Abstract
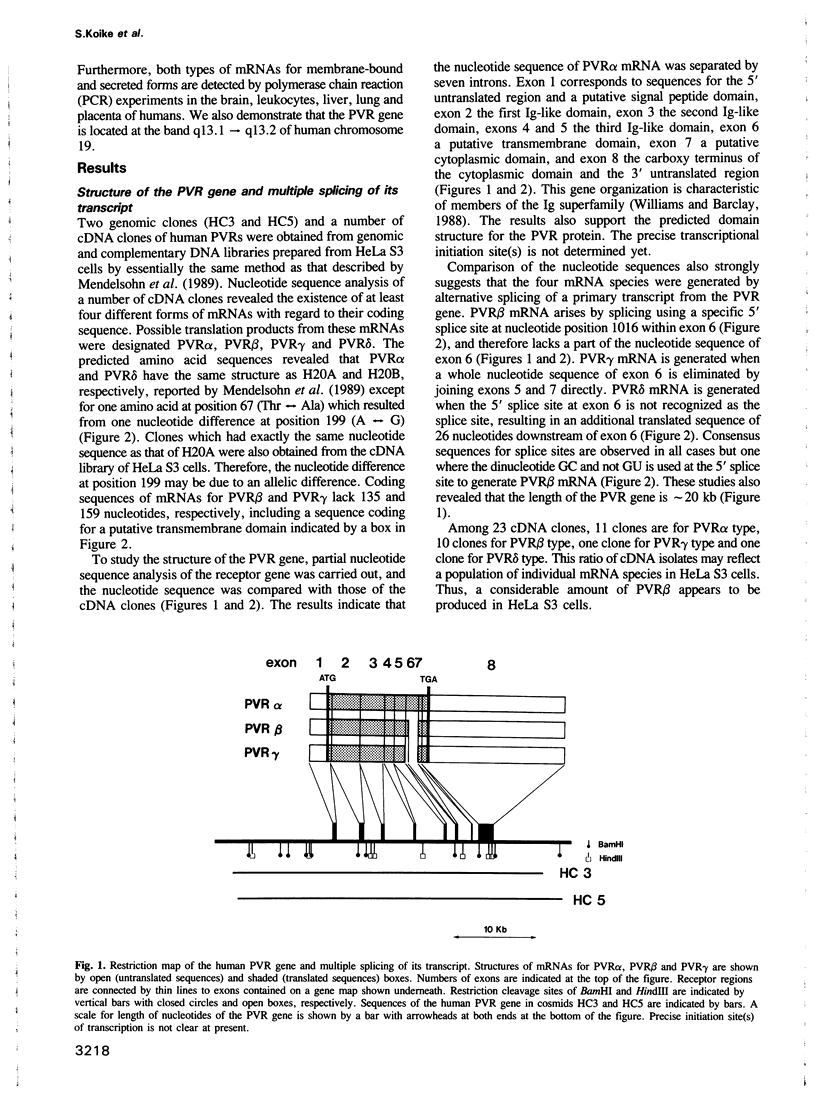
Both genomic and complementary DNA clones encoding poliovirus receptors were isolated from genomic and complementary DNA libraries prepared from HeLa S3 cells, respectively. Nucleotide sequence analysis of these cloned DNAs revealed that the poliovirus receptor gene is approximately 20 kb long and contains seven introns in the coding region, and that at least four mRNA isoforms referring to the coding sequence are generated by alternative splicing and appear to encode four different molecules, that is, PVR alpha, PVR beta, PVR gamma and PVR delta. The predicted amino acid sequences indicate that PVR alpha and PVR delta, corresponding to the previously described cDNA clones H20A and H20B, respectively, are integral membrane proteins while the other two molecules described here for the first time lack a putative transmembrane domain. Mouse cell transformants carrying PVR alpha were permissive for poliovirus infection, but those carrying PVR beta were hardly permissive. In contrast to PVR alpha, PVR beta was not detected on the surface of the mouse cell transformants but was detected in the culture fluid by an immunological method using a monoclonal antibody against poliovirus receptor. Three types of splicing products for PVR alpha, PVR beta and PVR gamma were detected by polymerase chain reactions using appropriate primers in poly(A)+ RNAs of the brain, leukocyte, liver, lung and placenta of humans; the choice of primers used did not permit detection of PVR delta. In situ hybridization using a cDNA fragment as a probe demonstrated that the PVR gene is located at the band q13.1----13.2 of human chromosome 19.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BODIAN D. Emerging concept of poliomyelitis infection. Science. 1955 Jul 15;122(3159):105–108. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3159.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower H. J., Barton C. H., Elsom V. L., Thompson J., Moore S. E., Dickson G., Walsh F. S. Alternative splicing generates a secreted form of N-CAM in muscle and brain. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):955–964. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90241-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., McLAREN L. C., SYVERTON J. T. The mammalian cell-virus relationship. IV. Infection of naturally insusceptible cells with enterovirus ribonucleic acid. J Exp Med. 1959 Jul 1;110(1):65–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Receptor affinities as major determinants of enterovirus tissue tropisms in humans. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:312–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura N., Kohara M., Abe S., Komatsu T., Tago K., Arita M., Nomoto A. Determinants in the 5' noncoding region of poliovirus Sabin 1 RNA that influence the attenuation phenotype. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1302–1309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1302-1309.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund T., Grosveld F. G., Flavell R. A. Isolation of transforming DNA by cosmid rescue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):520–524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Mechanism of entry into the cytosol of poliovirus type 1: requirement for low pH. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1194–1200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Johnson B., Lionetti K. A., Nobis P., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Transformation of a human poliovirus receptor gene into mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Pipkin P. A., Hockley D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Monoclonal antibodies which block cellular receptors of poliovirus. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobis P., Zibirre R., Meyer G., Kühne J., Warnecke G., Koch G. Production of a monoclonal antibody against an epitope on HeLa cells that is the functional poliovirus binding site. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2563–2569. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Kawaichi M., Brownstein M., Lee F., Yokota T., Arai K. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA; construction and screening of cDNA expression libraries for mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:3–28. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B. Pathogenesis of poliomyelitis; reappraisal in the light of new data. Science. 1956 Jun 29;123(3209):1151–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3209.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepley M. P., Sherry B., Weiner H. L. Monoclonal antibody identification of a 100-kDa membrane protein in HeLa cells and human spinal cord involved in poliovirus attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7743–7747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique T., McKinney R., Hung W. Y., Bartlett R. J., Bruns G., Mohandas T. K., Ropers H. H., Wilfert C., Roses A. D. The poliovirus sensitivity (PVS) gene is on chromosome 19q12----q13.2. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J. ACE1 regulates expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M. C., Satoh H., Sasaki M., Semba K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Regional location of a novel yes-related proto-oncogene, syn, on human chromosome 6 at band q21. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;77(11):1059–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]