Abstract
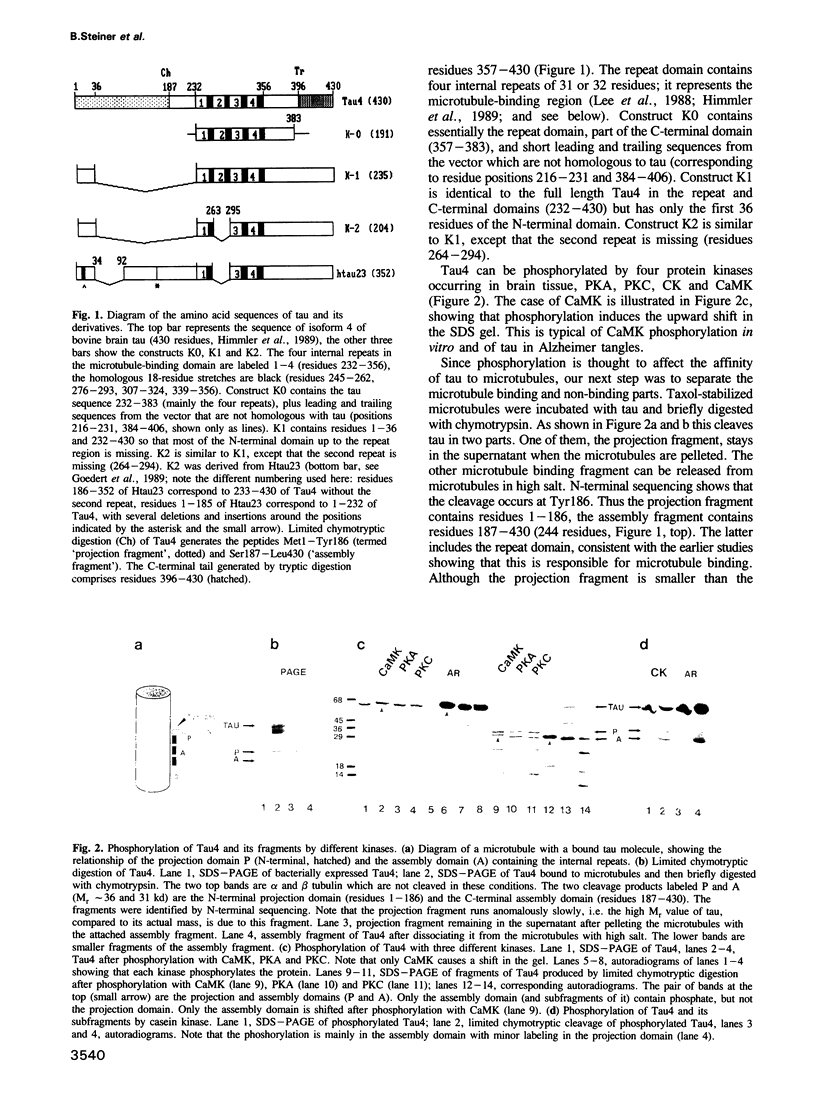
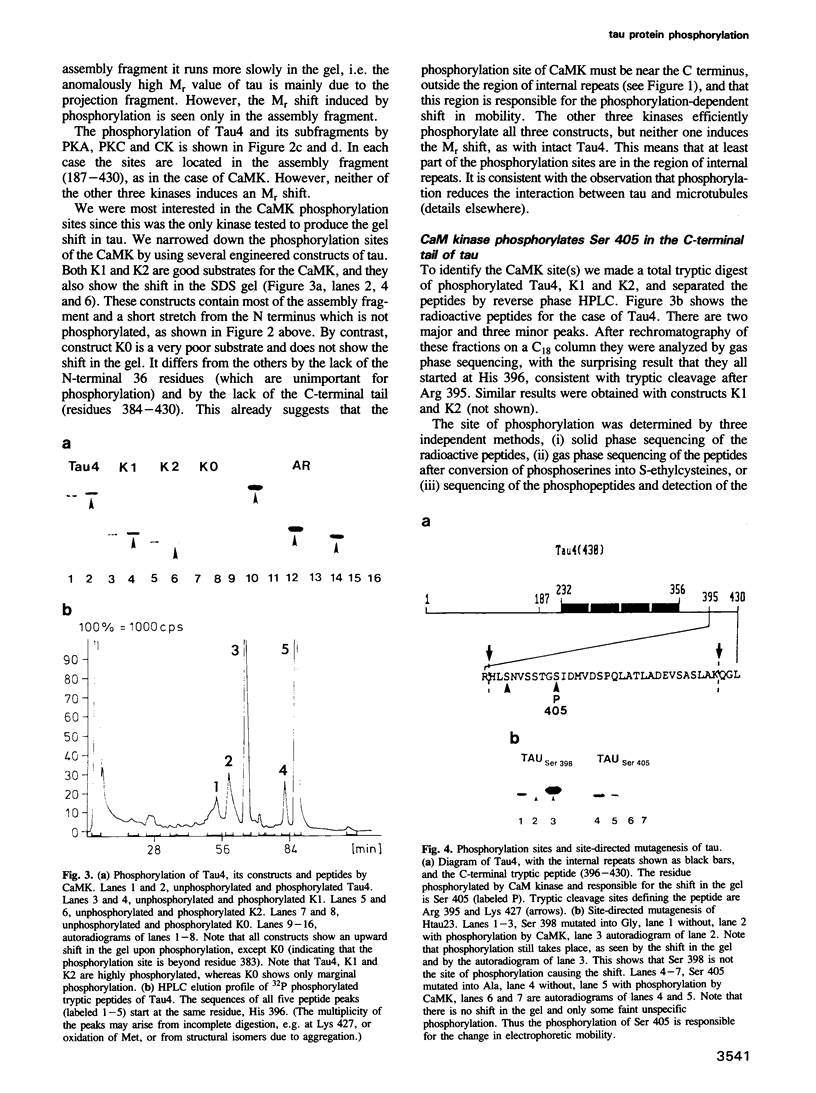
The microtubule array in neuronal cells undergoes extensive growth, dynamics and rearrangements during neurite outgrowth. While little is known about how these changes are regulated, microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) including tau protein are likely to perform an important role. Tau is one of the MAPs in mammalian brain. When isolated it is usually a mixture of several isoforms containing between 341 and 441 residues that arise from alternative splicing. Tau can be phosphorylated by several protein kinases. Phosphorylation at certain sites results in major structural and functional changes, as seen by changes in electrophoretic mobility, interaction with microtubules, molecular length and elasticity. Here we show that the sites of phosphorylation by four kinases (PKA, PKC, CK and CaMK) all lie in the C-terminal microtubule-binding half of tau, but only the phosphorylation by CaM kinase shows the pronounced shift in electrophoretic mobility characteristic for tau from Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. By using a combination of limited proteolysis, protein sequencing and protein engineering we show that a single phosphorylation site is responsible for this shift, located at Ser 405 in the C-terminal tail of the protein outside the region of internal repeats. Phosphorylation at this site not only reduces the electrophoretic mobility of tau, it also makes the protein long and stiff, as shown earlier. The site is likely to be phosphorylated in tau from Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barford D., Johnson L. N. The allosteric transition of glycogen phosphorylase. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):609–616. doi: 10.1038/340609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Cole R. D. Phosphorylation of tau proteins to a state like that in Alzheimer's brain is catalyzed by a calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase and modulated by phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17577–17583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Frankfurter A., Rebhun L. I. The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. G., Islam K., Chapman R. The multiple phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein MAP2 controls the MAP2:tubulin interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):609–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. Physical and chemical properties of purified tau factor and the role of tau in microtubule assembly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 25;116(2):227–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flament S., Delacourte A. Abnormal tau species are produced during Alzheimer's disease neurodegenerating process. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Jakes R., Rutherford D., Crowther R. A. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Walker J. E., Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4051–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Quinlan M., Wisniewski H. M., Binder L. I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagestedt T., Lichtenberg B., Wille H., Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E. Tau protein becomes long and stiff upon phosphorylation: correlation between paracrystalline structure and degree of phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1643–1651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W., Martin D. W., Jr Tau consists of a set of proteins with repeated C-terminal microtubule-binding domains and variable N-terminal domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1381–1388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A. Structure of the bovine tau gene: alternatively spliced transcripts generate a protein family. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1389–1396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson L., Frey T., Zeeberg B., Dalldorf F., Caplow M. Inhibition of microtubule assembly by phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2472–2479. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Joachim C. L., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4044–4048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Bakalis S., Neve R. L. Developmentally regulated expression of specific tau sequences. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1389–1397. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Binder L., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Lee G. Epitopes that span the tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Cowan N., Kirschner M. The primary structure and heterogeneity of tau protein from mouse brain. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):285–288. doi: 10.1126/science.3122323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg B., Mandelkow E. M., Hagestedt T., Mandelkow E. Structure and elasticity of microtubule-associated protein tau. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):359–362. doi: 10.1038/334359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. E., Mayr G. W. N pi-methylhistidine in myosin-light-chain kinase. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Dec;368(12):1607–1611. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. E., Meyer G. F., Dirks H., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Localization of phosphoserine residues in the alpha subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 10;188(2):367–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]