Abstract
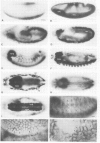
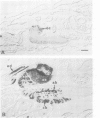
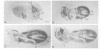
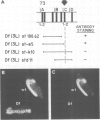
Monoclonal antibodies have served to characterize neurotactin, a novel Drosophila protein for which a role in cell adhesion is postulated. Neurotactin is a transmembrane protein, as indicated by epitope mapping and amino acid sequence. Similarly to other cell adhesion molecules, neurotactin accumulates in parts of the membrane where neurotactin-expressing cells contact each other. The protein is only detected during cell proliferation and differentiation, and it is found mainly in neural tissue and also in mesoderm and imaginal discs. Neurotactin has a large cytoplasmic domain rich in charged residues and an extracellular domain similar to cholinesterase that lacks the active site serine required for esterase activity. The extracellular domain also contains three copies of the tripeptide leucine-arginine-glutamate, a motif that forms the primary sequence of the adhesive site of vertebrate s-laminin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthalay Y., Hipeau-Jacquotte R., de la Escalera S., Jiménez F., Piovant M. Drosophila neurotactin mediates heterophilic cell adhesion. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3603–3609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bause E. Structural requirements of N-glycosylation of proteins. Studies with proline peptides as conformational probes. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):331–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2090331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieber A. J., Snow P. M., Hortsch M., Patel N. H., Jacobs J. R., Traquina Z. R., Schilling J., Goodman C. S. Drosophila neuroglian: a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with extensive homology to the vertebrate neural adhesion molecule L1. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):447–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixby J. L., Pratt R. S., Lilien J., Reichardt L. F. Neurite outgrowth on muscle cell surfaces involves extracellular matrix receptors as well as Ca2+-dependent and -independent cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2555–2559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogaert T., Brown N., Wilcox M. The Drosophila PS2 antigen is an invertebrate integrin that, like the fibronectin receptor, becomes localized to muscle attachments. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in the hormonal control of enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins T., Zinn K., McAllister L., Hoffmann F. M., Goodman C. S. Genetic analysis of a Drosophila neural cell adhesion molecule: interaction of fasciclin I and Abelson tyrosine kinase mutations. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):565–575. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Marchiori F., Borin G., Pinna L. A. Distinct structural requirements of Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase as evidenced by synthetic peptide substrates. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 6;184(1):72–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80656-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gertler F. B., Bennett R. L., Clark M. J., Hoffmann F. M. Drosophila abl tyrosine kinase in embryonic CNS axons: a role in axonogenesis is revealed through dosage-sensitive interactions with disabled. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Spierer P. The Ace locus of Drosophila melanogaster: structural gene for acetylcholinesterase with an unusual 5' leader. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2949–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. D., Porter B. E., Bulock J. W., Adams S. P., Merlie J. P., Sanes J. R. Primary sequence of a motor neuron-selective adhesive site in the synaptic basal lamina protein S-laminin. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):905–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90613-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M. Adhesion molecules and the hierarchy of neural development. Neuron. 1988 Mar;1(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander A. D. Understanding the molecules of neural cell contacts: emerging patterns of structure and function. Trends Neurosci. 1989 May;12(5):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockridge O., Bartels C. F., Vaughan T. A., Wong C. K., Norton S. E., Johnson L. L. Complete amino acid sequence of human serum cholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):549–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKrell A. J., Blumberg B., Haynes S. R., Fessler J. H. The lethal myospheroid gene of Drosophila encodes a membrane protein homologous to vertebrate integrin beta subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2633–2637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee-Quigley K., Vedvick T. S., Taylor P., Taylor S. S. Profile of the disulfide bonds in acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13565–13570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Lenk R. P. Enhanced graphic matrix analysis of nucleic acid and protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7665–7669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisen N., Baars S., Jiménez F. Isolation of mesoderm-specific genes expressed in the Drosophila embryo. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):457–464. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken L., Simons M. J., Swillens S., Massaer M., Vassart G. Primary structure of bovine thyroglobulin deduced from the sequence of its 8,431-base complementary DNA. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):647–651. doi: 10.1038/316647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Sedat J. Localization of antigenic determinants in whole Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell D. J., Goodman C. S. Drosophila substrate adhesion molecule: sequence of laminin B1 chain reveals domains of homology with mouse. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):463–473. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Shirayoshi Y., Okazaki K., Yasuda K., Takeichi M. Transformation of cell adhesion properties by exogenously introduced E-cadherin cDNA. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):341–343. doi: 10.1038/329341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson P. F., Fessler L. I., Nelson R. E., Sterne R. E., Campbell A. G., Fessler J. H. Glutactin, a novel Drosophila basement membrane-related glycoprotein with sequence similarity to serine esterases. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1219–1227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel N. H., Snow P. M., Goodman C. S. Characterization and cloning of fasciclin III: a glycoprotein expressed on a subset of neurons and axon pathways in Drosophila. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):975–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90706-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piovant M., Léna P. Membrane glycoproteins immunologically related to the human insulin receptor are associated with presumptive neuronal territories and developing neurones in Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 1988 May;103(1):145–156. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Jessell T. M. Cell adhesion molecules in vertebrate neural development. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jul;68(3):819–857. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.3.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Camp S., Maulet Y., Newton M., MacPhee-Quigley K., Taylor S. S., Friedmann T., Taylor P. Primary structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase deduced from its cDNA sequence. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):407–409. doi: 10.1038/319407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger M. A., Haffley L., Kaufman T. C. Characterization of amalgam: a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily from Drosophila. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow P. M., Bieber A. J., Goodman C. S. Fasciclin III: a novel homophilic adhesion molecule in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. The cadherins: cell-cell adhesion molecules controlling animal morphogenesis. Development. 1988 Apr;102(4):639–655. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tearle R. G., Belote J. M., McKeown M., Baker B. S., Howells A. J. Cloning and characterization of the scarlet gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):595–606. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. B., Bastiani M. J., Bate M., Goodman C. S. From grasshopper to Drosophila: a common plan for neuronal development. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):203–207. doi: 10.1038/310203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Neuronal differentiation in Drosophila ommatidium. Dev Biol. 1987 Apr;120(2):366–376. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truman J. W., Bate M. Spatial and temporal patterns of neurogenesis in the central nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1988 Jan;125(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]