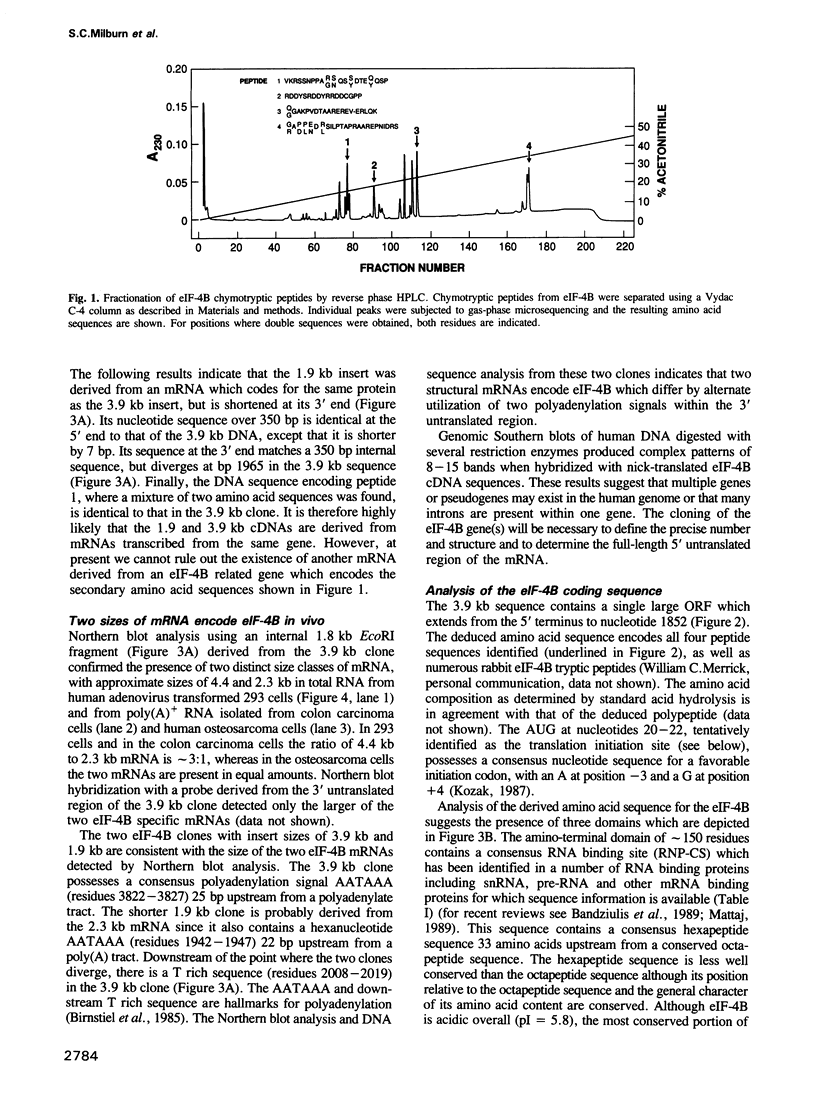
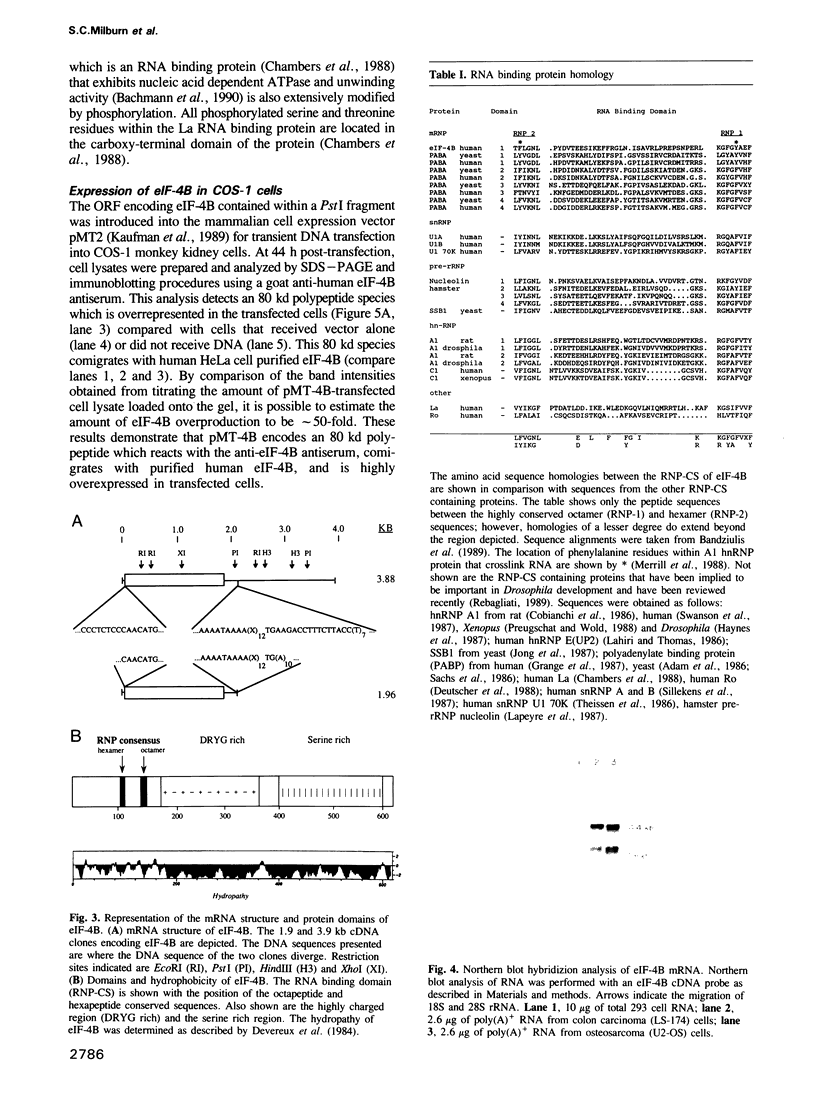
Abstract
Eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 4B (eIF-4B) is an 80,000 dalton polypeptide which is essential for the binding of mRNA to ribosomes. A highly purified preparation of eIF-4B from HeLa cells was subjected to enzymatic cleavage and amino-terminal amino acid sequence analysis. Degenerate oligonucleotide probes were used to isolate a 3851 bp cDNA encoding eIF-4B from a human cDNA library. The DNA encodes a protein comprising 611 residues with a mass of 69,843 daltons. The amino-terminal domain of eIF-4B contains a consensus RNA binding domain present in a number of other RNA binding proteins. Expression of eIF-4B in transfected COS-1 cells yielded a polypeptide which reacted with anti-eIF-4B antiserum and comigrated with purified eIF-4B. Expression of eIF-4B in COS-1 cells resulted in a general inhibition of translation, possibly due to a 50-fold eIF-4B overproduction.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Thach R. E., Merrick W. C. The ATP-dependent interaction of eukaryotic initiation factors with mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3826–3832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C. Biochemical evidence supporting a mechanism for cap-independent and internal initiation of eukaryotic mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6016–6019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Pfeifer K., Schröder H. C., Müller W. E. Characterization of the autoantigen La as a nucleic acid-dependent ATPase/dATPase with melting properties. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90718-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Hershey J. W. The mechanism of action of protein synthesis initiation factors from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3078–3087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs R. T., Gregor P., Idriss S., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Regulation of sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster via alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):739–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown-Luedi M. L., Meyer L. J., Milburn S. C., Yau P. M., Corbett S., Hershey J. W. Protein synthesis initiation factors from human HeLa cells and rabbit reticulocytes are similar: comparison of protein structure, activities, and immunochemical properties. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4202–4206. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. S., Clark J. M., Jr Eucaryotic initiation factor 4B of wheat germ binds to the translation initiation region of a messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):809–815. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Kenan D., Martin B. J., Keene J. D. Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18043–18051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. B., Zachar Z., Bingham P. M. Developmental expression of a regulatory gene is programmed at the level of splicing. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4095–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., Karpel R. L., Williams K. R., Notario V., Wilson S. H. Mammalian heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex protein A1. Large-scale overproduction in Escherichia coli and cooperative binding to single-stranded nucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):1063–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Wilson S. H. Structure of rodent helix-destabilizing protein revealed by cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3536–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Harley J. B., Keene J. D. Molecular analysis of the 60-kDa human Ro ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9479–9483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Identification and quantitation of levels of protein synthesis initiation factors in crude HeLa cell lysates by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7228–7235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Hümbelin M., Darveau A., Lee K. A., Milburn S., Hershey J. W., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Involvement of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A in the cap recognition process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss D. J., Woodley C. L., Wahba A. J. A fluorescence study of the binding of eucaryotic initiation factors to messenger RNA and messenger RNA analogues. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., de Sa C. M., Oddos J., Pictet R. Human mRNA polyadenylate binding protein: evolutionary conservation of a nucleic acid binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4771–4787. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Satler C. A., Merrick W. C. RNA-stimulated ATPase activity of eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8648–8654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Rebbert M. L., Mozer B. A., Forquignon F., Dawid I. B. pen repeat sequences are GGN clusters and encode a glycine-rich domain in a Drosophila cDNA homologous to the rat helix destabilizing protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1819–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Protein phosphorylation controls translation rates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20823–20826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong A. Y., Clark M. W., Gilbert M., Oehm A., Campbell J. L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SSB1 protein and its relationship to nucleolar RNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2947–2955. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Pathak V. K., Hershey J. W. The phosphorylation state of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 alters translational efficiency of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):946–958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Amplification and expression of sequences cotransfected with a modular dihydrofolate reductase complementary dna gene. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):601–621. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzel E. A., Mulligan J. A., Sommercorn J., Krebs E. G. Substrate specificity determinants for casein kinase II as deduced from studies with synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9136–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri D. K., Thomas J. O. A cDNA clone of the hnRNP C proteins and its homology with the single-stranded DNA binding protein UP2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4077–4094. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Nucleolin, the major nucleolar protein of growing eukaryotic cells: an unusual protein structure revealed by the nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Strauss M., Carroll M. C., Steinmetz M., Meo T. A previously undetected MHC gene with an unusual periodic structure. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.3353717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. A binding consensus: RNA-protein interactions in splicing, snRNPs, and sex. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill B. M., Stone K. L., Cobianchi F., Wilson S. H., Williams K. R. Phenylalanines that are conserved among several RNA-binding proteins form part of a nucleic acid-binding pocket in the A1 heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3307–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer L. J., Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W. Immunochemical characterization of mammalian protein synthesis initiation factors. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4206–4212. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn S. C., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Identification of the 80-kDa protein that crosslinks to the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs as initiation factor eIF-4B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jul;264(1):348–350. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90604-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Photochemical cross-linking of cap binding proteins to eucaryotic mRNAs: effect of mRNA 5' secondary structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3222–3230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Solowiejczyk D., Ballantine M., Schwartz E., Surrey S. "Nonrandom" DNA sequence analysis in bacteriophage M13 by the dideoxy chain-termination method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Wold B. Isolation and characterization of a Xenopus laevis C protein cDNA: structure and expression of a heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9669–9673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigodich R. V., Shamoo Y., Williams K. R., Chase J. W., Konigsberg W. H., Coleman J. E. 1H NMR (500 MHz) identification of aromatic residues of gene 32 protein involved in DNA binding by use of protein containing perdeuterated aromatic residues and by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3666–3672. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Recycling of messenger RNA cap-binding proteins mediated by eukaryotic initiation factor 4B. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11466–11470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Kramer J. C., Cladaras M. H., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. ATP-dependent unwinding of messenger RNA structure by eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7651–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. An RNA recognition motif in the bicoid protein. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):231–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90834-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Edery I., Meerovitch K., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Bidirectional RNA helicase activity of eucaryotic translation initiation factors 4A and 4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W., Kornberg R. D. A single domain of yeast poly(A)-binding protein is necessary and sufficient for RNA binding and cell viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3268–3276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillekens P. T., Habets W. J., Beijer R. P., van Venrooij W. J. cDNA cloning of the human U1 snRNA-associated A protein: extensive homology between U1 and U2 snRNP-specific proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3841–3848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Cap-binding proteins of eukaryotic messenger RNA: functions in initiation and control of translation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:173–207. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Nakagawa T. Y., LeVan K., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure of human nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle C proteins: conservation of sequence and domain structures in heterogeneous nuclear RNA, mRNA, and pre-rRNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theissen H., Etzerodt M., Reuter R., Schneider C., Lottspeich F., Argos P., Lührmann R., Philipson L. Cloning of the human cDNA for the U1 RNA-associated 70K protein. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3209–3217. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Erni B., Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. II. The assembly of the initiation complex with purified initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):755–767. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L. A sensitive and rapid method for recombinant phage screening. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:389–395. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Chou T. B., Bingham P. M. Evidence that a regulatory gene autoregulates splicing of its transcript. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4105–4111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]