Abstract
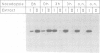
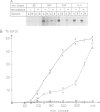
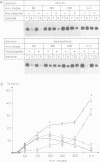
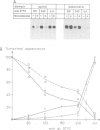
Endogenous plasma membrane proteins are sorted from two sites in the human intestinal epithelial cell line Caco-2. Apical proteins are transported from the Golgi apparatus to the apical domain along a direct pathway and an indirect pathway via the basolateral membrane. In contrast, basolateral proteins never appear in the apical plasma membrane. Here we report on the effect of the microtubule-active drug nocodazole on the post-synthetic transport and sorting of plasma membrane proteins. Pulse-chase radiolabeling was combined with domain-specific cell surface assays to monitor the appearance of three apical and one basolateral protein in plasma membrane domains. Nocodazole was found to drastically retard both the direct transport of apical proteins from the Golgi apparatus and the indirect transport (transcytosis) from the basolateral membrane to the apical cell surface. In contrast, neither the transport rates of the basolateral membrane nor the sorting itself were significantly affected by the nocodazole treatment. We conclude that an intact microtubular network facilitates, but is not necessarily required for, the transport of apical membrane proteins along the two post-Golgi pathways to the brush border.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacallao R., Antony C., Dotti C., Karsenti E., Stelzer E. H., Simons K. The subcellular organization of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells during the formation of a polarized epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2817–2832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacallao R., Antony C., Dotti C., Karsenti E., Stelzer E. H., Simons K. The subcellular organization of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells during the formation of a polarized epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2817–2832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartles J. R., Feracci H. M., Stieger B., Hubbard A. L. Biogenesis of the rat hepatocyte plasma membrane in vivo: comparison of the pathways taken by apical and basolateral proteins using subcellular fractionation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1241–1251. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G., Carlet E., Wild G., Parsons S. Influence of colchicine and vinblastine on the intracellular migration of secretory and membrane glycoproteins: III. Inhibition of intracellular migration of membrane glycoproteins in rat intestinal columnar cells and hepatocytes as visualized by light and electron-microscope radioautography after 3H-fucose injection. Am J Anat. 1984 Aug;170(4):545–566. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001700404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., Ginsel L. A., Mulder-Stapel A. A., Onderwater J. J., Daems W. T. The effect of colchicine on the intracellular transport of 3H-fucose-labelled glycoproteins in the absorptive cells of cultured human small-intestinal tissue. An autoradiographical and biochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;215(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00236244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan M. J., Anderson H. C., Palade G. E., Jamieson J. D. Intracellular sorting and polarized cell surface delivery of (Na+,K+)ATPase, an endogenous component of MDCK cell basolateral plasma membranes. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):623–631. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90888-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen E. M., Cowell G. M., Poulsen S. S. Biosynthesis of intestinal microvillar proteins. Role of the Golgi complex and microtubules. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 15;216(1):37–42. doi: 10.1042/bj2160037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Brabander M. J., Van de Veire R. M., Aerts F. E., Borgers M., Janssen P. A. The effects of methyl (5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl) carbamate, (R 17934; NSC 238159), a new synthetic antitumoral drug interfering with microtubules, on mammalian cells cultured in vitro. Cancer Res. 1976 Mar;36(3):905–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers U., Klumperman J., Hauri H. P. Nocodazole, a microtubule-active drug, interferes with apical protein delivery in cultured intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):13–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger A., Pavelka M., Gangl A. Effect of colchicine on rat small intestinal absorptive cells. II. Distribution of label after incorporation of [3H]fucose into plasma membrane glycoproteins. J Ultrastruct Res. 1983 Dec;85(3):260–271. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(83)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G., Borisy G. G. Microtubule distribution in cultured cells and intact tissues: improved immunolabeling resolution through the use of reversible embedment cytochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6889–6893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen S. J., Allan C. H., Trier J. S. Demonstration of microtubules in the terminal web of mature absorptive cells from the small intestine of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Jun;248(3):709–711. doi: 10.1007/BF00216503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Bucher K. Immunoblotting with monoclonal antibodies: importance of the blocking solution. Anal Biochem. 1986 Dec;159(2):386–389. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst J. J., Hurwitz R., Sunshine P., Kretchmer N. Effect of colchicine on intestinal disaccharidases: correlation with biochemical aspects of cellular renewal. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):530–536. doi: 10.1172/JCI106263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugon J. S., Bennett G., Pothier P., Ngoma Z. Loss of microtubules and alteration of glycoprotein migration in organ cultures of mouse intestine exposed to nocodazole or colchicine. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Jun;248(3):653–662. doi: 10.1007/BF00216496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Microtubules, membrane traffic, and cell organization. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90206-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E. Microtubules containing detyrosinated tubulin are less dynamic. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2597–2606. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Le Bivic A., Sargiacomo M., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Steady-state distribution and biogenesis of endogenous Madin-Darby canine kidney glycoproteins: evidence for intracellular sorting and polarized cell surface delivery. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2117–2127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Sorting of an apical plasma membrane glycoprotein occurs before it reaches the cell surface in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2131–2139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Brauchbar M., Bucher K., Hauri H. P. Sorting of endogenous plasma membrane proteins occurs from two sites in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Stieger B., Klumperman J., Ginsel L., Hauri H. P. Endocytosis, recycling, and lysosomal delivery of brush border hydrolases in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3503–3512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misek D. E., Bard E., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Biogenesis of epithelial cell polarity: intracellular sorting and vectorial exocytosis of an apical plasma membrane glycoprotein. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90460-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Nakane P. K., Brown W. R. Translocation of dimeric IgA through neoplastic colon cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2359–2368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parczyk K., Haase W., Kondor-Koch C. Microtubules are involved in the secretion of proteins at the apical cell surface of the polarized epithelial cell, Madin-Darby canine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16837–16846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. MAP 1C is a microtubule-activated ATPase which translocates microtubules in vitro and has dynein-like properties. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1273–1282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavelka M., Ellinger A. Effect of colchicine on the Golgi apparatus and on GERL of rat jejunal absorptive cells. Ultrastructural localization of thiamine pyrophosphatase and acid phosphatase activity. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;24(1):53–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavelka M., Gangl A. Effects of colchicine on the intestinal transport of endogenous lipid. Ultrastructural, biochemical, and radiochemical studies in fasting rats. Gastroenterology. 1983 Mar;84(3):544–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Bravo R., Simons K. Transcytosis of the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus after implantation into the apical membrane of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. II. Involvement of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):803–809. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaroni A., Kirsch K., Weiser M. M. Synthesis of membrane glycoproteins in rat small-intestinal villus cells. Effect of colchicine on the redistribution of L-[1,5,6-3H]fucose-labelled membrane glycoproteins among Golgi, lateral basal and microvillus membranes. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 15;182(1):213–221. doi: 10.1042/bj1820213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Ivanov I. E., Plesken H., Sabatini D. D. Polarized delivery of viral glycoproteins to the apical and basolateral plasma membranes of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells infected with temperature-sensitive viruses. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):136–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Ivanov I. E., Sabatini D. D. Microtubule-acting drugs lead to the nonpolarized delivery of the influenza hemagglutinin to the cell surface of polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):231–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogalski A. A., Singer S. J. Associations of elements of the Golgi apparatus with microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1092–1100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas P. J., Misek D. E., Vega-Salas D. E., Gundersen D., Cereijido M., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Microtubules and actin filaments are not critically involved in the biogenesis of epithelial cell surface polarity. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1853–1867. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandoz D., Lainé M. C., Nicolas G. Distribution of microtubules within the intestinal terminal web as revealed by quick-freezing and cryosubstitution. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;39(2):481–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp B. J., Vale R. D., Sheetz M. P., Reese T. S. Single microtubules from squid axoplasm support bidirectional movement of organelles. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M. Cell motility: multiple microtubule motors. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):118–120. doi: 10.1038/343118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Fransen J. A., Bächi T., Ginsel L., Hauri H. P. Identification, by a monoclonal antibody, of a 53-kD protein associated with a tubulo-vesicular compartment at the cis-side of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1643–1653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon F. Direct identification of microtubule-associated proteins by selective extraction of cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:139–147. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbings H. How is microtubule-based organelle translocation regulated? J Cell Sci. 1990 Jan;95(Pt 1):5–7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., Matter K., Baur B., Bucher K., Höchli M., Hauri H. P. Dissection of the asynchronous transport of intestinal microvillar hydrolases to the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1853–1861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Moskalewski S. Microtubules and the organization of the Golgi complex. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jul;159(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. R., Tartakoff A. M. The response of the Golgi complex to microtubule alterations: the roles of metabolic energy and membrane traffic in Golgi complex organization. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2081–2088. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Goldstein L. S. One motor, many tails: an expanding repertoire of force-generating enzymes. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):883–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90334-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D. Intracellular transport using microtubule-based motors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:347–378. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80099-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Sluijs P., Bennett M. K., Antony C., Simons K., Kreis T. E. Binding of exocytic vesicles from MDCK cells to microtubules in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1990 Apr;95(Pt 4):545–553. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.4.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]