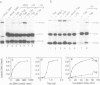
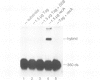
Abstract
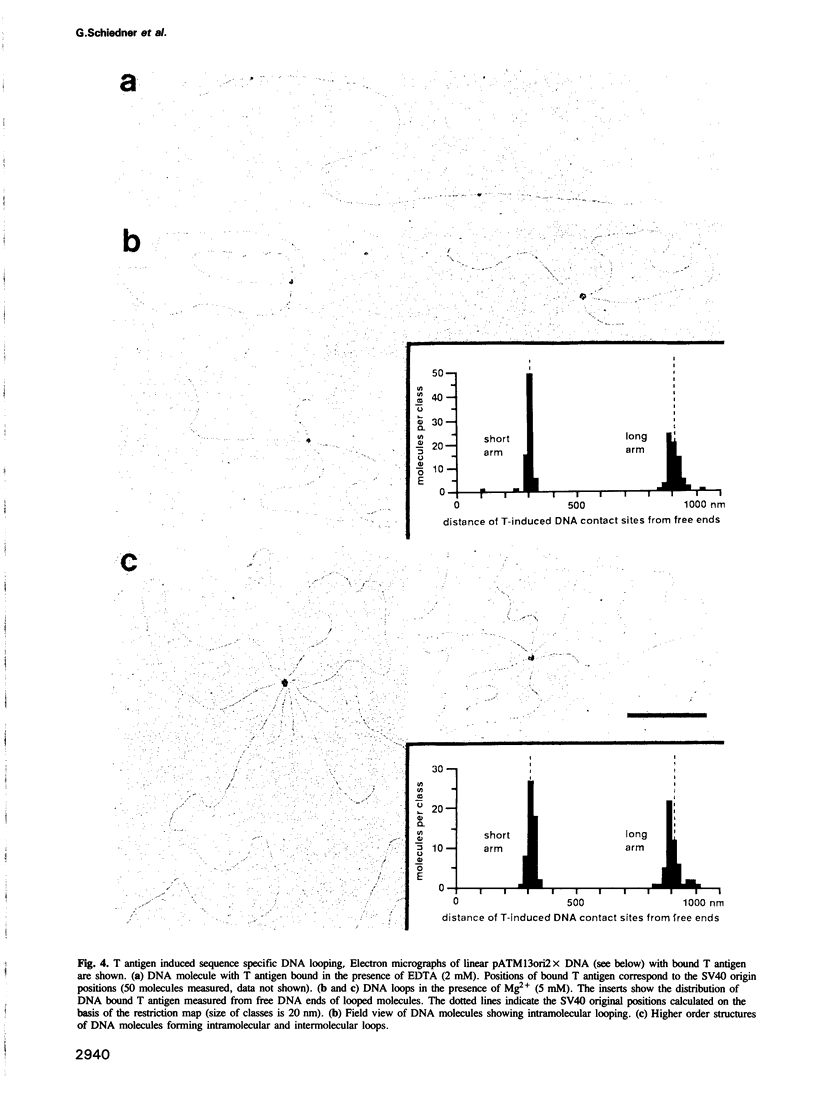
Simian virus 40 large tumour antigen (T antigen) is shown to catalyse the formation of duplex DNA from complementary strands in specific conditions. The activity is dependent on an excess of unspecific double-stranded DNA and seems not to function by T antigen mediated destabilization of secondary structure. Rather, protein-protein contacts between T antigen molecules appear to be involved. Protein-protein interactions between T antigen molecules bound to physically separated DNA sites are also demonstrated by the formation of specific DNA loops and by cyclization of DNA molecules with 3'-extended single-stranded ends where T antigen specifically binds to the single-stranded/double-stranded junctions. The relevance of these properties for T antigen functions in DNA replication, transcription and(or) recombination is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai N., Arai K., Kornberg A. Complexes of Rep protein with ATP and DNA as a basis for helicase action. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5287–5293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auborn K. J., Markowitz R. B., Wang E., Yu Y. T., Prives C. Simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen binds specifically to double-stranded DNA but not to single-stranded DNA or DNA/RNA hybrids containing the SV40 regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2204–2208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2204-2208.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. H., Basilico C. Induction of sister chromatid exchange by polyoma large viral tumor antigen in transformed rat fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1982 May;42(5):1909–1912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant F. R., Lehman I. R. On the mechanism of renaturation of complementary DNA strands by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerni C., Mougneau E., Zerlin M., Julius M., Marcu K. B., Cuzin F. c-myc and functionally related oncogenes induce both high rates of sister chromatid exchange and abnormal karyotypes in rat fibroblasts. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;132:193–201. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71562-4_28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia W., Rigby P. W. Fate of viral DNA in nonpermissive cells infected with simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6638–6642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Baldwin R. L. Catalysis of DNA reassociation by the Escherichia coli DNA binding protein: A polyamine-dependent reaction. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):441–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley E. C., West S. C. Homologous pairing and the formation of nascent synaptic intermediates between regions of duplex DNA by RecA protein. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):987–995. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90632-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymes of general recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:229–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Borowiec J. A., Ishimi Y., Deb S., Tegtmeyer P., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen requires three core replication origin domains for DNA unwinding and replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8267–8271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Valle G., Fenton R. G., Basilico C. Polyoma large T antigen regulates the integration of viral DNA sequences into the genome of transformed cells. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganea D., Moore P., Chekuri L., Kucherlapati R. Characterization of an ATP-dependent DNA strand transferase from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3124–3130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacherio D., Hager L. P. A poly(dT)-stimulated ATPase activity associated with simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8113–8116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J. D. Bacterial gene regulation from distant DNA sites. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):193–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90955-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Hochschild A., Ptashne M. DNA loops induced by cooperative binding of lambda repressor. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):750–752. doi: 10.1038/322750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr, Gurney E. G. Spontaneous rearrangement of integrated simian virus 40 DNA in nine transformed rodent cell lines. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):165–174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.165-174.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker D., Fluck M. M. High-level recombination specific to polyomavirus genomes targeted to the integration-transformation pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):995–1004. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel S. S., Krysan P. J., Calos M. P., DuBridge R. B. Use of simian virus 40 replication to amplify Epstein-Barr virus shuttle vectors in human cells. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3738–3746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3738-3746.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Laroche T., Brand A. H., Gasser S. M. RAP-1 factor is necessary for DNA loop formation in vitro at the silent mating type locus HML. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90788-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Tabata S., Bouchard R. A., Piñon R., Stern H. General recombination mechanisms in extracts of meiotic cells. Chromosoma. 1985;93(2):140–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00293161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin M., de Villiers J., Weber F., Schaffner W. High frequency of homologous recombination in mammalian cells between endogenous and introduced SV40 genomes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Essential contact residues within SV40 large T antigen binding sites I and II identified by alkylation-interference. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausing K., Scheidtmann K. H., Baumann E. A., Knippers R. Effects of in vitro dephosphorylation on DNA-binding and DNA helicase activities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1258–1265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1258-1265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E., Holloman W. K. Homologous pairing of DNA molecules promoted by a protein from Ustilago. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Clow J., Krupp R. A. Properties of the duplex DNA-dependent ATPase activity of Escherichia coli RecA protein and its role in branch migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Niemöller M., Amouyal M., Revet B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. lac repressor forms loops with linear DNA carrying two suitably spaced lac operators. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1481–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. II. Nature of the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur H., Walter G. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the carboxy terminus of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):483–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.483-491.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Hough P. V., Wall J. S., Dodson M., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. ATP-dependent assembly of double hexamers of SV40 T antigen at the viral origin of DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):658–662. doi: 10.1038/338658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz B., Schlehofer J. R., Zur Hausen H., Huber B., Fanning E. HSV- and chemical carcinogen-induced amplification of SV40 DNA sequences in transformed cells is cell-line-dependent. Int J Cancer. 1985 Apr 15;35(4):521–525. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. G., Sander M., Lowenhaupt K., Rich A. Sensitive homologous recombination strand-transfer assay: partial purification of a Drosophila melanogaster enzyme and detection of sequence effects on the strand-transfer activity of RecA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5854–5858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVey D., Brizuela L., Mohr I., Marshak D. R., Gluzman Y., Beach D. Phosphorylation of large tumour antigen by cdc2 stimulates SV40 DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):503–507. doi: 10.1038/341503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. R., Hirt B., Weil R. Mouse cellular DNA enclosed in polyoma viral capsids (pseudovirions). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1381–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Bullock P., Botchan M. Simian virus 40 T antigen is required for viral excision from chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7534–7538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Stillman B., Gluzman Y. Regulation of SV40 DNA replication by phosphorylation of T antigen. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenarh M., Henning R. Self-assembly of simian virus 40 large T antigen oligomers by divalent cations. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):531–538. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.531-538.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Williams R. C., Tjian R. Oligomeric structure of a simian virus 40 T antigen in free form and bound to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müeller-Storm H. P., Sogo J. M., Schaffner W. An enhancer stimulates transcription in trans when attached to the promoter via a protein bridge. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Bradt C. I., Toji L. H., Godley M., Segawa M. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges by transformation with simian virus 40. Cancer Res. 1978 Apr;38(4):960–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkin L. C., Steinberg V. I., Kosz-Vnenchak M. Human glioblastoma cells persistently infected with simian virus 40 carry nondefective episomal viral DNA and acquire the transformed phenotype and numerous chromosomal abnormalities. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):658–666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.658-666.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Wabiko H., Tsurimoto T., Horii T., Masukata H., Ogawa H. Characteristics of purified recA protein and the regulation of its synthesis in vivo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):909–915. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piché A., Bourgaux P. Resolution of a polyomavirus-mouse hybrid replicon: viral function required for recombination. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):845–850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.845-850.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Homologous pairing and strand exchange in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:405–437. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Craig N. L., Phizicky E. M. Activity of the Escherichia coli recA-gene product. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):917–920. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubnitz J., Subramani S. Rapid assay for extrachromosomal homologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):529–537. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Knippers R., Stahl H. RNA unwinding activity of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):955–963. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90334-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Wessel R., Stahl H. SV40 T antigen catalyzed duplex DNA unwinding. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;144:37–45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74578-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Wessel R., Stahl H. Sequence independent duplex DNA opening reaction catalysed by SV40 large tumor antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):93–106. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif R. New properties of simian virus 40 large T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1463–1471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Homologous recombination in E. coli: multiple pathways for multiple reasons. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):807–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90929-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillman T., Giacherio D., Hager L. P. Single strand DNA binding of simian virus 40 tumor antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3100–3104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Zentgraf H., Knippers R. A large-tumor-antigen-specific monoclonal antibody inhibits DNA replication of simian virus 40 minichromosomes in an in vitro elongation system. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):473–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.473-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Knippers R. The simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 9;910(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Debatisse M., Giulotto E., Wahl G. M. Recent progress in understanding mechanisms of mammalian DNA amplification. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stary A., James M. R., Sarasin A. High recombination rate of an Epstein-Barr virus-simian virus 40 hybrid shuttle vector in human cells. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3837–3843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3837-3843.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak A., DiCapua E., Koller T. Unwinding of duplex DNA in complexes with recA protein. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):811–820. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B., Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. T antigen and template requirements for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2933–2939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss M., Lübbe L., Kiessling U., Platzer M., Griffin B. E. The mutagenic and immortalizing potential of polyoma virus large T antigen. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;144:129–134. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74578-2_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Lewton B. A., DeLucia A. L., Wilson V. G., Ryder K. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of protein bound to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):151–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.151-161.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider H. J., Sogo J. M., Koller T. A routine method for protein-free spreading of double- and single-stranded nucleic acid molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):83–87. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahls W. P., Moore P. D. Homologous recombination enhancement conferred by the Z-DNA motif d(TG)30 is abrogated by simian virus 40 T antigen binding to adjacent DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):794–800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. ATP-dependent renaturation of DNA catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):126–130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C. Protein-DNA interactions in genetic recombination. Trends Genet. 1988 Jan;4(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiekowski M., Dröge P., Stahl H. Monoclonal antibodies as probes for a function of large T antigen during the elongation process of simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):411–418. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.411-418.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiekowski M., Schwarz M. W., Stahl H. Simian virus 40 large T antigen DNA helicase. Characterization of the ATPase-dependent DNA unwinding activity and its substrate requirements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):436–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]