Abstract
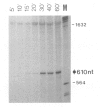
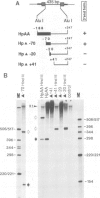
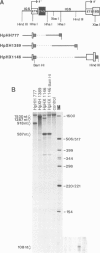
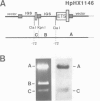
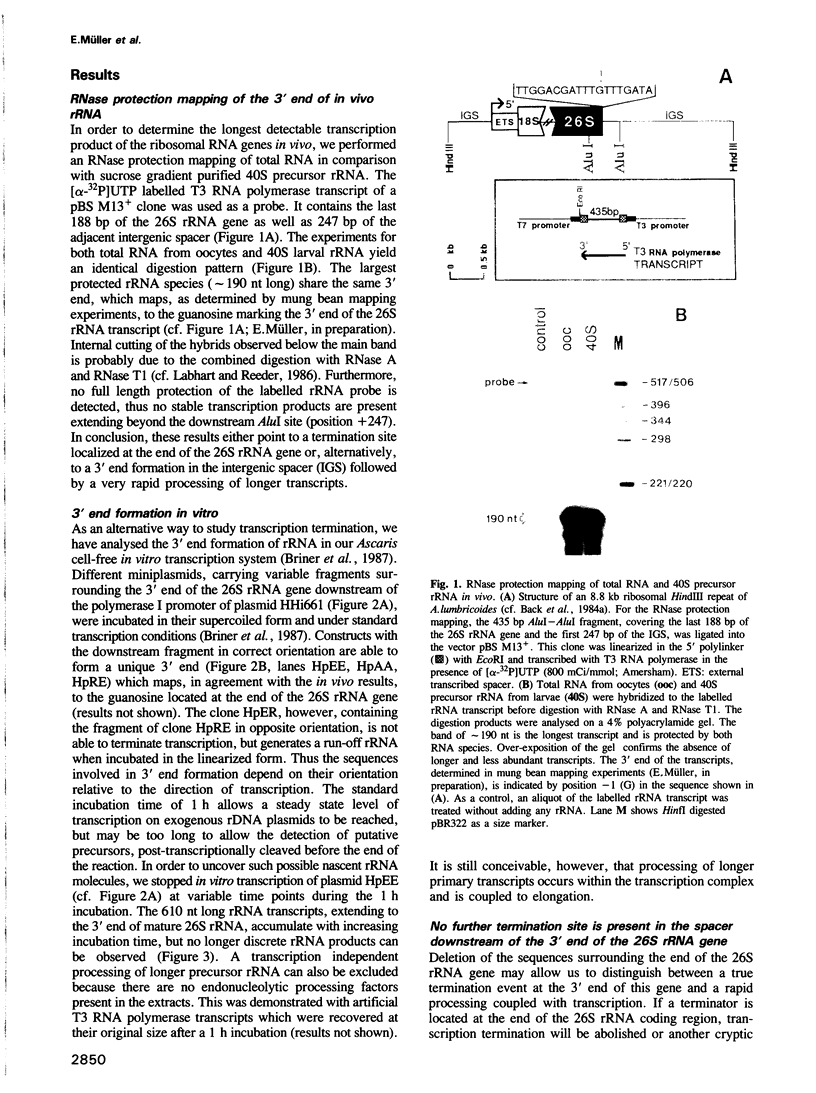
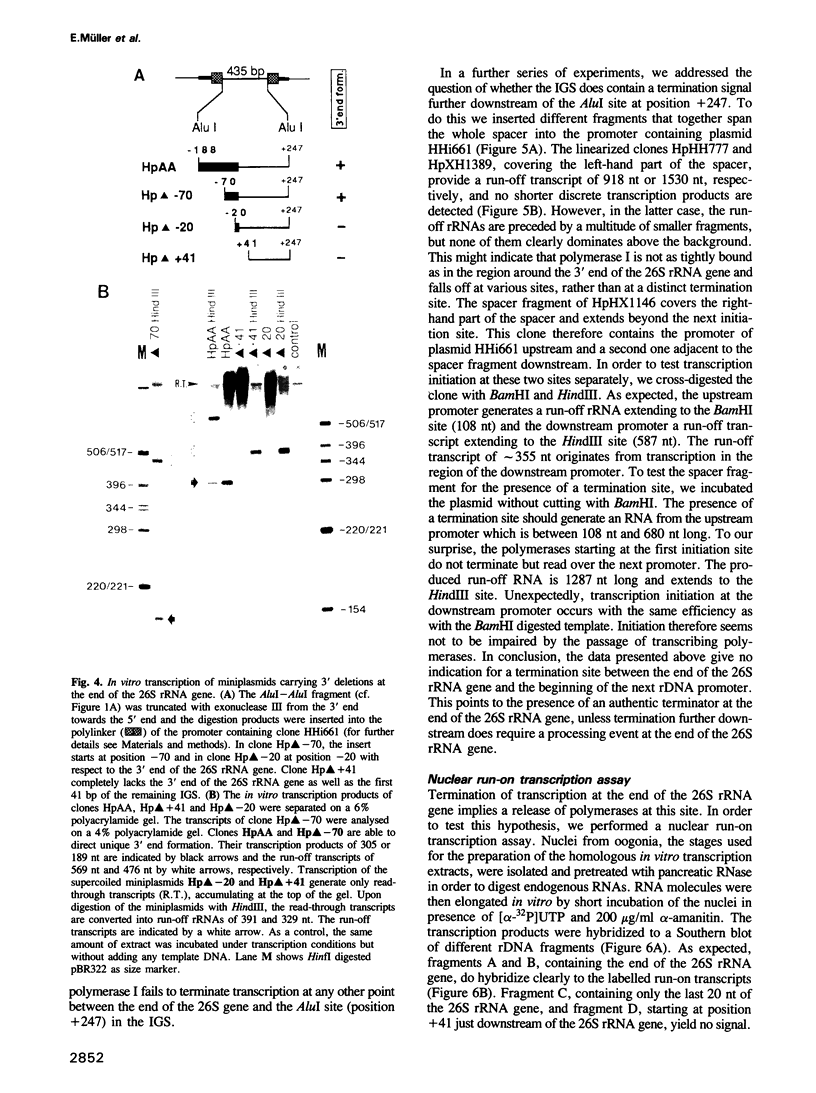
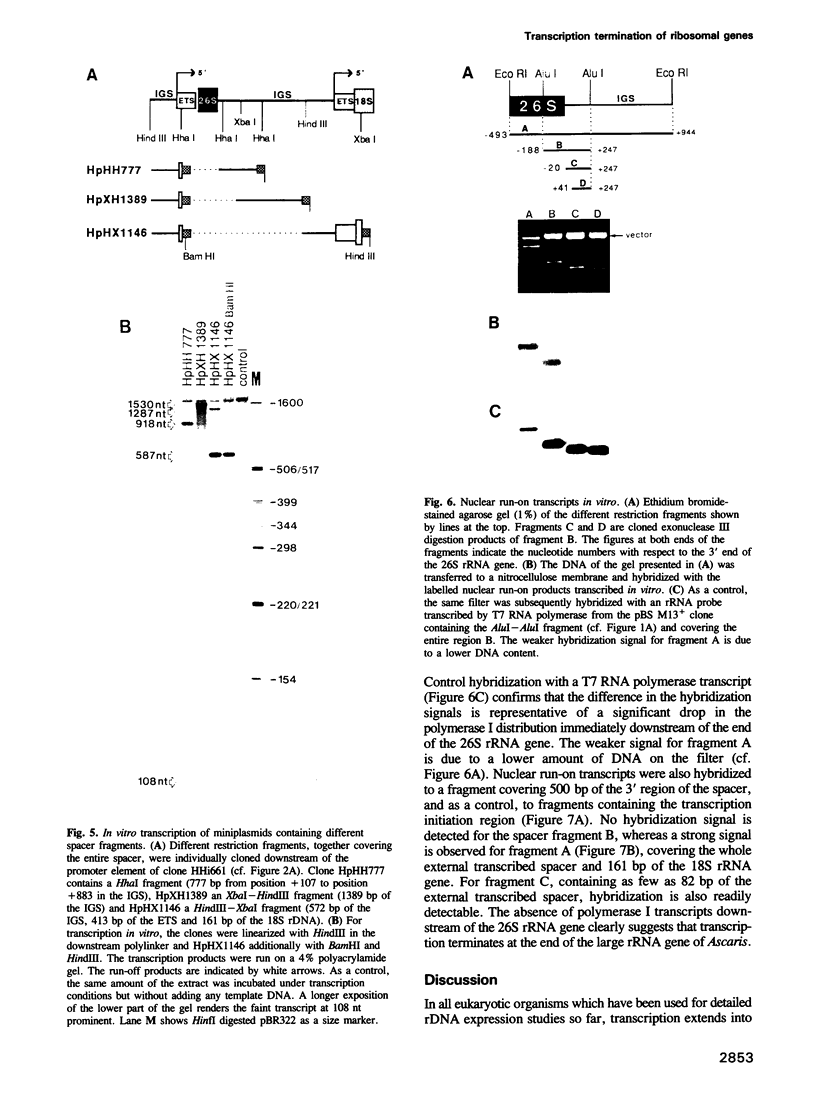
We studied termination of transcription of the ribosomal RNA genes in Ascaris lumbricoides, the first representative in the phylum of nemathelminthes analysed so far. RNase protection experiments in vivo reveal that the 3' end of the precursor rRNA coincides with the end of mature 26S rRNA. Promoter-containing miniplasmids are able to direct unique 3' end formation in vitro at a site identical to that observed in vivo, whereas deletion of these sequences abolishes 3' end formation throughout the entire spacer. A nuclear run-on experiment in vitro confirms the drop of polymerase I concentration down-stream of this site. The termination site for polymerase I transcription of the rDNA operon in A. lumbricoides is therefore unique, and located at the very end of the 26S rRNA gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Back E., Müller F., Tobler H. Structural organization of the two main rDNA size classes of Ascaris lumbricoides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1313–1332. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back E., Van Meir E., Müller F., Schaller D., Neuhaus H., Aeby P., Tobler H. Intervening sequences in the ribosomal RNA genes of Ascaris lumbricoides: DNA sequences at junctions and genomic organization. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2523–2529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. M., Platt T. Pol I transcription: which comes first, the end or the beginning? Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):839–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch I., Schoneberg C., Grummt I. Purification and characterization of TTFI, a factor that mediates termination of mouse ribosomal DNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3891–3897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H., Tjian R. Molecular mechanisms governing species-specific transcription of ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):489–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briner G., Müller E., Neuhaus H., Back E., Müller F., Tobler H. Localization of the in vivo and in vitro transcription initiation site and comparative analysis of the flanking sequences in the two main size classes of Ascaris lumbricoides rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6515–6538. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., Vassalli P. Modulations of functional activity in differentiated macrophages are accompanied by early and transient increase or decrease in c-fos gene transcription. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):949–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. The ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis is transcribed as part of the primary ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6041–6051. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway M. A transcription factor, TFIS, interacts with both the promoter and enhancer of the Xenopus rRNA genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1768–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Sulston J. E., Coulson A. R. The rDNA of C. elegans: sequence and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2345–2364. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Sorbaz H., Hofmann A., Roth E. Spacer sequences downstream of the 28S RNA coding region are part of the mouse rDNA transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2293–2304. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines TJ, Bionta RM, Blewitt G, Bratton CB, Casper D, Claus R, Cortez BG, Errede S, Foster GW, Gajewski W. Calculation of atmospheric neutrino-induced backgrounds in a nucleon-decay search. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Oct 20;57(16):1986–1989. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.57.1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Unusual enhancer function in yeast rRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4986–4993. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Oliemans J., Offenberg H., Dekker A. F., Piper P. W., Planta R. J., Klootwijk J. 3'-End formation of transcripts from the yeast rRNA operon. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2703–2710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermekchiev M. B., Grummt I. Natural point mutations within rat rDNA transcription terminator elements reveal the functional importance of single bases for factor binding and termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4131–4143. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. A point mutation uncouples RNA 3'-end formation and termination during ribosomal gene transcription in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):269–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Heat shock stabilizes highly unstable transcripts of the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):56–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestel R., Yip M., Holland J. P., Wang E., Kang J., Holland M. J. Sequences within the spacer region of yeast rRNA cistrons that stimulate 35S rRNA synthesis in vivo mediate RNA polymerase I-dependent promoter and terminator activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1243–1254. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Kominami R., Yoshikura H., Sudo K., Muramatsu M. Transcription termination and RNA processing in the 3'-end spacer of mouse ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2043–2058. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Mitchelson K., de Winter R. The promotion of ribosomal transcription in eukaryotes. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1985;2:207–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus H., Müller F., Etter A., Tobler H. Type I-like intervening sequences are found in the rDNA of the nematode Ascaris lumbricoides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7689–7707. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. A., Bond U. Analysis of pre-rRNAs in heat-shocked HeLa cells allows identification of the upstream termination site of human polymerase I transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2500–2512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., McStay B., Schultz M. C., Bell S. P., Reeder R. H. The Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers bind an essential polymerase I transcription factor, xUBF. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1779–1788. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Labhart P., McStay B. Processing and termination of RNA polymerase I transcripts. Bioessays. 1987 Mar;6(3):108–112. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Pittet A. C. Two promoters of different strengths control the transcription of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a in the parotid gland and the liver. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skryabin K. G., Eldarov M. A., Larionov V. L., Bayev A. A., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Veldman G. M., Planta R. J., Georgiev O. I., Hadjiolov A. A. Structure and function of the nontranscribed spacer regions of yeast rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2955–2968. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sáfrány G., Kominami R., Muramatsu M., Hidvégi E. J. Transcription of human ribosomal DNA may terminate at multiple sites. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Dover G. A. Transcription of the tandem array of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster does not terminate at any fixed point. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1267–1273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker K., Wong W. M., Nazar R. N. Termination region in rRNA genes from a eucaryotic thermophile, Thermomyces lanuginosus. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):377–381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sande C. A., Kulkens T., Kramer A. B., de Wijs I. J., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Termination of transcription by yeast RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9127–9146. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]