Abstract
The granule/perforin exocytosis model of CTL mediated cytolysis proposes that CTL, upon recognition of the specific targets, release the cytolytic, pore-forming protein perforin into the intercellular space which then mediates the cytotoxic effect. However, direct evidence for the involvement of perforin is still lacking, and indeed, recent results even seem incompatible with the model. To determine directly the role of perforin in CTL cytotoxicity, perforin antisense oligonucleotides were exogenously added during the stimulation of mouse spleen derived T cells and human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL), respectively. Perforin protein expression in lymphocytes was reduced by up to 65%, and cytotoxicity of stimulated T cells by as much as 69% (5.7-fold). These results provide the first experimental evidence for a crucial role of perforin in lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity.
Full text
PDF
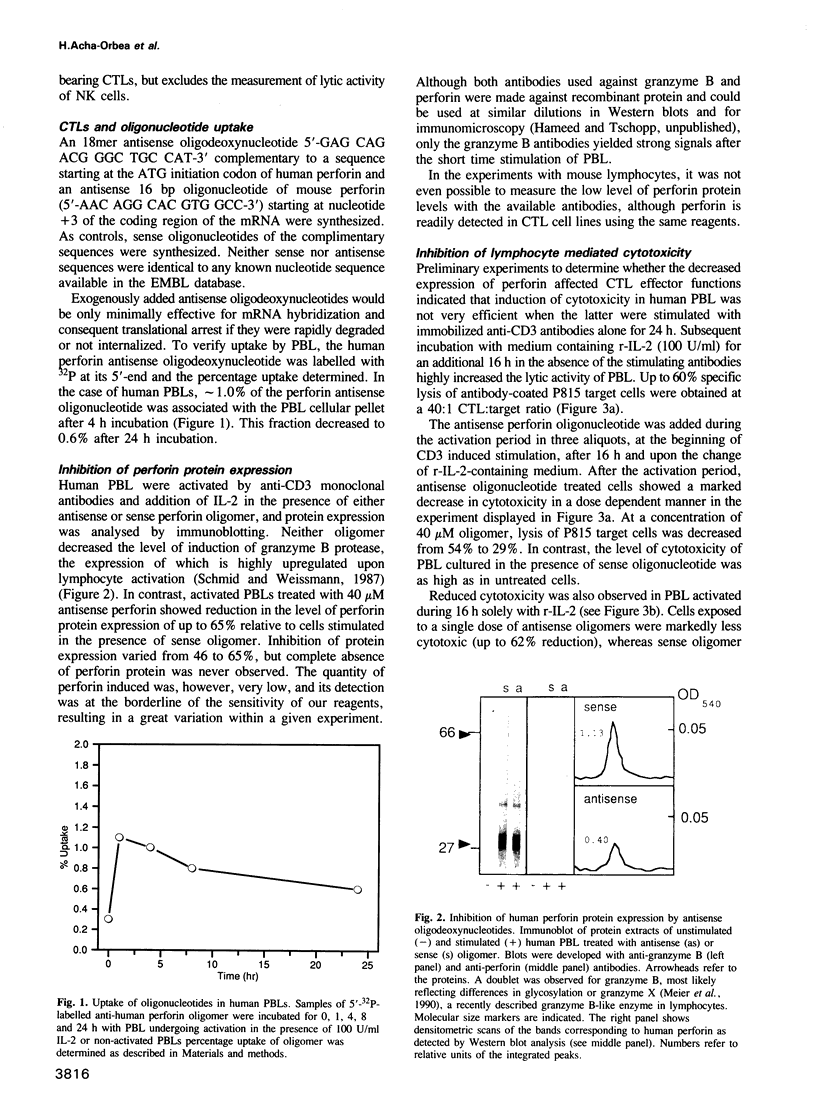
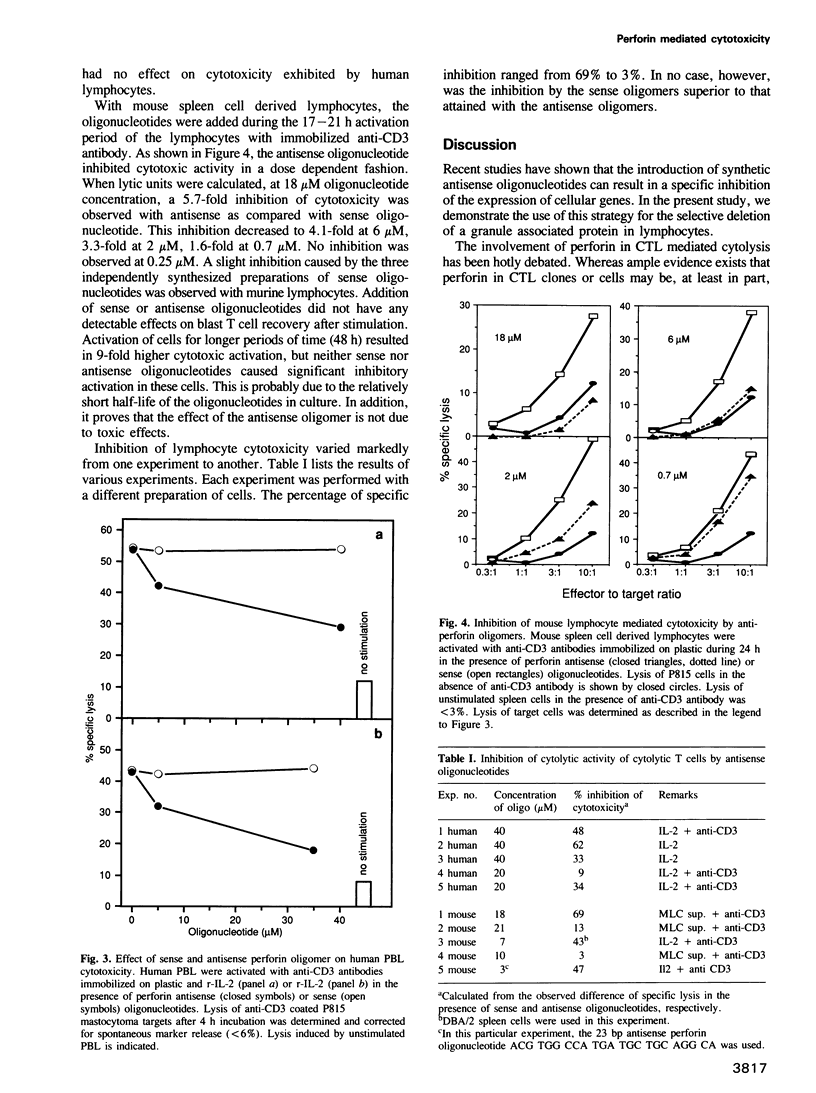


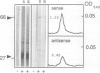
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G., Rosen D. Highly lytic in vivo primed cytolytic T lymphocytes devoid of lytic granules and BLT-esterase activity acquire these constituents in the presence of T cell growth factors upon blast transformation in vitro. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1429–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bories D., Raynal M. C., Solomon D. H., Darzynkiewicz Z., Cayre Y. E. Down-regulation of a serine protease, myeloblastin, causes growth arrest and differentiation of promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90752-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrel S., Lamarre D., Isler P., Rapin C., Fleury S., Salvi S., Sekaly R. P., Cerottini J. C. A positive signal is transduced via surface CD4 molecules. Res Immunol. 1989 Jun-Aug;140(5-6):545–561. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(89)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity, allograft rejection, and tumor immunity. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:67–132. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Persechini P. M., Chang S., Liu C. C., Cohen J. J., Young J. D. Purified perforin induces target cell lysis but not DNA fragmentation. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1451–1456. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sanz J. A., Plaetinck G., Velotti F., Masson D., Tschopp J., MacDonald H. R., Nabholz M. Perforin is present only in normal activated Lyt2+ T lymphocytes and not in L3T4+ cells, but the serine protease granzyme A is made by both subsets. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):933–938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz A. M., Calabretta B. A c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits normal human hematopoiesis in vitro. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.2461588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Ferris D. K., Vinocour M., Holt J. T., Farrar W. L. Specific inhibition of c-myc protein biosynthesis using an antisense synthetic deoxy-oligonucleotide in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2431–2435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P., Yue C. C. The role of cytoplasmic granules in lymphocyte cytotoxicity. Prog Allergy. 1988;40:82–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. M., Rypniewski W. R., Law J. H., Rayment I. The molecular structure of insecticyanin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta L. at 2.6 A resolution. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G. Antisense "pseudogenetics". Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(1):81–91. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krähenbühl O., Rey C., Jenne D., Lanzavecchia A., Groscurth P., Carrel S., Tschopp J. Characterization of granzymes A and B isolated from granules of cloned human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3471–3477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Joag S. V., Kwon B. S., Young J. D. Induction of perforin and serine esterases in a murine cytotoxic T lymphocyte clone. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1196–1201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier M., Kwong P. C., Frégeau C. J., Atkinson E. A., Burrington M., Ehrman N., Sorensen O., Lin C. C., Wilkins J., Bleackley R. C. Cloning of a gene that encodes a new member of the human cytotoxic cell protease family. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4042–4049. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miescher G. C., Schreyer M., MacDonald H. R. Production and characterization of a rat monoclonal antibody against the murine CD3 molecular complex. Immunol Lett. 1989 Dec;23(2):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Kane K. P., Mescher M. F., Clark W. R. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated lysis without release of serine esterase. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):71–72. doi: 10.1038/330071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. J., Geuze H. J., Van der Donk H. A., Slot J. W., Griffith J. M., Stam N. J., Clevers H. C., Borst J. Molecules relevant for T cell-target cell interaction are present in cytolytic granules of human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1469–1475. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R. Molecular mechanisms of cytolysis by complement and by cytolytic lymphocytes. J Cell Biochem. 1986;30(2):133–170. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240300205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H. Internal disintegration model of cytotoxic lymphocyte-induced target damage. Immunol Rev. 1983;72:97–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid J., Weissmann C. Induction of mRNA for a serine protease and a beta-thromboglobulin-like protein in mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):250–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Takio K., Okumura K. Homology of perforin to the ninth component of complement (C9). Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):525–527. doi: 10.1038/334525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trenn G., Takayama H., Sitkovsky M. V. Exocytosis of cytolytic granules may not be required for target cell lysis by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):72–74. doi: 10.1038/330072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Nabholz M. Perforin-mediated target cell lysis by cytolytic T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:279–302. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. L., Bacon T. A., Gonzalez A., Freeman D. L., Lyman G. H., Wickstrom E. Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell proliferation and c-myc protein expression are inhibited by an antisense pentadecadeoxynucleotide targeted against c-myc mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1028–1032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D. Killing of target cells by lymphocytes: a mechanistic view. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):250–314. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Li E., Sajjadi F., Subramani S., Jaenisch R. Germ-line transmission of a disrupted beta 2-microglobulin gene produced by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):435–438. doi: 10.1038/342435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]