Abstract
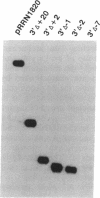
By using a recently developed in vitro transcription assay, the 16S/23S rRNA-encoding DNA promoter from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. B12 was dissected by deletion and linker substitution mutagenesis. The analysis of 5' and 3' deletion mutants defined a core promoter region between positions -38 and -2 containing all information for efficient and specific transcription. Further characterization of this region by linker substitution mutagenesis indicated two sequence elements important for promoter function--one located between positions -38 and -25 (distal promoter element) and the other one located between positions -11 and -2 (proximal promoter element). The distal promoter element encompassed the TATA-like "box A" element located approximately 26 nucleotides upstream of the majority of transcription start sites in archaebacteria (Archaeobacteria). All mutations within this box A motif virtually abolished promoter function. Complete inactivation of the proximal promoter element was dependent on extensive mutagenesis; this element is not conserved between archaebacterial promoters except for a high A + T content in stable RNA gene promoters from Sulfolobus. Mutants containing insertions or deletions between the distal and proximal promoter elements were only slightly affected in their transcription efficiency but displayed a shift in their major initiation site, retaining an essentially fixed distance between the distal promoter element and the transcription start site. Thus, efficient transcription and start-site selection were dependent on a conserved TATA-like sequence centered approximately 26 nucleotides upstream of the initiation site, a situation unlike that of eubacterial promoters but resembling the core structure of most eukaryotic RNA polymerase II (and some RNA polymerase III) promoters. This finding suggests a common evolutionary origin of these promoters consistent with the known similarities between archaebacterial and eukaryotic RNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama T., Takanami M., Ohtsuka E., Taniyama Y., Marumoto R., Sato H., Ikehara M. Essential structure of E. coli promoter: effect of spacer length between the two consensus sequences on promoter function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5855–5864. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berghöfer B., Kröckel L., Körtner C., Truss M., Schallenberg J., Klein A. Relatedness of archaebacterial RNA polymerase core subunits to their eubacterial and eukaryotic equivalents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8113–8128. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P., Trifonov E. N. Compilation and analysis of eukaryotic POL II promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):10009–10026. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.10009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Schnabel R., Sentenac A., Zillig W. Archaebacteria and eukaryotes possess DNA-dependent RNA polymerases of a common type. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1291–1294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüdepohl U., Reiter W. D., Zillig W. In vitro transcription of two rRNA genes of the archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. B12 indicates a factor requirement for specific initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5851–5855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Promoter selectivity of prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Trends Genet. 1988 Oct;4(10):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaine B. P., Gupta R., Woese C. R. Putative introns in tRNA genes of prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3309–3312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Gropp F., Lottspeich F., Zillig W., Garrett R. A. Sequence, organization, transcription and evolution of RNA polymerase subunit genes from the archaebacterial extreme halophiles Halobacterium halobium and Halococcus morrhuae. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Moorefield B., Pieler T. Common mechanisms of promoter recognition by RNA polymerases II and III. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pühler G., Leffers H., Gropp F., Palm P., Klenk H. P., Lottspeich F., Garrett R. A., Zillig W. Archaebacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerases testify to the evolution of the eukaryotic nuclear genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4569–4573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pühler G., Lottspeich F., Zillig W. Organization and nucleotide sequence of the genes encoding the large subunits A, B and C of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4517–4534. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P. Identification and characterization of a defective SSV1 genome integrated into a tRNA gene in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. B12. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Mar;221(1):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00280369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Voos W., Kaniecki J., Grampp B., Schulz W., Zillig W. Putative promoter elements for the ribosomal RNA genes of the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. strain B12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5581–5595. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Zillig W. Analysis of transcription in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus indicates that archaebacterial promoters are homologous to eukaryotic pol II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):1–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B. Surprises in polymerase III transcription. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Wich G. An archaebacterial promoter element for stable RNA genes with homology to the TATA box of higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):151–163. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B. Transcription elements and factors of RNA polymerase B promoters of higher eukaryotes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(2):77–120. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Hummel H., Jarsch M., Bär U., Böck A. Transcription signals for stable RNA genes in Methanococcus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2459–2479. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]