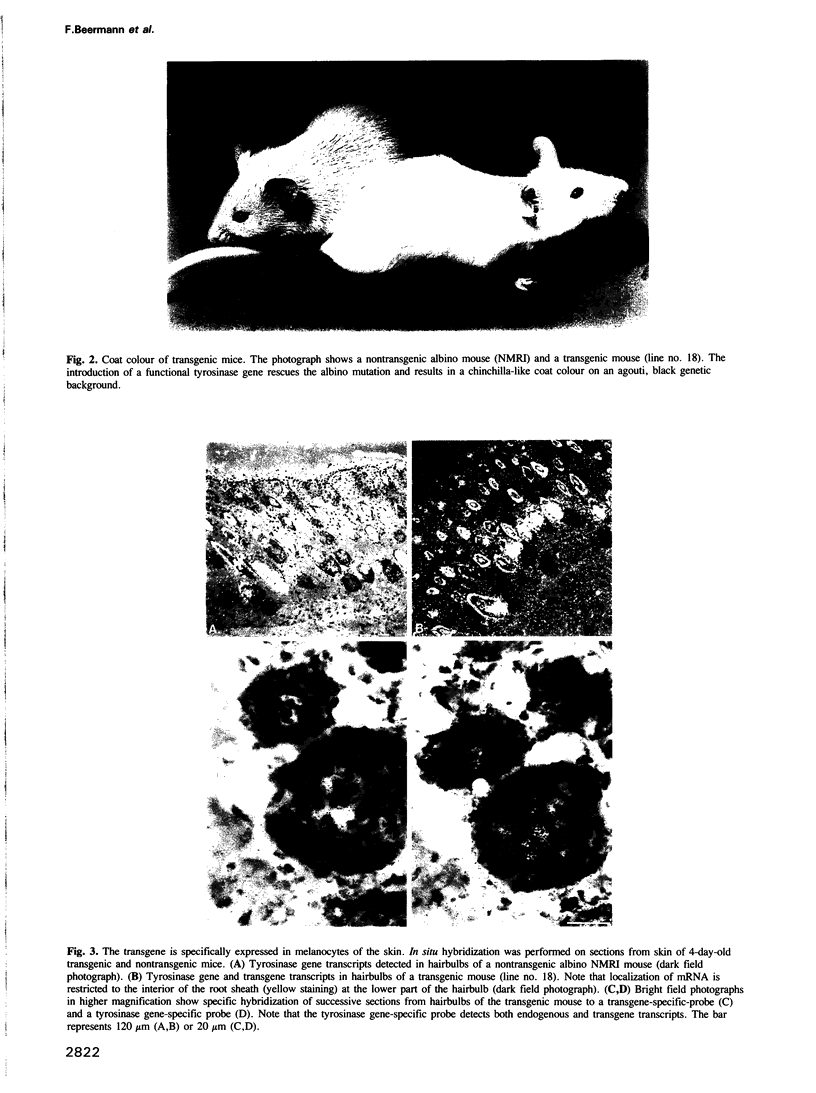
Abstract
The c-locus of the mouse is thought to encode tyrosinase, the key enzyme for melanin synthesis in melanocytes of the skin and the eye. Recently, a mouse cDNA was isolated and shown to confer tyrosine activity on a cell line which expressed no specialized functions for melanin synthesis. To verify that the isolated tyrosinase gene is encoded at the genetically well characterized c-locus, a minigene was assembled from tyrosinase cDNA and tyrosinase genomic DNA and used for generation of transgenic mice. Following microinjection of this construct into fertilized eggs of an albino mouse strain, transgenic mice were obtained which showed pigmentation in skin and eyes. By in situ hybridization, we show expression of the transgene in melanocytes of the hairbulb and in the pigmented cell layers of the eye. We conclude that we have rescued the albino mutation (c/c) by introduction and expression of a functional tyrosinase gene.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J. The neural crest cell lineage problem: neuropoiesis? Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beermann F., Hummler E., Franke U., Hansmann I. Allocation of a transgenic c-myc integration site to mouse chromosome 8B3-C1. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;49(4):311–312. doi: 10.1159/000132685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Ouhayoun J. P., Bader B. L., Collin C., Grund C., Lee I., Franke W. W. Extensive changes in cytokeratin expression patterns in pathologically affected human gingiva. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;58(1):59–77. doi: 10.1007/BF02890059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Allen J. M., Behringer R. R., Gelinas R. E., Palmiter R. D. Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN D. L. Effect of genic substitution on the incorporation of tyrosine into the melanin of mouse skin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Mar;96:562–568. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Concordet J. P., Kaplan J. C., Kahn A. Illegitimate transcription: transcription of any gene in any cell type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2617–2621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaban R., Moellmann G., Tamura A., Kwon B. S., Kuklinska E., Pomerantz S. H., Lerner A. B. Tyrosinases of murine melanocytes with mutations at the albino locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7241–7245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Jiménez M. Analysis of mammalian pigmentation at the molecular level. Pigment Cell Res. 1989 Mar-Apr;2(2):75–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1989.tb00166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Jr Mammalian monophenol monooxygenase (tyrosinase): purification, properties, and reactions catalyzed. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:154–165. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)42024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J. Tyrosinase activity in subcellular fractions of black and albino mice. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 19;245(142):81–83. doi: 10.1038/newbio245081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. J. A cDNA encoding tyrosinase-related protein maps to the brown locus in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4392–4396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Haq A. K., Pomerantz S. H., Halaban R. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for human tyrosinase that maps at the mouse c-albino locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7473–7477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Wakulchik M., Haq A. K., Halaban R., Kestler D. Sequence analysis of mouse tyrosinase cDNA and the effect of melanotropin on its gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1301–1309. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Bosch F. X., Romano V., Zimbelmann R., Höfler H., Franke W. W. Cytokeratin expression in simple epithelia. III. Detection of mRNAs encoding human cytokeratins nos. 8 and 18 in normal and tumor cells by hybridization with cDNA sequences in vitro and in situ. Differentiation. 1986;33(1):69–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. The origins of cellular diversity in the mammalian central nervous system. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):815–821. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90934-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movaghar M. Tyrosinase activity in the first coat of agouti and black mice. Pigment Cell Res. 1989 Sep-Oct;2(5):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1989.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Ruppert S., Schmid E., Schütz G. Functional analysis of alternatively spliced tyrosinase gene transcripts. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2723–2730. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H., Li J. P. Tyrosinase in the skin of albino hamsters and mice. Nature. 1974 Nov 15;252(5480):241–243. doi: 10.1038/252241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman T. P., Specht L. A., Gershon M. D., Joh T. H., Teitelman G., Pickel V. M., Reis D. J. Catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes are expressed in replicating cells of the peripheral but not the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6221–6225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Müller G., Kwon B., Schütz G. Multiple transcripts of the mouse tyrosinase gene are generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2715–2722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03125.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B., Russell W. L. A Study of the Physiological Genetics of Coat Color in the Mouse by Means of the Dopa Reaction in Frozen Sections of Skin. Genetics. 1948 May;33(3):237–262. doi: 10.1093/genetics/33.3.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Baltimore D. Activation of immunoglobulin kappa gene rearrangement correlates with induction of germline kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):1001–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibahara S., Tomita Y., Sakakura T., Nager C., Chaudhuri B., Müller R. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding mouse tyrosinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2413–2427. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Russell L. B., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Allelic variation within the Emv-15 locus defines genomic sequences closely linked to the agouti locus on mouse chromosome 2. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):85–92. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda A., Tomita Y., Okinaga S., Tagami H., Shibahara S. Functional analysis of the cDNA encoding human tyrosinase precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):984–990. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90770-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamate H. B., Hirobe T., Wakamatsu K., Ito S., Shibahara S., Ishikawa K. Levels of tyrosinase and its mRNA in coat-color mutants of C57BL/10J congenic mice: effects of genic substitution at the agouti, brown, albino, dilute, and pink-eyed dilution loci. J Exp Zool. 1989 Jun;250(3):304–311. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402500310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terao M., Tabe L., Garattini E., Sartori D., Studer M., Mintz B. Isolation and characterization of variant cDNAs encoding mouse tyrosinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):848–853. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Takeuchi S., Kudo T., Sato C., Takeuchi T. Melanin production in cultured albino melanocytes transfected with mouse tyrosinase cDNA. Jpn J Genet. 1989 Apr;64(2):121–135. doi: 10.1266/jjg.64.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









