Abstract
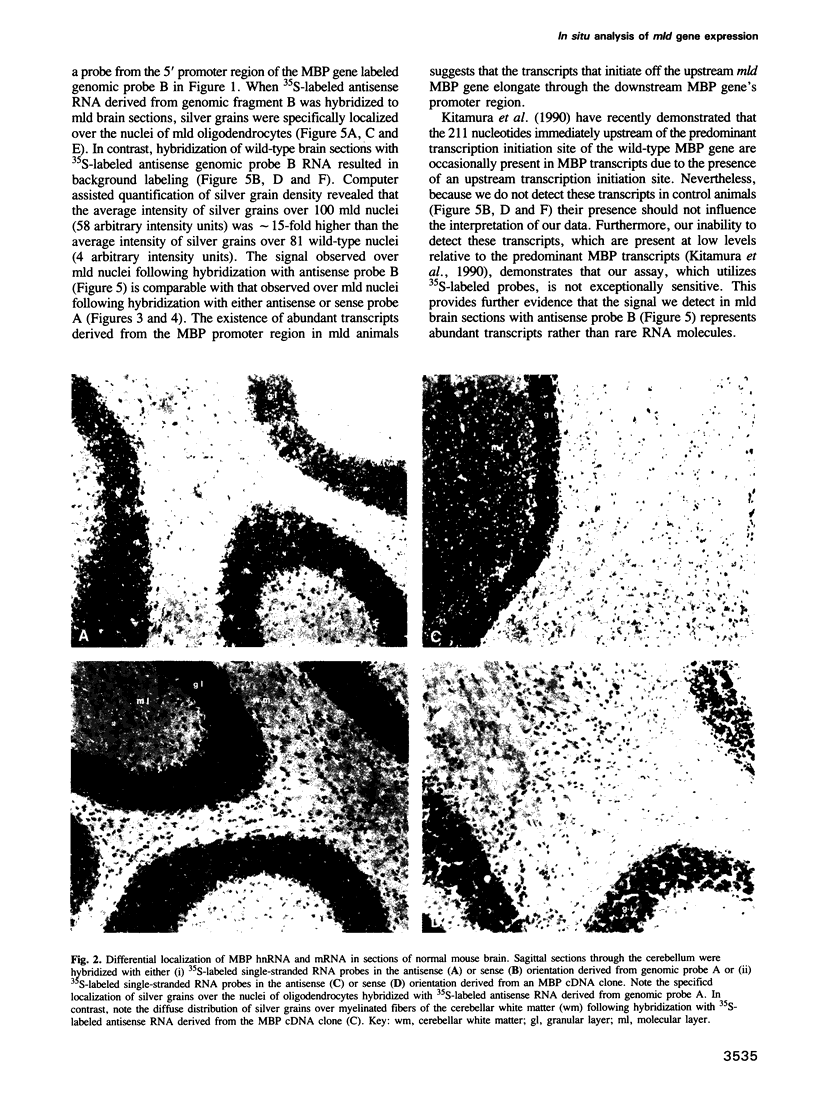
Mice homozygous for the recessive mutation myelin deficient (mld) exhibit a severe deficit in the synthesis of myelin basic protein (MBP). The primary defect in mld mice is an unusual rearrangement of the MBP gene. The mld MBP locus consists of two tandem MBP genes that span approximately 90 kb of DNA; the upstream gene contains an extensive inversion of its 3' region, while the downstream gene appears identical to the wild-type gene. In this report, the aberrant expression of the mld MBP locus was examined by in situ hybridization with MBP genomic and cDNA probes. In situ hybridization with a single-stranded genomic probe from the inverted region of the mld MBP gene revealed that primary transcripts initiating from the upstream MBP promoter elongate through the inverted region generating abundant antisense MBP heterogeneous nucleus RNA (hnRNA) transcripts in mld oligodendrocytes. Little or no antisense MBP RNA was detected in cytoplasmic regions in mld brain sections indicating that the antisense MBP hnRNA transcripts are not processed and transported out of the nucleus. Furthermore, we provide evidence that these abnormal transcripts elongate through the downstream MBP gene's promoter region, suggesting that transcription of the downstream mld MBP gene is inhibited by readthrough transcripts that originate at the upstream promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Promoter occlusion: transcription through a promoter may inhibit its activity. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akowitz A. A., Barbarese E., Scheld K., Carson J. H. Structure and expression of myelin basic protein gene sequences in the mld mutant mouse: reiteration and rearrangement of the MBP gene. Genetics. 1987 Jul;116(3):447–464. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Promoter occlusion during ribosomal RNA transcription. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman S. A., Bursztajn S., Bowen B., Gilbert W. Localization of an acetylcholine receptor intron to the nuclear membrane. Science. 1990 Jan 12;247(4939):212–214. doi: 10.1126/science.1688472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnoni A. T., Campagnoni C. W., Bourre J. M., Jacque C., Baumann N. Cell-free synthesis of myelin basic proteins in normal and dysmyelinating mutant mice. J Neurochem. 1984 Mar;42(3):733–739. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman D. R., Kreibich G., Frey A. B., Sabatini D. D. Synthesis and incorporation of myelin polypeptides into CNS myelin. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):598–608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. Role of transcriptional interference in the Drosophila melanogaster Adh promoter switch. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):279–282. doi: 10.1038/337279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle D. P., Schweikart K. M. Myelin deficient, a new neurological mutant in the mouse. J Hered. 1977 Sep-Oct;68(5):331–332. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremeau R. T., Jr, Autelitano D. J., Blum M., Wilcox J., Roberts J. L. Intervening sequence-specific in situ hybridization: detection of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene primary transcript in individual neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Nov;6(2-3):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremeau R. T., Jr, Lundblad J. R., Pritchett D. B., Wilcox J. N., Roberts J. L. Regulation of pro-opiomelanocortin gene transcription in individual cell nuclei. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1265–1269. doi: 10.1126/science.3775385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausler B., Somerville R. L. Interaction in vivo between strong closely spaced constitutive promoters. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 25;127(3):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Berg P. Effects of the position of the simian virus 40 enhancer on expression of multiple transcription units in a single plasmid. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2593–2601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Newman S. L., Campagnoni C. W., Verdi J. M., Mohandas T., Handley V. W., Campagnoni A. T. Expression of a novel transcript of the myelin basic protein gene. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):2032–2041. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthieu J. M., Almazan G., Waehneldt T. V. Intrinsic myelin proteins are normally synthesized in vitro in the myelin-deficient (mld) mutant mouse. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(4-5):246–250. doi: 10.1159/000112351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthieu J. M., Ginalski H., Friede R. L., Cohen S. R., Doolittle D. P. Absence of myelin basic protein and major dense line in CNS myelin of the mld mutant mouse. Brain Res. 1980 Jun 2;191(1):278–283. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90333-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Lai C., Nave K. A., Lenoir D., Ogata J., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequences of two mRNAs for rat brain myelin proteolipid protein. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):931–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano H., Ikenaka K., Mikoshiba K. Recombination within the upstream gene of duplicated myelin basic protein genes of myelin deficient shimld mouse results in the production of antisense RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3407–3412. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano H., Miura M., Moriguchi A., Ikenaka K., Tsukada Y., Mikoshiba K. Inefficient transcription of the myelin basic protein gene possibly causes hypomyelination in myelin-deficient mutant mice. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):470–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano H., Tamura T., Miura M., Aoyama A., Ikenaka K., Oshimura M., Mikoshiba K. Gene organization and transcription of duplicated MBP genes of myelin deficient (shi(mld)) mutant mouse. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):77–83. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02785.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popko B., Puckett C., Hood L. A novel mutation in myelin-deficient mice results in unstable myelin basic protein gene transcripts. Neuron. 1988 May;1(3):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popko B., Puckett C., Lai E., Shine H. D., Readhead C., Takahashi N., Hunt S. W., 3rd, Sidman R. L., Hood L. Myelin deficient mice: expression of myelin basic protein and generation of mice with varying levels of myelin. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):713–721. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90249-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Transcriptional interference and termination between duplicated alpha-globin gene constructs suggests a novel mechanism for gene regulation. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):562–565. doi: 10.1038/322562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Readhead C., Popko B., Takahashi N., Shine H. D., Saavedra R. A., Sidman R. L., Hood L. Expression of a myelin basic protein gene in transgenic shiverer mice: correction of the dysmyelinating phenotype. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):703–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach A., Boylan K., Horvath S., Prusiner S. B., Hood L. E. Characterization of cloned cDNA representing rat myelin basic protein: absence of expression in brain of shiverer mutant mice. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):799–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90536-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch J. M., Brown-Luedi M., Cooper B. J., Matthieu J. M. Mice heterozygous for the mld mutation have intermediate levels of myelin basic protein mRNA and its translation products. Brain Res. 1986 Nov;387(2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch J. M., Cooper B. J., Ramirez M., Matthieu J. M. Expression of only one myelin basic protein allele in mouse is compatible with normal myelination. Brain Res. 1987 Dec;427(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch J. M., Tosic M., Roach A., Matthieu J. M. The duplicated myelin basic protein gene in mld mutant mice does not impair transcription. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 16;477(1-2):292–299. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Roach A., Teplow D. B., Prusiner S. B., Hood L. Cloning and characterization of the myelin basic protein gene from mouse: one gene can encode both 14 kd and 18.5 kd MBPs by alternate use of exons. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosic M., Roach A., de Rivaz J. C., Dolivo M., Matthieu J. M. Post-transcriptional events are responsible for low expression of myelin basic protein in myelin deficient mice: role of natural antisense RNA. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):401–406. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Moench T., Pulley M., Barbosa E., Tennekoon G., Griffin J. Spatial segregation of mRNA encoding myelin-specific proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vales L. D., Darnell J. E., Jr Promoter occlusion prevents transcription of adenovirus polypeptide IX mRNA until after DNA replication. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):49–59. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]