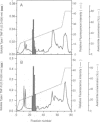
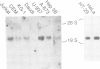
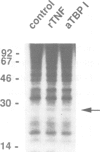
Abstract
Two proteins which specifically bind tumor necrosis factor (TNF) have recently been isolated from human urine in our laboratory. The two proteins cross-react immunologically with two species of cell surface TNF receptors (TNF-R). Antibodies against one of the two TNF binding proteins (TBPI) were found to have effects characteristic of TNF, including stimulating phosphorylation of specific cellular proteins. Oligonucleotide probes designed on the basis of the NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of TBPI were used to clone the cDNA for the structurally related cell surface type 1 TNF-R. It is notable that although this receptor can signal the phosphorylation of cellular proteins, it appears from its amino acid sequence to be devoid of intrinsic protein kinase activity. The extracellular domain of the receptor is composed of four internal cysteine-rich repeats, homologous to structures repeated four times in the extracellular domains of the nerve growth factor receptor and the B lymphocytes surface antigen CDw40. The amino acid composition and size of the extracellular domain of the type I TNF-R closely resemble those of TBPI. The COOH-terminal amino acid sequence of the four cysteine rich repeats within the extracellular domain of the type I TNF-R matches the COOH-terminal sequence of TBPI. Amino acid sequences in the extracellular domain also fully match other sequences found in TBPI. On the other hand, amino acid sequences in the soluble form of the type II TNF-R (TBPII), while indicating a marked homology of structure, did not suggest any identity between this protein and the extracellular domain of the type I TNF-R. CHO cells transfected with type I TNF-R cDNA produced both cell surface and soluble forms of the receptor. The receptor produced by CHO cells was recognized by several monoclonal antibodies against TBPI, reacting with several distinct epitopes in this molecule. These data suggest that the soluble forms of the TNF-Rs are structurally identical to the extracellular cytokine binding domains of these receptors and are consistent with the notion that the soluble forms are, at least partly, derived from the same transcripts that encode the cell surface receptors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aden D. P., Fogel A., Plotkin S., Damjanov I., Knowles B. B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):615–616. doi: 10.1038/282615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. C., Dixon J. E. A procedure for in situ alkylation of cystine residues on glass fiber prior to protein microsequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1987 Mar;161(2):524–528. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90484-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., McCandless S., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Binding of human tumor necrosis factor to high affinity receptors on HeLa and lymphoblastoid cells sensitive to growth inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13395–13397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braesch-Andersen S., Paulie S., Koho H., Nika H., Aspenström P., Perlmann P. Biochemical characteristics and partial amino acid sequence of the receptor-like human B cell and carcinoma antigen CDw40. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):562–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernajovsky Y., Mory Y., Chen L., Marks Z., Novick D., Rubinstein M., Revel M. Efficient constitutive production of human fibroblast interferon by hamster cells transformed with the IFN-beta 1 gene fused to an SV40 early promoter. DNA. 1984 Aug;3(4):297–308. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiStefano P. S., Johnson E. M., Jr Identification of a truncated form of the nerve growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):270–274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Aderka D., Rubinstein M., Rotman D., Wallach D. A tumor necrosis factor-binding protein purified to homogeneity from human urine protects cells from tumor necrosis factor toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11974–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Novick D., Wallach D. Two tumor necrosis factor-binding proteins purified from human urine. Evidence for immunological cross-reactivity with cell surface tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1531–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Brockhaus M., Loetscher H., Nonstad U., Shalaby R. Characterization of binding and biological effects of monoclonal antibodies against a human tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):415–426. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY G. E., LAZARUS H., FARBER S., UZMAN B. G., BOONE B. A., MCCARTHY R. E. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF HUMAN LYMPHOBLASTS FROM PERIPHERAL BLOOD OF A CHILD WITH ACUTE LEUKEMIA. Cancer. 1965 Apr;18:522–529. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196504)18:4<522::aid-cncr2820180418>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Smart J. E., Burridge K., Helfman D. M., Thomas G. P. Co-existence of vinculin and a vinculin-like protein of higher molecular weight in smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11024–11031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giard D. J., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Arnstein P., Kersey J. H., Dosik H., Parks W. P. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1417–1423. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. V. Identification of an interleukin 2-producing human leukemia T cell line. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1709–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Friend D., Ziegler S. F., Jerzy R., Falk B. A., Gimpel S., Cosman D., Dower S. K., March C. J., Namen A. E. Cloning of the human and murine interleukin-7 receptors: demonstration of a soluble form and homology to a new receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90342-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepburn A., Demolle D., Boeynaems J. m., Fiers W., Dumont J. E. Rapid phosphorylation of a 27 kDa protein induced by tumor necrosis factor. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80892-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Remy R., Brockhaus M., van Loon A. P. Two different cell types have different major receptors for human tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14927–14934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtmann H., Wallach D. Down regulation of the receptors for tumor necrosis factor by interleukin 1 and 4 beta-phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1161–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel S., Hahn T., Holtmann H., Wallach D. Binding of human TNF-alpha to high-affinity cell surface receptors: effect of IFN. Immunol Lett. 1986 Apr;12(4):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Lanahan A., Buck C. R., Sehgal A., Morgan C., Mercer E., Bothwell M., Chao M. Expression and structure of the human NGF receptor. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90619-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Taylor S. S., Sefton B. M. Direct evidence that oncogenic tyrosine kinases and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase have homologous ATP-binding sites. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):589–592. doi: 10.1038/310589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor increase phosphorylation of fibroblast proteins. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Golde D. W. Acute myelogenous leukemia: a human cell line responsive to colony-stimulating activity. Science. 1978 Jun 9;200(4346):1153–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.306682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Cellular receptor for 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor: specific binding, affinity labeling, and relationship to sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5756–5760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Engelmann H., Wallach D., Rubinstein M. Soluble cytokine receptors are present in normal human urine. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1409–1414. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Lantz M., Nilsson E., Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Adolf G. Isolation and characterization of a tumor necrosis factor binding protein from urine. Eur J Haematol. 1989 Mar;42(3):270–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1989.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa H., Josimovic-Alasevic O., Diamantstein T. Interleukin 2 receptors are released by cells in vitro and in vivo. I. Detection of soluble IL 2 receptors in cell culture supernatants and in the serum of mice by an immunoradiometric assay. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Apr;16(4):467–469. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidgeon C., Williard R. L., Schroeder S. C. Amino acids bracketing the predicted transmembrane domains of membrane proteins. Pharm Res. 1989 Sep;6(9):779–786. doi: 10.1023/a:1015975530850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radeke M. J., Misko T. P., Hsu C., Herzenberg L. A., Shooter E. M. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the rat nerve growth factor receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):593–597. doi: 10.1038/325593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Kutny R. M. Structure-function relationships for the IL 2-receptor system. IV. Analysis of the sequence and ligand-binding properties of soluble Tac protein. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):855–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lanahan A., Perez-Albuerne E., Nathans D. jun-D: a third member of the jun gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1500–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Scheurich P., Pfizenmaier K., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor signal transduction. Tissue-specific serine phosphorylation of a 26-kDa cytosolic protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3562–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11966–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Wickens M. Two phases in the addition of a poly(A) tail. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1401–1412. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Clark E. A., Seed B. A B-lymphocyte activation molecule related to the nerve growth factor receptor and induced by cytokines in carcinomas. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03521.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Moschera J. High-performance liquid chromatography and picomole-level detection of peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):7–16. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor: specific binding and internalization in sensitive and resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7626–7630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zupan A. A., Osborne P. A., Smith C. E., Siegel N. R., Leimgruber R. M., Johnson E. M., Jr Identification, purification, and characterization of truncated forms of the human nerve growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11714–11720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]