Abstract
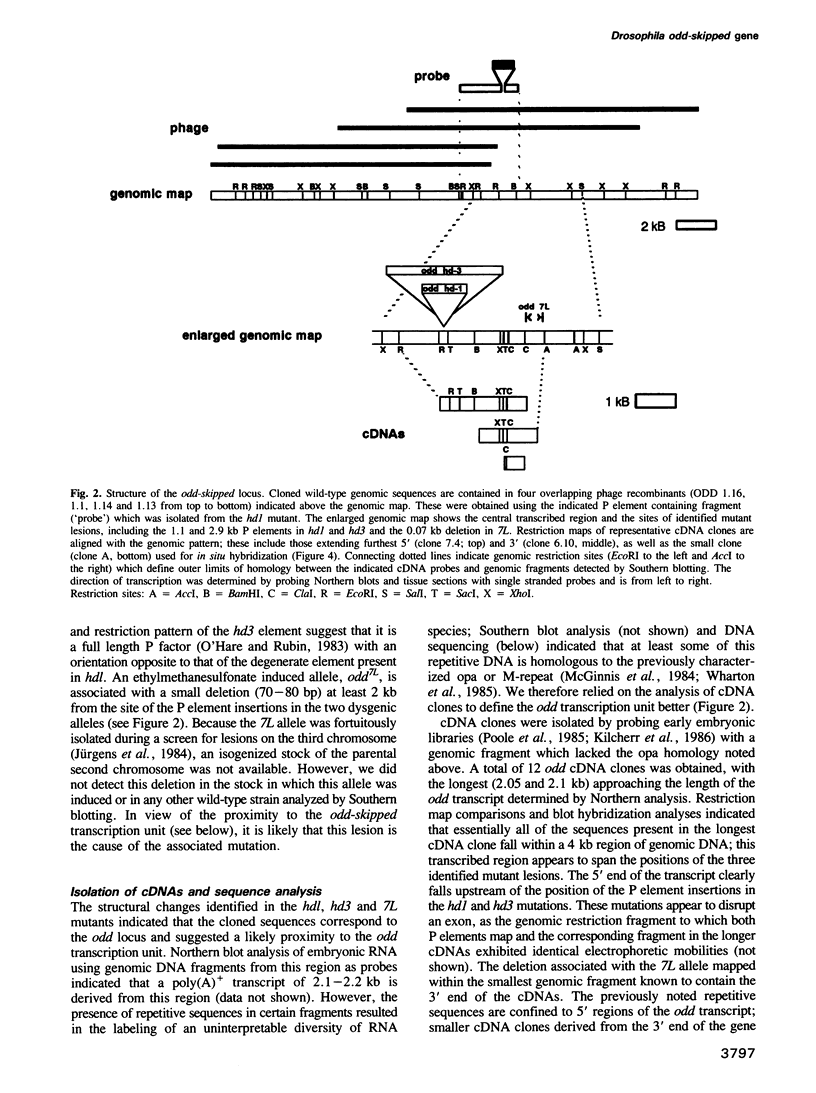
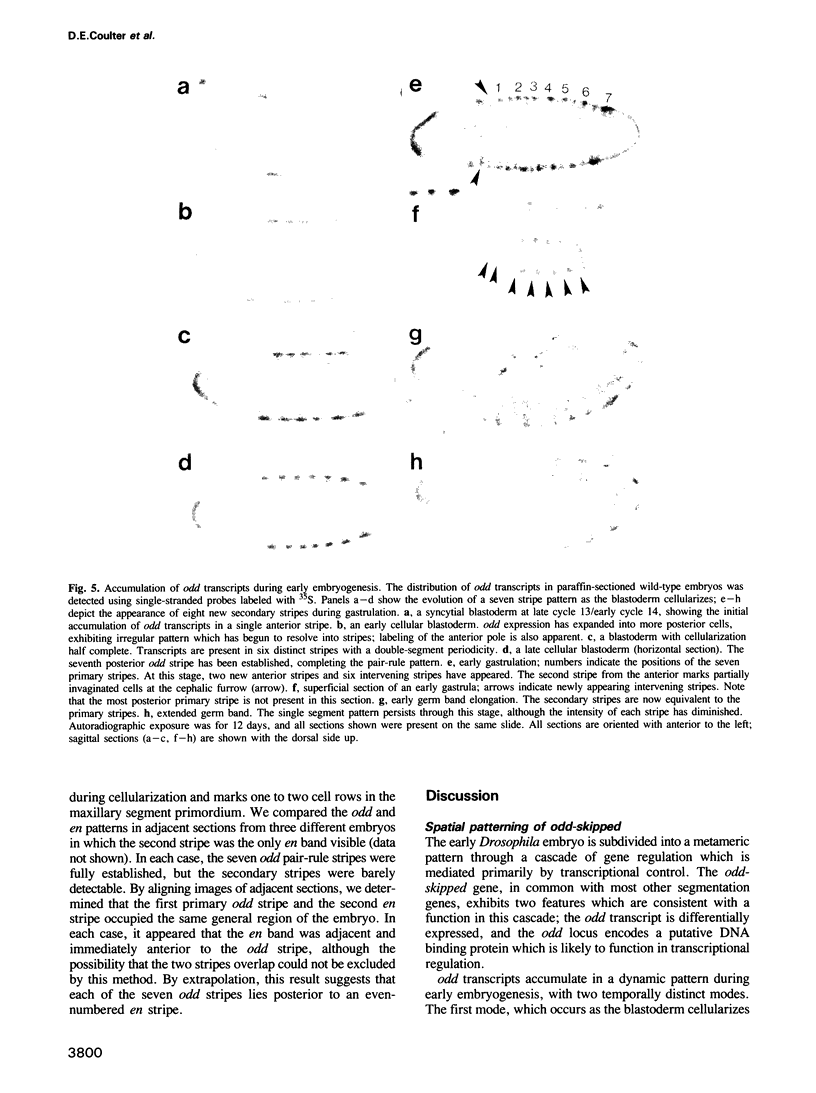
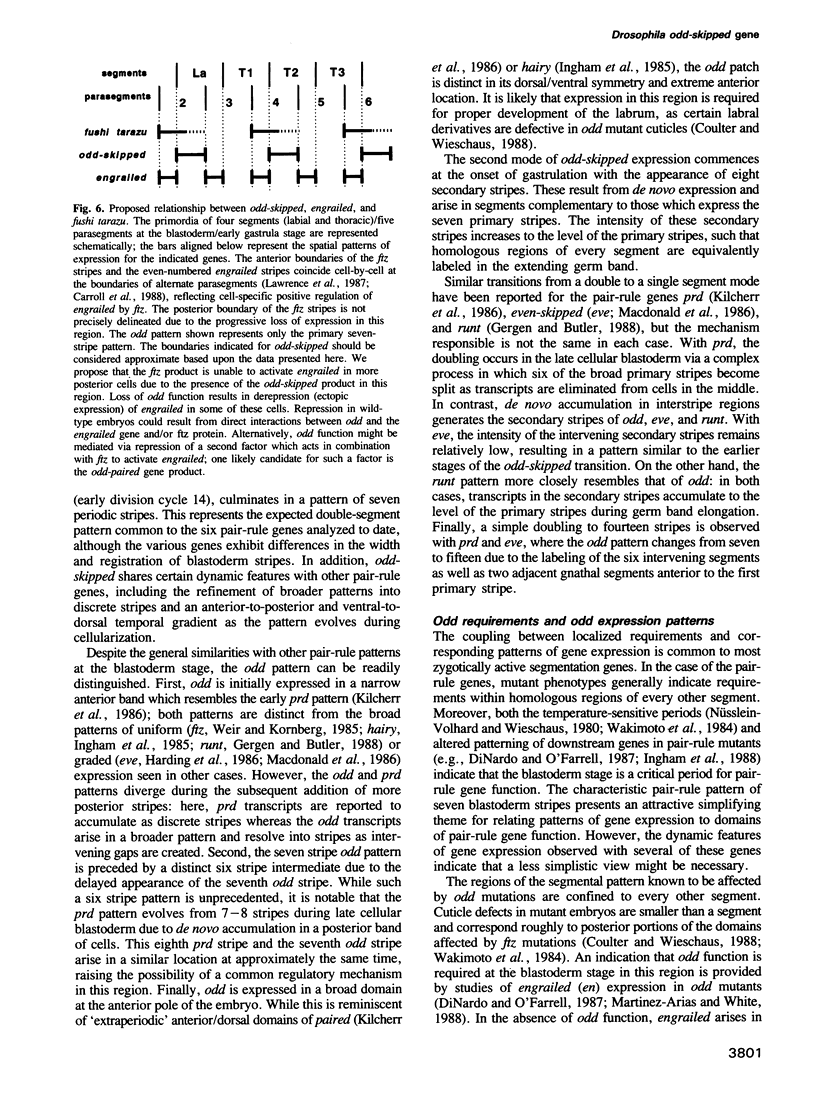
odd-skipped (odd) is one of eight known pair-rule genes that establish portions of alternating segments during Drosophila embryogenesis; odd mutant embryos exhibit pattern defects in anterior regions of odd-numbered segments. P element transposon tagging was used to clone 25 kb of DNA from the odd genomic region. Molecular analysis of phenotypic revertants confirmed that the P element used to tag the locus was responsible for the corresponding odd mutation, and significant structural changes were identified in two additional odd mutants. Several cDNA clones derived from a 2.2 kb embryonic transcript were isolated and the longest was sequenced. The predicted odd protein of 392 amino acids is highly basic and contains four tandem Cys-Cys/His-His zinc finger repeats, consistent with a presumed function for odd as a DNA binding protein and transcriptional regulator. In situ hybridization analysis indicated that odd transcripts accumulate in a dynamic pattern during early embryogenesis, with two temporally distinct modes of expression. The first mode results in a 'pair-rule' pattern of seven stripes at the blastoderm stage, representing the expected double segment periodicity. During gastrulation, the seven primary stripes are supplemented by secondary stripes which appear in alternate segments, resulting in the equivalent labeling of every segment in the extended germ band. Similar double to single segment transitions have now been reported for four of the six pair-rule genes analyzed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carroll S. B., DiNardo S., O'Farrell P. H., White R. A., Scott M. P. Temporal and spatial relationships between segmentation and homeotic gene expression in Drosophila embryos: distributions of the fushi tarazu, engrailed, Sex combs reduced, Antennapedia, and Ultrabithorax proteins. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):350–360. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. E., Wieschaus E. Gene activities and segmental patterning in Drosophila: analysis of odd-skipped and pair-rule double mutants. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1812–1823. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., O'Farrell P. H. Establishment and refinement of segmental pattern in the Drosophila embryo: spatial control of engrailed expression by pair-rule genes. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1212–1225. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Butler B. A. Isolation of the Drosophila segmentation gene runt and analysis of its expression during embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1179–1193. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Macdonald P., Maniatis T. Early and late periodic patterns of even skipped expression are controlled by distinct regulatory elements that respond to different spatial cues. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90916-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Spatial distribution of transcripts from the segmentation gene fushi tarazu during Drosophila embryonic development. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):833–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90418-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding K., Hoey T., Warrior R., Levine M. Autoregulatory and gap gene response elements of the even-skipped promoter of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1205–1212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding K., Rushlow C., Doyle H. J., Hoey T., Levine M. Cross-regulatory interactions among pair-rule genes in Drosophila. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):953–959. doi: 10.1126/science.3755551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J. Regulation and function of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Evans R. M. Multiple and cooperative trans-activation domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):899–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard K., Ingham P., Rushlow C. Region-specific alleles of the Drosophila segmentation gene hairy. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):1037–1046. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Baker N. E., Martinez-Arias A. Regulation of segment polarity genes in the Drosophila blastoderm by fushi tarazu and even skipped. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):73–75. doi: 10.1038/331073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. The molecular genetics of embryonic pattern formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):25–34. doi: 10.1038/335025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Pinchin S. M. Pattern abnormalities induced by ectopic expression of the Drosophila gene hairy are associated with repression of ftz transcription. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90636-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Pinchin S. M., Schedl P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Mirault M. E. Genetic and molecular analysis of the 87A7 and 87C1 heat-inducible loci of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1351–1358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg T., Sidén I., O'Farrell P., Simon M. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: in situ localization of transcripts reveals compartment-specific expression. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. A., Johnston P., Macdonald P., Struhl G. Borders of parasegments in Drosophila embryos are delimited by the fushi tarazu and even-skipped genes. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):440–442. doi: 10.1038/328440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Ingham P., Struhl G. Isolation, structure, and expression of even-skipped: a second pair-rule gene of Drosophila containing a homeo box. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):721–734. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maine E. M., Salz H. K., Cline T. W., Schedl P. The Sex-lethal gene of Drosophila: DNA alterations associated with sex-specific lethal mutations. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Garber R. L., Wirz J., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. A homologous protein-coding sequence in Drosophila homeotic genes and its conservation in other metazoans. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muriel W. J., Cole J., Lehmann A. R. Molecular analysis of ouabain-resistant mutants of the mouse lymphoma cell line L5178Y. Mutagenesis. 1987 Sep;2(5):383–389. doi: 10.1093/mutage/2.5.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauber U., Pankratz M. J., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Klemm U., Jäckle H. Abdominal segmentation of the Drosophila embryo requires a hormone receptor-like protein encoded by the gap gene knirps. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):489–492. doi: 10.1038/336489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenic T. V., Slusarski D. C., Kroll K. L., Holmgren R. A. Cloning and characterization of the segment polarity gene cubitus interruptus Dominant of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1053–1067. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Kauvar L. M., Drees B., Kornberg T. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: structural analysis of an embryonic transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G. Near-reciprocal phenotypes caused by inactivation or indiscriminate expression of the Drosophila segmentation gene ftz. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):677–680. doi: 10.1038/318677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubota S., Schedl P. Hybrid dysgenesis-induced revertants of insertions at the 5' end of the rudimentary gene in Drosophila melanogaster: transposon-induced control mutations. Genetics. 1986 Sep;114(1):165–182. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakimoto B. T., Turner F. R., Kaufman T. C. Defects in embryogenesis in mutants associated with the antennapedia gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):147–172. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir M. P., Kornberg T. Patterns of engrailed and fushi tarazu transcripts reveal novel intermediate stages in Drosophila segmentation. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):433–439. doi: 10.1038/318433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Yedvobnick B., Finnerty V. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. opa: a novel family of transcribed repeats shared by the Notch locus and other developmentally regulated loci in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]