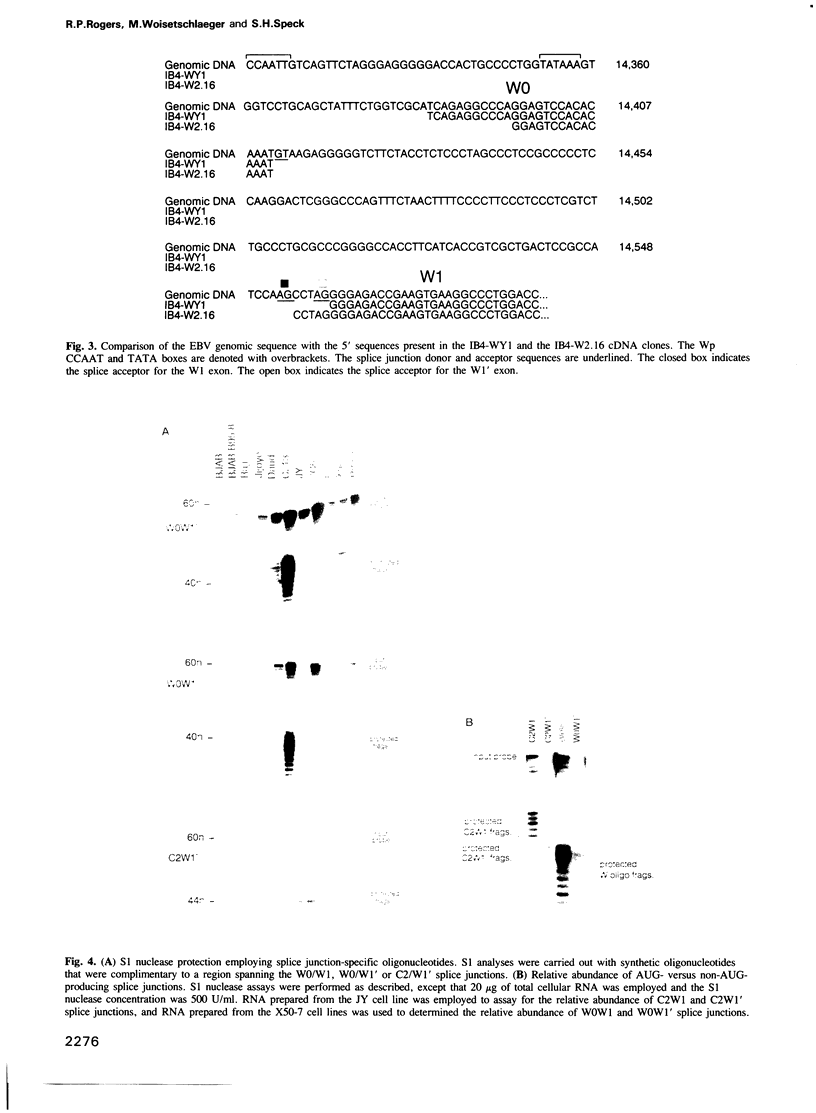
Of the 10 viral genes known to be expressed during Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latency, six encode nuclear antigens (EBNAs), all of which are expressed from a long primary transcript by means of alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation sites. The primary transcript is generated by either of two promoters which operate in a mutually exclusive fashion in different clonal cell lines. All mRNAs from either promoter have exons in common from the BamHI W viral genomic fragment (the major internal repeat, IR1) which encode the N-terminal portion of one of the nuclear antigens (EBNA 4). In addition to the coding regions for EBNA 4, EBNA mRNAs encode another EBNA (i.e. EBNA 1, 2, 3A, 3B or 3C) downstream. We show that alternative splicing determines whether the translation initiation codon for EBNA 4 is present or absent, thus permitting the generation of mRNAs in which the first translation initiation codon is either that for the EBNA 4 gene or for the other EBNA gene encoded downstream. This mechanism presumably ensures efficient translation of all the EBNA genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M. Epstein-Barr virus mRNAs produced by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7103–7114. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Broz S. D., Levinson A. D. Expression of the H-ras proto-oncogene is controlled by alternative splicing. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ernberg I., Uno M., Ono Y., Klein G., Lerner R. A. An Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA5) partly encoded by the transformation-associated Bam WYH region of EBV DNA: preferential expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke J., Rowe M., Kallin B., Ernberg I., Rosén A., Dillner J., Klein G. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies against Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 5 (EBNA-5) detect multiple protein species in Burkitt's lymphoma and lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3870–3878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3870-3878.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers R. P., Speck S. H. Bidirectional transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus major internal repeat. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2426–2429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2426-2429.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada K., Yamamoto M., Tabata T., Smith M., Tanaka A., Nonoyama M. Expression of EBNA-3 family in fresh B lymphocytes infected with Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski B. A., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Sex-specific alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene results from sequence-dependent splice site blockage. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Pfitzner A., Strominger J. L. An Epstein-Barr virus transcript from a latently infected, growth-transformed B-cell line encodes a highly repetitive polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9298–9302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Warren N. A promoter of Epstein-Barr virus that can function during latent infection can be transactivated by EBNA-1, a viral protein required for viral DNA replication during latent infection. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2644–2649. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2644-2649.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek D. F., Smith C. W., Nadal-Ginard B. The rat alpha-tropomyosin gene generates a minimum of six different mRNAs coding for striated, smooth, and nonmuscle isoforms by alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):679–694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Mutually exclusive use of viral promoters in Epstein-Barr virus latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6498–6502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




